Suzhou Huang
Calibration of Human Driving Behavior and Preference Using Naturalistic Traffic Data
May 05, 2021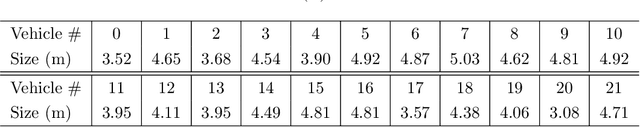
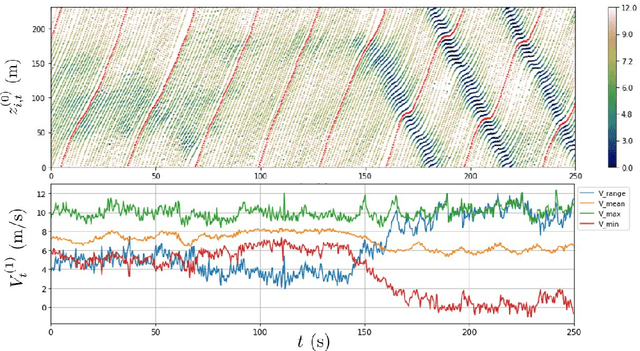
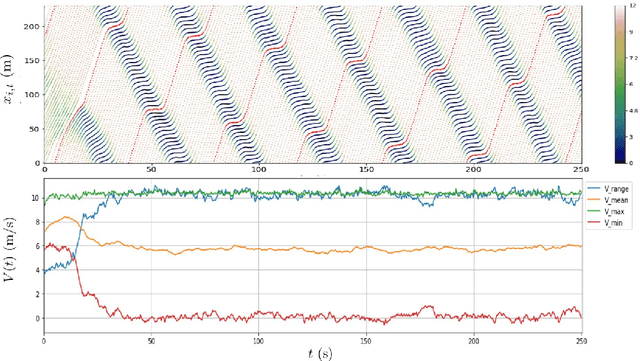
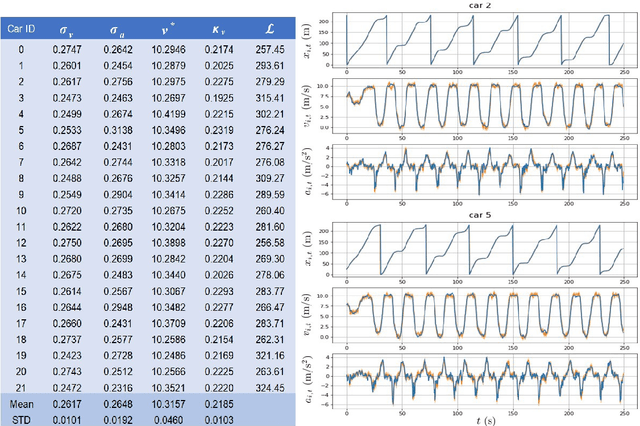
Abstract:Understanding human driving behaviors quantitatively is critical even in the era when connected and autonomous vehicles and smart infrastructure are becoming ever more prevalent. This is particularly so as that mixed traffic settings, where autonomous vehicles and human driven vehicles co-exist, are expected to persist for quite some time. Towards this end it is necessary that we have a comprehensive modeling framework for decision-making within which human driving preferences can be inferred statistically from observed driving behaviors in realistic and naturalistic traffic settings. Leveraging a recently proposed computational framework for smart vehicles in a smart world using multi-agent based simulation and optimization, we first recapitulate how the forward problem of driving decision-making is modeled as a state space model. We then show how the model can be inverted to estimate driver preferences from naturalistic traffic data using the standard Kalman filter technique. We explicitly illustrate our approach using the vehicle trajectory data from Sugiyama experiment that was originally meant to demonstrate how stop-and-go shockwave can arise spontaneously without bottlenecks. Not only the estimated state filter can fit the observed data well for each individual vehicle, the inferred utility functions can also re-produce quantitatively similar pattern of the observed collective behaviors. One distinct advantage of our approach is the drastically reduced computational burden. This is possible because our forward model treats driving decision process, which is intrinsically dynamic with multi-agent interactions, as a sequence of independent static optimization problems contingent on the state with a finite look ahead anticipation. Consequently we can practically sidestep solving an interacting dynamic inversion problem that would have been much more computationally demanding.
Towards a Systematic Computational Framework for Modeling Multi-Agent Decision-Making at Micro Level for Smart Vehicles in a Smart World
Sep 25, 2020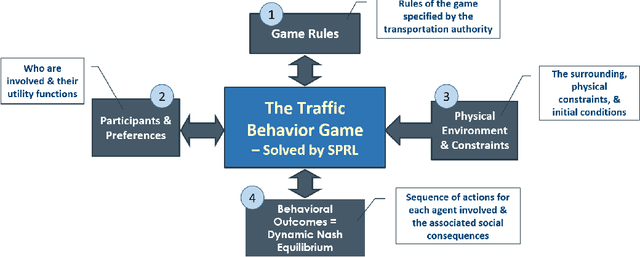
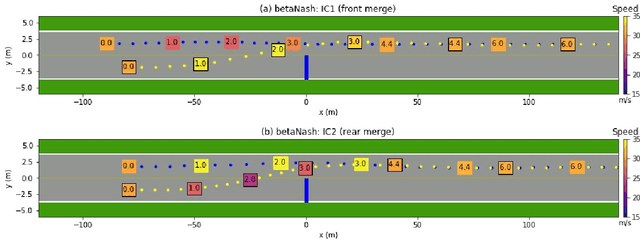
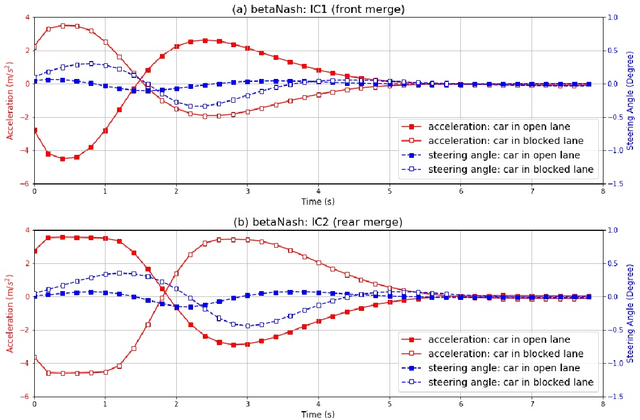
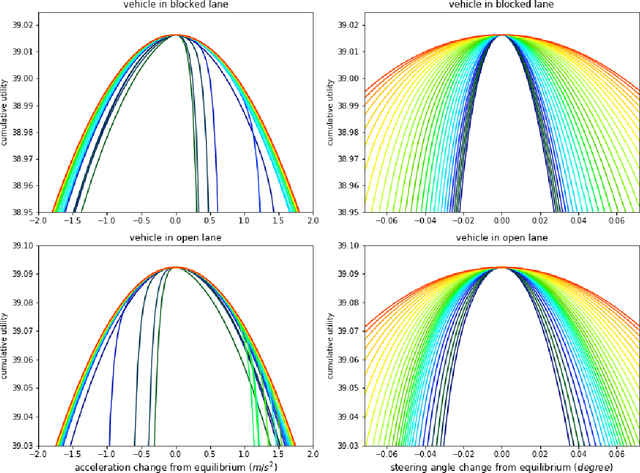
Abstract:We propose a multi-agent based computational framework for modeling decision-making and strategic interaction at micro level for smart vehicles in a smart world. The concepts of Markov game and best response dynamics are heavily leveraged. Our aim is to make the framework conceptually sound and computationally practical for a range of realistic applications, including micro path planning for autonomous vehicles. To this end, we first convert the would-be stochastic game problem into a closely related deterministic one by introducing risk premium in the utility function for each individual agent. We show how the sub-game perfect Nash equilibrium of the simplified deterministic game can be solved by an algorithm based on best response dynamics. In order to better model human driving behaviors with bounded rationality, we seek to further simplify the solution concept by replacing the Nash equilibrium condition with a heuristic and adaptive optimization with finite look-ahead anticipation. In addition, the algorithm corresponding to the new solution concept drastically improves the computational efficiency. To demonstrate how our approach can be applied to realistic traffic settings, we conduct a simulation experiment: to derive merging and yielding behaviors on a double-lane highway with an unexpected barrier. Despite assumption differences involved in the two solution concepts, the derived numerical solutions show that the endogenized driving behaviors are very similar. We also briefly comment on how the proposed framework can be further extended in a number of directions in our forthcoming work, such as behavioral calibration using real traffic video data, computational mechanism design for traffic policy optimization, and so on.
A Game Theoretic Approach for Parking Spot Search with Limited Parking Lot Information
May 11, 2020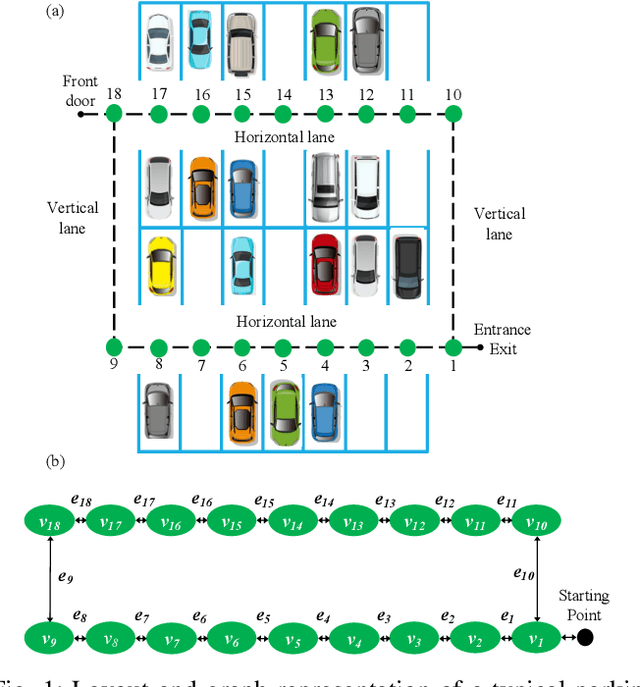
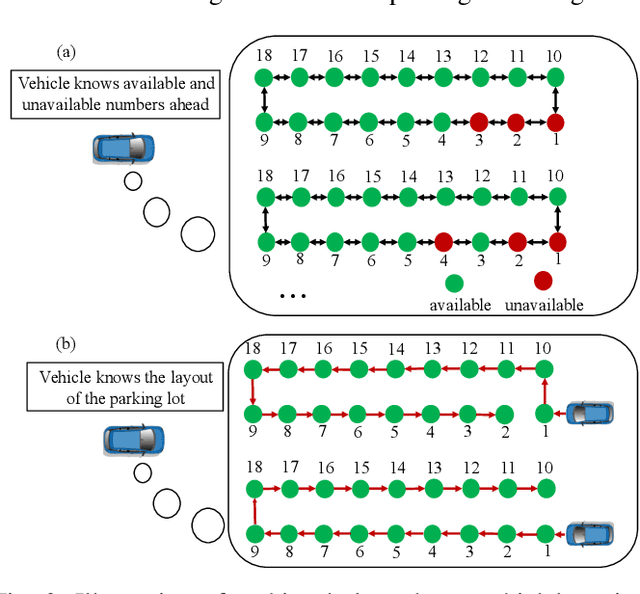
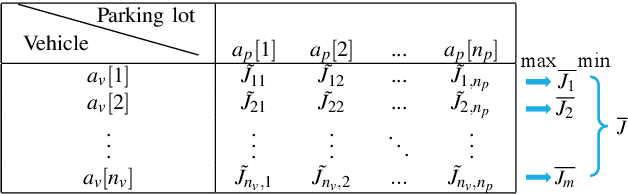
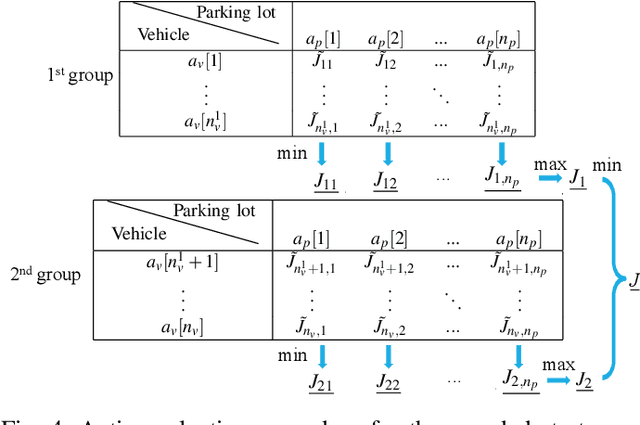
Abstract:We propose a game theoretic approach to address the problem of searching for available parking spots in a parking lot and picking the ``optimal'' one to park. The approach exploits limited information provided by the parking lot, i.e., its layout and the current number of cars in it. Considering the fact that such information is or can be easily made available for many structured parking lots, the proposed approach can be applicable without requiring major updates to existing parking facilities. For large parking lots, a sampling-based strategy is integrated with the proposed approach to overcome the associated computational challenge. The proposed approach is compared against a state-of-the-art heuristic-based parking spot search strategy in the literature through simulation studies and demonstrates its advantage in terms of achieving lower cost function values.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge