Tanishq Gupta
Strategic Pseudo-Goal Perturbation for Deadlock-Free Multi-Agent Navigation in Social Mini-Games
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:This work introduces a Strategic Pseudo-Goal Perturbation (SPGP) technique, a novel approach to resolve deadlock situations in multi-agent navigation scenarios. Leveraging the robust framework of Safety Barrier Certificates, our method integrates a strategic perturbation mechanism that guides agents through social mini-games where deadlock and collision occur frequently. The method adopts a strategic calculation process where agents, upon encountering a deadlock select a pseudo goal within a predefined radius around the current position to resolve the deadlock among agents. The calculation is based on controlled strategic algorithm, ensuring that deviation towards pseudo-goal is both purposeful and effective in resolution of deadlock. Once the agent reaches the pseudo goal, it resumes the path towards the original goal, thereby enhancing navigational efficiency and safety. Experimental results demonstrates SPGP's efficacy in reducing deadlock instances and improving overall system throughput in variety of multi-agent navigation scenarios.
DiSCoMaT: Distantly Supervised Composition Extraction from Tables in Materials Science Articles
Jul 10, 2022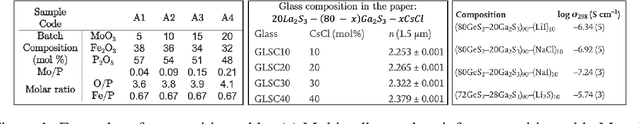
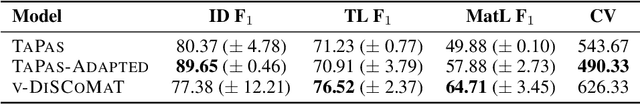
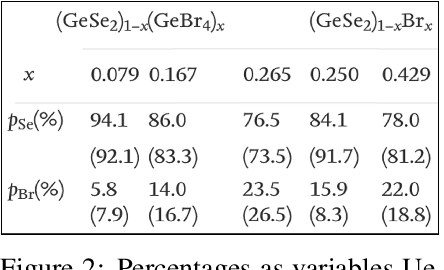
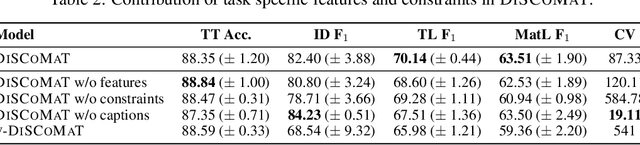
Abstract:A crucial component in the curation of KB for a scientific domain is information extraction from tables in the domain's published articles -- tables carry important information (often numeric), which must be adequately extracted for a comprehensive machine understanding of an article. Existing table extractors assume prior knowledge of table structure and format, which may not be known in scientific tables. We study a specific and challenging table extraction problem: extracting compositions of materials (e.g., glasses, alloys). We first observe that materials science researchers organize similar compositions in a wide variety of table styles, necessitating an intelligent model for table understanding and composition extraction. Consequently, we define this novel task as a challenge for the ML community and create a training dataset comprising 4,408 distantly supervised tables, along with 1,475 manually annotated dev and test tables. We also present DiSCoMaT, a strong baseline geared towards this specific task, which combines multiple graph neural networks with several task-specific regular expressions, features, and constraints. We show that DiSCoMaT outperforms recent table processing architectures by significant margins.
MatSciBERT: A Materials Domain Language Model for Text Mining and Information Extraction
Sep 30, 2021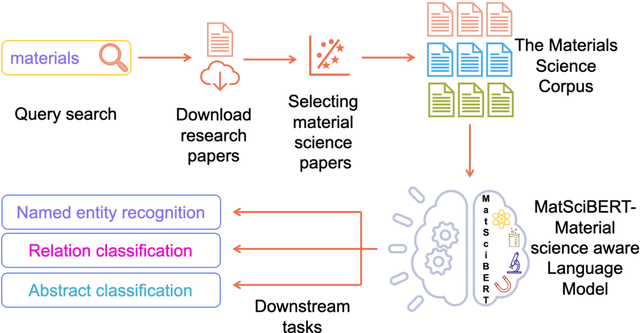
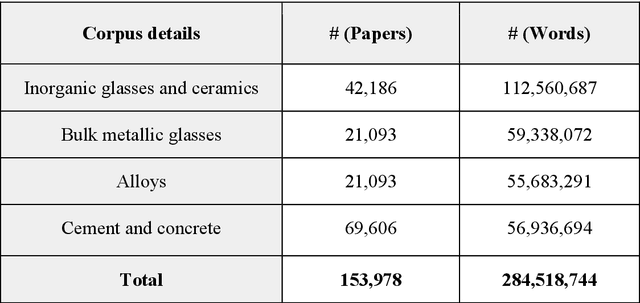
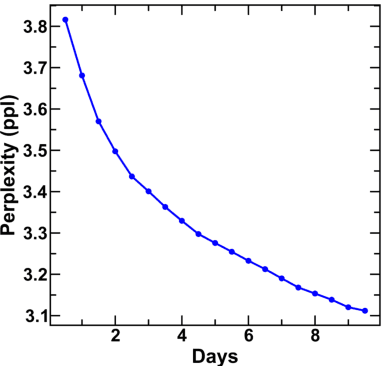
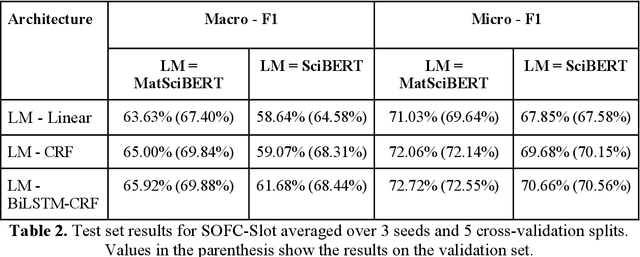
Abstract:An overwhelmingly large amount of knowledge in the materials domain is generated and stored as text published in peer-reviewed scientific literature. Recent developments in natural language processing, such as bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) models, provide promising tools to extract information from these texts. However, direct application of these models in the materials domain may yield suboptimal results as the models themselves may not be trained on notations and jargon that are specific to the domain. Here, we present a materials-aware language model, namely, MatSciBERT, which is trained on a large corpus of scientific literature published in the materials domain. We further evaluate the performance of MatSciBERT on three downstream tasks, namely, abstract classification, named entity recognition, and relation extraction, on different materials datasets. We show that MatSciBERT outperforms SciBERT, a language model trained on science corpus, on all the tasks. Further, we discuss some of the applications of MatSciBERT in the materials domain for extracting information, which can, in turn, contribute to materials discovery or optimization. Finally, to make the work accessible to the larger materials community, we make the pretrained and finetuned weights and the models of MatSciBERT freely accessible.
SalKG: Learning From Knowledge Graph Explanations for Commonsense Reasoning
Apr 18, 2021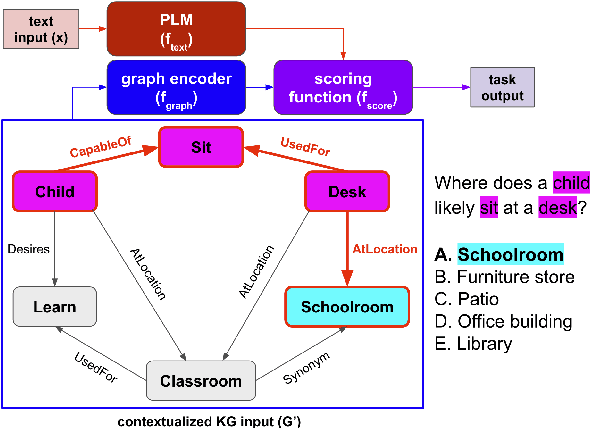
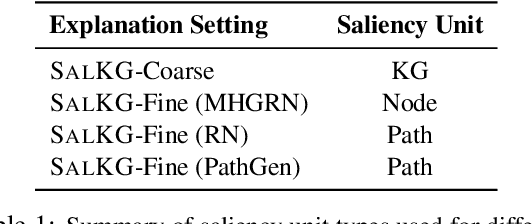
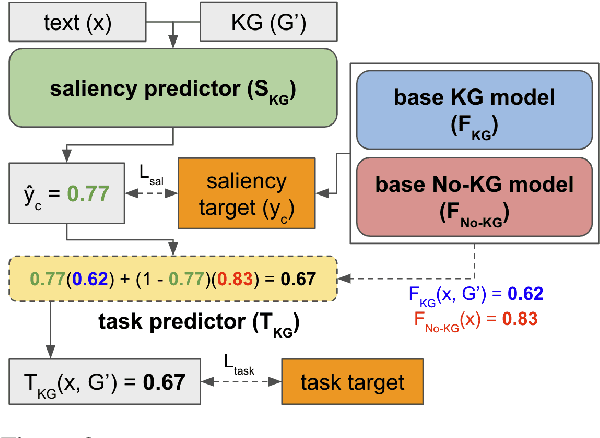
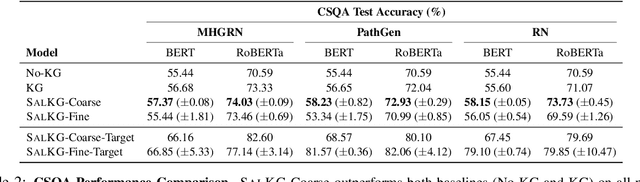
Abstract:Augmenting pre-trained language models with knowledge graphs (KGs) has achieved success on various commonsense reasoning tasks. Although some works have attempted to explain the behavior of such KG-augmented models by indicating which KG inputs are salient (i.e., important for the model's prediction), it is not always clear how these explanations should be used to make the model better. In this paper, we explore whether KG explanations can be used as supervision for teaching these KG-augmented models how to filter out unhelpful KG information. To this end, we propose SalKG, a simple framework for learning from KG explanations of both coarse (Is the KG salient?) and fine (Which parts of the KG are salient?) granularity. Given the explanations generated from a task's training set, SalKG trains KG-augmented models to solve the task by focusing on KG information highlighted by the explanations as salient. Across two popular commonsense QA benchmarks and three KG-augmented models, we find that SalKG's training process can consistently improve model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge