Jonghun Park
Voice Conversion with Diverse Intonation using Conditional Variational Auto-Encoder
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Voice conversion is a task of synthesizing an utterance with target speaker's voice while maintaining linguistic information of the source utterance. While a speaker can produce varying utterances from a single script with different intonations, conventional voice conversion models were limited to producing only one result per source input. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel approach for voice conversion with diverse intonations using conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE). Experiments have shown that the speaker's style feature can be mapped into a latent space with Gaussian distribution. We have also been able to convert voices with more diverse intonation by making the posterior of the latent space more complex with inverse autoregressive flow (IAF). As a result, the converted voice not only has a diversity of intonations, but also has better sound quality than the model without CVAE.
Note-Level Singing Melody Transcription for Time-Aligned Musical Score Generation
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:Automatic music transcription converts audio recordings into symbolic representations, facilitating music analysis, retrieval, and generation. A musical note is characterized by pitch, onset, and offset in an audio domain, whereas it is defined in terms of pitch and note value in a musical score domain. A time-aligned score, derived from timing information along with pitch and note value, allows matching a part of the score with the corresponding part of the music audio, enabling various applications. In this paper, we consider an extended version of the traditional note-level transcription task that recognizes onset, offset, and pitch, through including extraction of additional note value to generate a time-aligned score from an audio input. To address this new challenge, we propose an end-to-end framework that integrates recognition of the note value, pitch, and temporal information. This approach avoids error accumulation inherent in multi-stage methods and enhances accuracy through mutual reinforcement. Our framework employs tokenized representations specifically targeted for this task, through incorporating note value information. Furthermore, we introduce a pseudo-labeling technique to address a scarcity problem of annotated note value data. This technique produces approximate note value labels from existing datasets for the traditional note-level transcription. Experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed model in note-level transcription tasks when compared to existing state-of-the-art approaches. We also introduce new evaluation metrics that assess both temporal and note value aspects to demonstrate the robustness of the model. Moreover, qualitative assessments via visualized musical scores confirmed the effectiveness of our model in capturing the note values.
e-CLIP: Large-Scale Vision-Language Representation Learning in E-commerce
Jul 01, 2022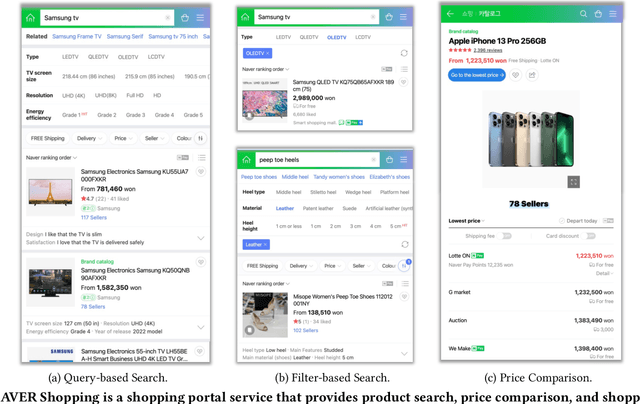
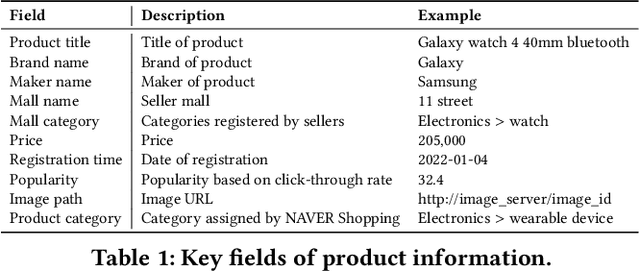
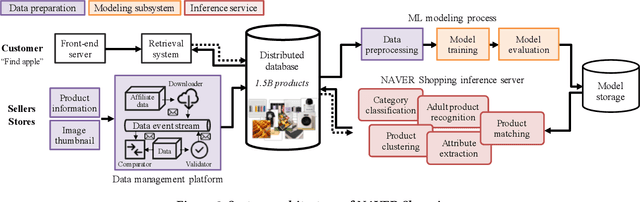
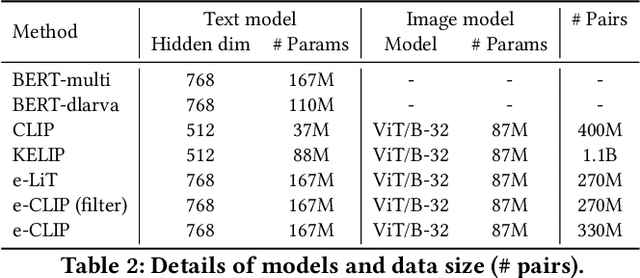
Abstract:Understanding vision and language representations of product content is vital for search and recommendation applications in e-commerce. As a backbone for online shopping platforms and inspired by the recent success in representation learning research, we propose a contrastive learning framework that aligns language and visual models using unlabeled raw product text and images. We present techniques we used to train large-scale representation learning models and share solutions that address domain-specific challenges. We study the performance using our pre-trained model as backbones for diverse downstream tasks, including category classification, attribute extraction, product matching, product clustering, and adult product recognition. Experimental results show that our proposed method outperforms the baseline in each downstream task regarding both single modality and multiple modalities.
Learning a Word-Level Language Model with Sentence-Level Noise Contrastive Estimation for Contextual Sentence Probability Estimation
Mar 14, 2021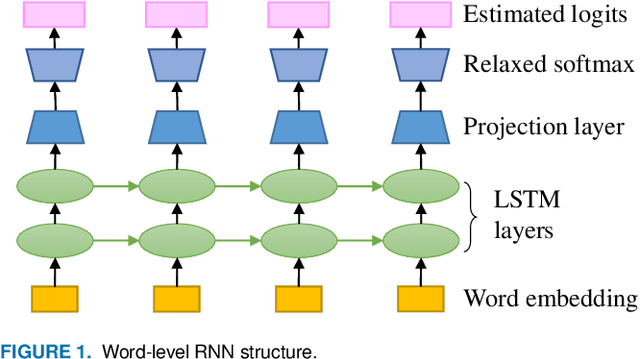
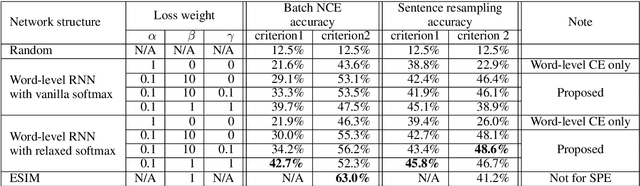
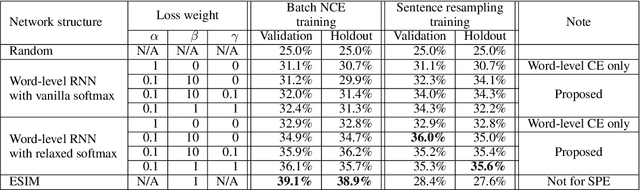
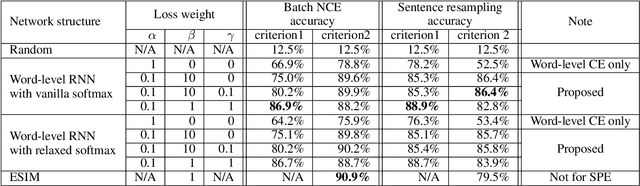
Abstract:Inferring the probability distribution of sentences or word sequences is a key process in natural language processing. While word-level language models (LMs) have been widely adopted for computing the joint probabilities of word sequences, they have difficulty in capturing a context long enough for sentence probability estimation (SPE). To overcome this, recent studies introduced training methods using sentence-level noise-contrastive estimation (NCE) with recurrent neural networks (RNNs). In this work, we attempt to extend it for contextual SPE, which aims to estimate a conditional sentence probability given a previous text. The proposed NCE samples negative sentences independently of a previous text so that the trained model gives higher probabilities to the sentences that are more consistent with \textcolor{blue}{the} context. We apply our method to a simple word-level RNN LM to focus on the effect of the sentence-level NCE training rather than on the network architecture. The quality of estimation was evaluated against multiple-choice cloze-style questions including both human and automatically generated questions. The experimental results show that the proposed method improved the SPE quality for the word-level RNN LM.
Image-to-Image Retrieval by Learning Similarity between Scene Graphs
Dec 29, 2020

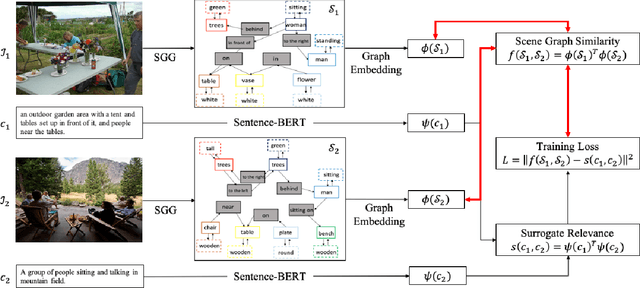
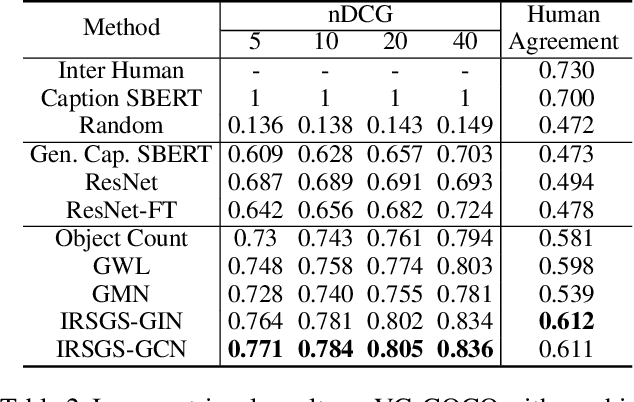
Abstract:As a scene graph compactly summarizes the high-level content of an image in a structured and symbolic manner, the similarity between scene graphs of two images reflects the relevance of their contents. Based on this idea, we propose a novel approach for image-to-image retrieval using scene graph similarity measured by graph neural networks. In our approach, graph neural networks are trained to predict the proxy image relevance measure, computed from human-annotated captions using a pre-trained sentence similarity model. We collect and publish the dataset for image relevance measured by human annotators to evaluate retrieval algorithms. The collected dataset shows that our method agrees well with the human perception of image similarity than other competitive baselines.
A Bi-directional Transformer for Musical Chord Recognition
Jul 05, 2019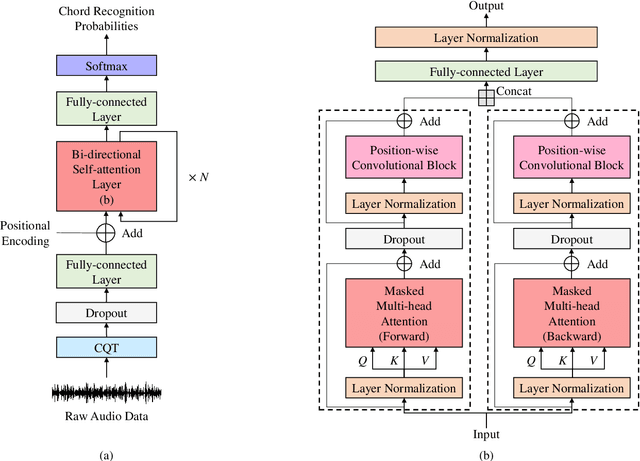
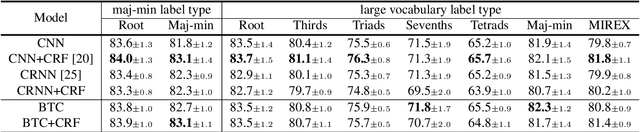
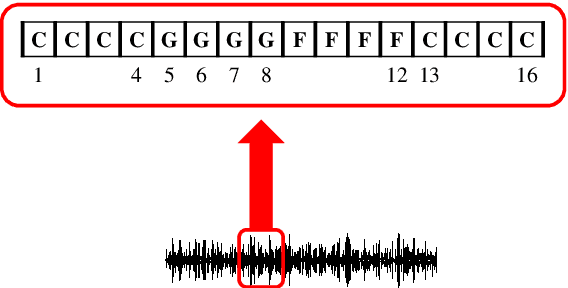
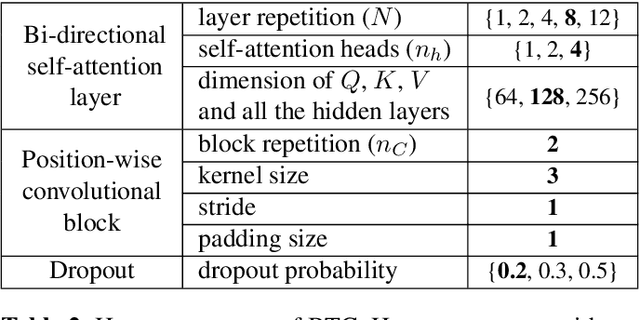
Abstract:Chord recognition is an important task since chords are highly abstract and descriptive features of music. For effective chord recognition, it is essential to utilize relevant context in audio sequence. While various machine learning models such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have been employed for the task, most of them have limitations in capturing long-term dependency or require training of an additional model. In this work, we utilize a self-attention mechanism for chord recognition to focus on certain regions of chords. Training of the proposed bi-directional Transformer for chord recognition (BTC) consists of a single phase while showing competitive performance. Through an attention map analysis, we have visualized how attention was performed. It turns out that the model was able to divide segments of chords by utilizing adaptive receptive field of the attention mechanism. Furthermore, it was observed that the model was able to effectively capture long-term dependencies, making use of essential information regardless of distance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge