Tejas Prabhune
Multimodal Segmentation for Vocal Tract Modeling
Jun 22, 2024



Abstract:Accurate modeling of the vocal tract is necessary to construct articulatory representations for interpretable speech processing and linguistics. However, vocal tract modeling is challenging because many internal articulators are occluded from external motion capture technologies. Real-time magnetic resonance imaging (RT-MRI) allows measuring precise movements of internal articulators during speech, but annotated datasets of MRI are limited in size due to time-consuming and computationally expensive labeling methods. We first present a deep labeling strategy for the RT-MRI video using a vision-only segmentation approach. We then introduce a multimodal algorithm using audio to improve segmentation of vocal articulators. Together, we set a new benchmark for vocal tract modeling in MRI video segmentation and use this to release labels for a 75-speaker RT-MRI dataset, increasing the amount of labeled public RT-MRI data of the vocal tract by over a factor of 9. The code and dataset labels can be found at \url{rishiraij.github.io/multimodal-mri-avatar/}.
Contrastive learning-based pretraining improves representation and transferability of diabetic retinopathy classification models
Aug 24, 2022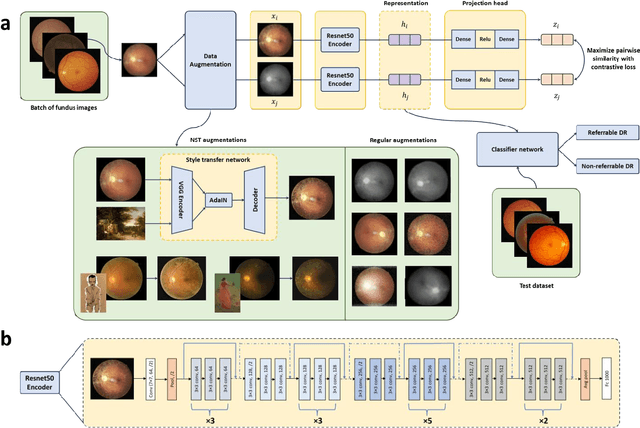
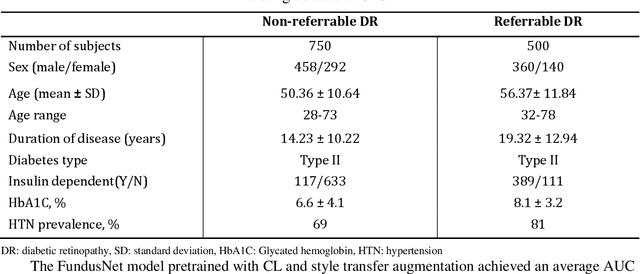
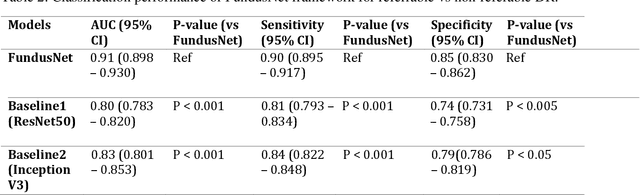
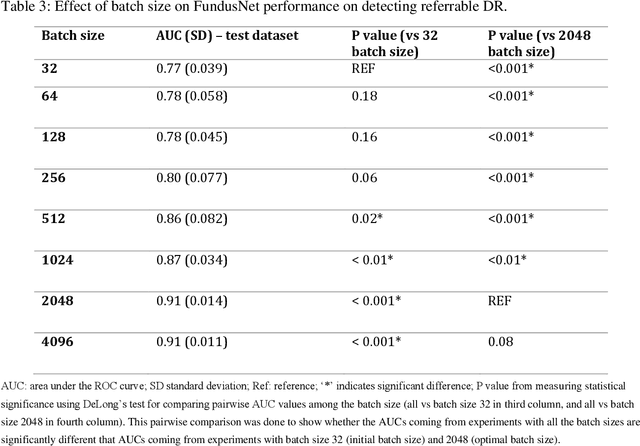
Abstract:Self supervised contrastive learning based pretraining allows development of robust and generalized deep learning models with small, labeled datasets, reducing the burden of label generation. This paper aims to evaluate the effect of CL based pretraining on the performance of referrable vs non referrable diabetic retinopathy (DR) classification. We have developed a CL based framework with neural style transfer (NST) augmentation to produce models with better representations and initializations for the detection of DR in color fundus images. We compare our CL pretrained model performance with two state of the art baseline models pretrained with Imagenet weights. We further investigate the model performance with reduced labeled training data (down to 10 percent) to test the robustness of the model when trained with small, labeled datasets. The model is trained and validated on the EyePACS dataset and tested independently on clinical data from the University of Illinois, Chicago (UIC). Compared to baseline models, our CL pretrained FundusNet model had higher AUC (CI) values (0.91 (0.898 to 0.930) vs 0.80 (0.783 to 0.820) and 0.83 (0.801 to 0.853) on UIC data). At 10 percent labeled training data, the FundusNet AUC was 0.81 (0.78 to 0.84) vs 0.58 (0.56 to 0.64) and 0.63 (0.60 to 0.66) in baseline models, when tested on the UIC dataset. CL based pretraining with NST significantly improves DL classification performance, helps the model generalize well (transferable from EyePACS to UIC data), and allows training with small, annotated datasets, therefore reducing ground truth annotation burden of the clinicians.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge