Taekang Woo
e-CLIP: Large-Scale Vision-Language Representation Learning in E-commerce
Jul 01, 2022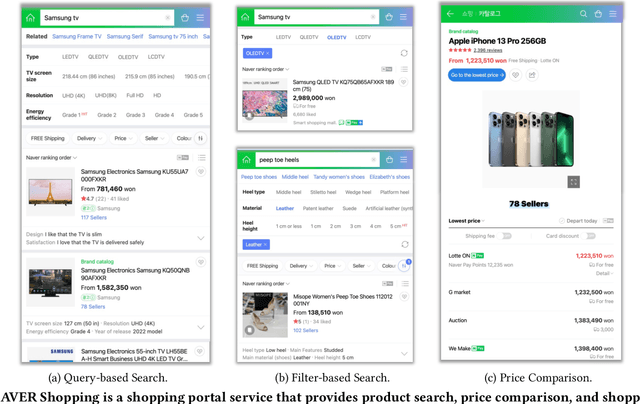
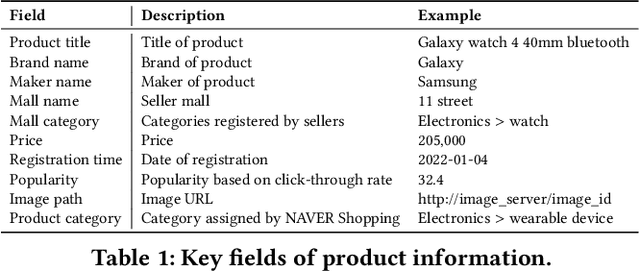
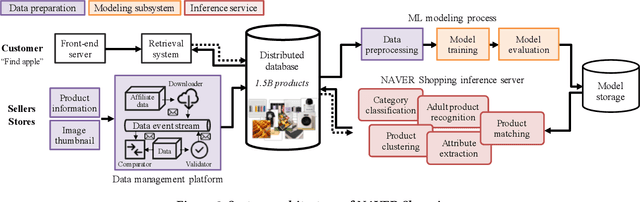
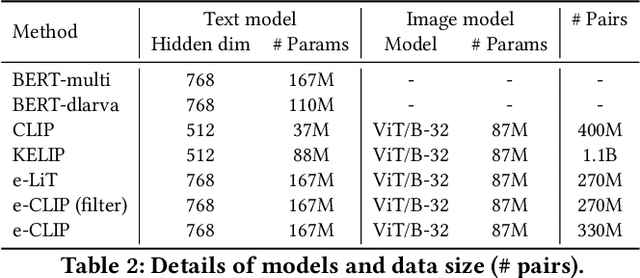
Abstract:Understanding vision and language representations of product content is vital for search and recommendation applications in e-commerce. As a backbone for online shopping platforms and inspired by the recent success in representation learning research, we propose a contrastive learning framework that aligns language and visual models using unlabeled raw product text and images. We present techniques we used to train large-scale representation learning models and share solutions that address domain-specific challenges. We study the performance using our pre-trained model as backbones for diverse downstream tasks, including category classification, attribute extraction, product matching, product clustering, and adult product recognition. Experimental results show that our proposed method outperforms the baseline in each downstream task regarding both single modality and multiple modalities.
SBNet: Segmentation-based Network for Natural Language-based Vehicle Search
Apr 22, 2021

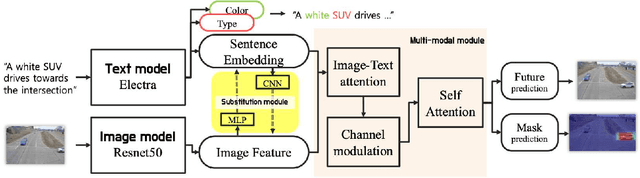
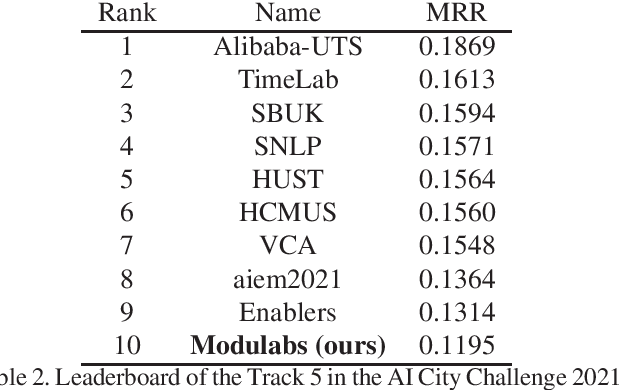
Abstract:Natural language-based vehicle retrieval is a task to find a target vehicle within a given image based on a natural language description as a query. This technology can be applied to various areas including police searching for a suspect vehicle. However, it is challenging due to the ambiguity of language descriptions and the difficulty of processing multi-modal data. To tackle this problem, we propose a deep neural network called SBNet that performs natural language-based segmentation for vehicle retrieval. We also propose two task-specific modules to improve performance: a substitution module that helps features from different domains to be embedded in the same space and a future prediction module that learns temporal information. SBnet has been trained using the CityFlow-NL dataset that contains 2,498 tracks of vehicles with three unique natural language descriptions each and tested 530 unique vehicle tracks and their corresponding query sets. SBNet achieved a significant improvement over the baseline in the natural language-based vehicle tracking track in the AI City Challenge 2021.
Multi-Attention-Based Soft Partition Network for Vehicle Re-Identification
Apr 21, 2021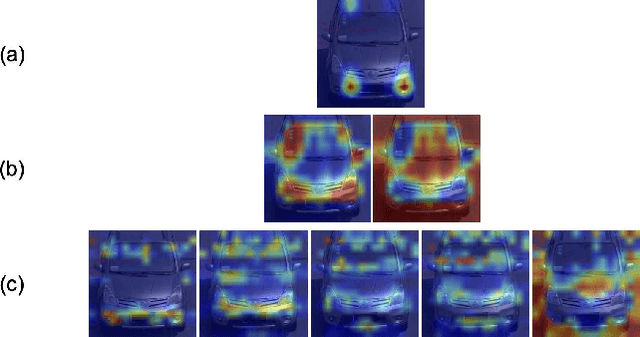
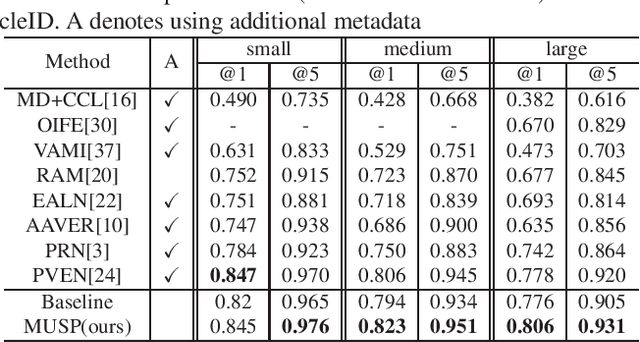
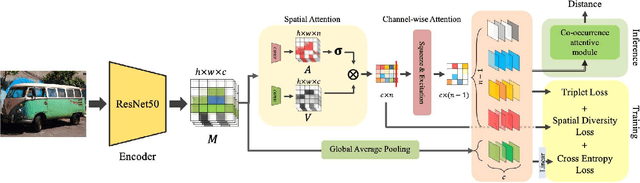
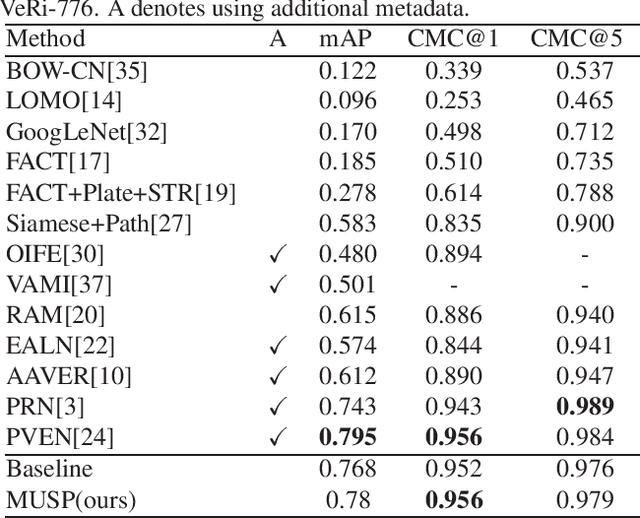
Abstract:Vehicle re-identification (Re-ID) distinguishes between the same vehicle and other vehicles in images. It is challenging due to significant intra-instance differences between identical vehicles from different views and subtle inter-instance differences of similar vehicles. Researchers have tried to address this problem by extracting features robust to variations of viewpoints and environments. More recently, they tried to improve performance by using additional metadata such as key points, orientation, and temporal information. Although these attempts have been relatively successful, they all require expensive annotations. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel deep neural network called a multi-attention-based soft partition (MUSP) network to solve this problem. This network does not use metadata and only uses multiple soft attentions to identify a specific vehicle area. This function was performed by metadata in previous studies. Experiments verified that MUSP achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance for the VehicleID dataset without any additional annotations and was comparable to VeRi-776 and VERI-Wild.
Wide-Residual-Inception Networks for Real-time Object Detection
Jul 17, 2017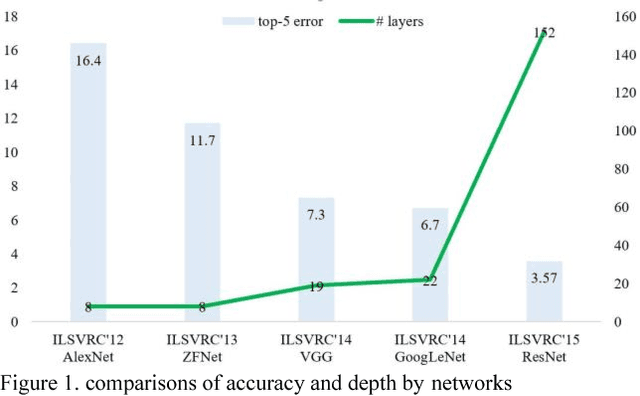
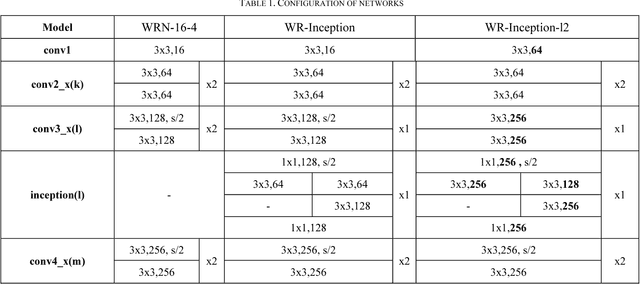
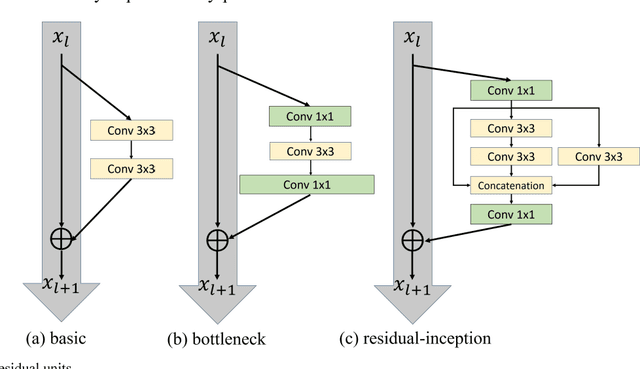
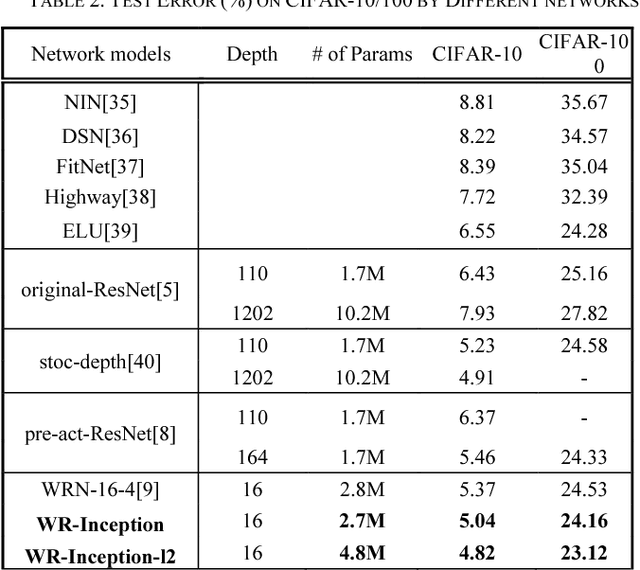
Abstract:Since convolutional neural network(CNN)models emerged,several tasks in computer vision have actively deployed CNN models for feature extraction. However,the conventional CNN models have a high computational cost and require high memory capacity, which is impractical and unaffordable for commercial applications such as real-time on-road object detection on embedded boards or mobile platforms. To tackle this limitation of CNN models, this paper proposes a wide-residual-inception (WR-Inception) network, which constructs the architecture based on a residual inception unit that captures objects of various sizes on the same feature map, as well as shallower and wider layers, compared to state-of-the-art networks like ResNet. To verify the proposed networks, this paper conducted two experiments; one is a classification task on CIFAR-10/100 and the other is an on-road object detection task using a Single-Shot Multi-box Detector(SSD) on the KITTI dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge