Sultan Daud Khan
VisDrone-CC2020: The Vision Meets Drone Crowd Counting Challenge Results
Jul 19, 2021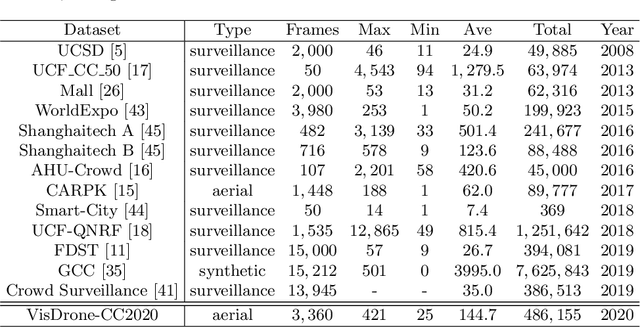

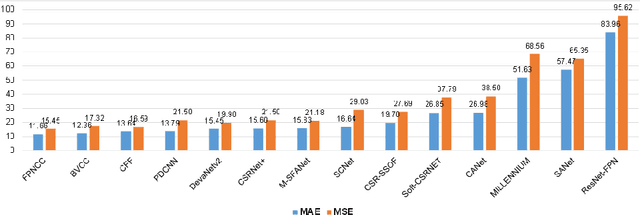
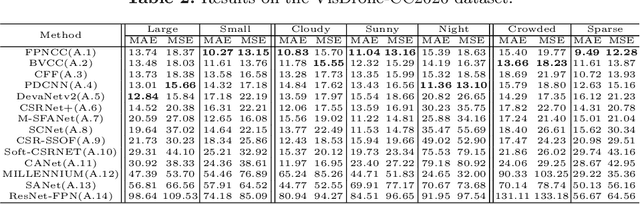
Abstract:Crowd counting on the drone platform is an interesting topic in computer vision, which brings new challenges such as small object inference, background clutter and wide viewpoint. However, there are few algorithms focusing on crowd counting on the drone-captured data due to the lack of comprehensive datasets. To this end, we collect a large-scale dataset and organize the Vision Meets Drone Crowd Counting Challenge (VisDrone-CC2020) in conjunction with the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2020) to promote the developments in the related fields. The collected dataset is formed by $3,360$ images, including $2,460$ images for training, and $900$ images for testing. Specifically, we manually annotate persons with points in each video frame. There are $14$ algorithms from $15$ institutes submitted to the VisDrone-CC2020 Challenge. We provide a detailed analysis of the evaluation results and conclude the challenge. More information can be found at the website: \url{http://www.aiskyeye.com/}.
* The method description of A7 Mutil-Scale Aware based SFANet (M-SFANet) is updated and missing references are added
A survey of advances in vision-based vehicle re-identification
May 30, 2019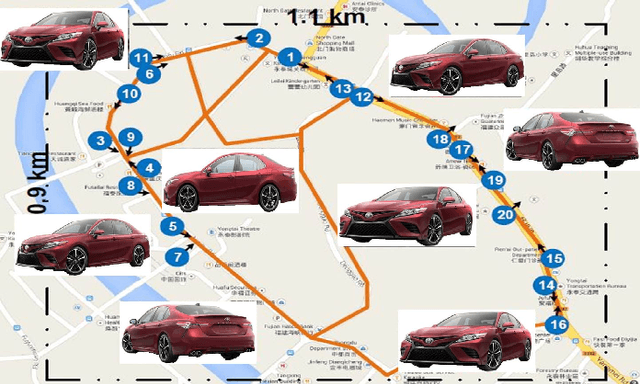
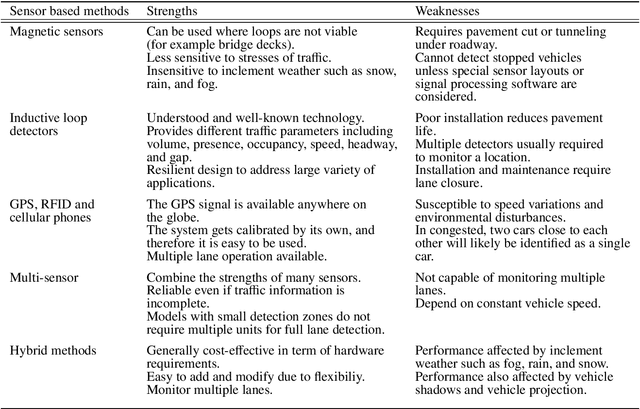
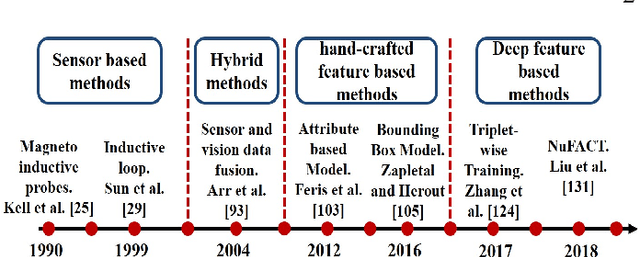
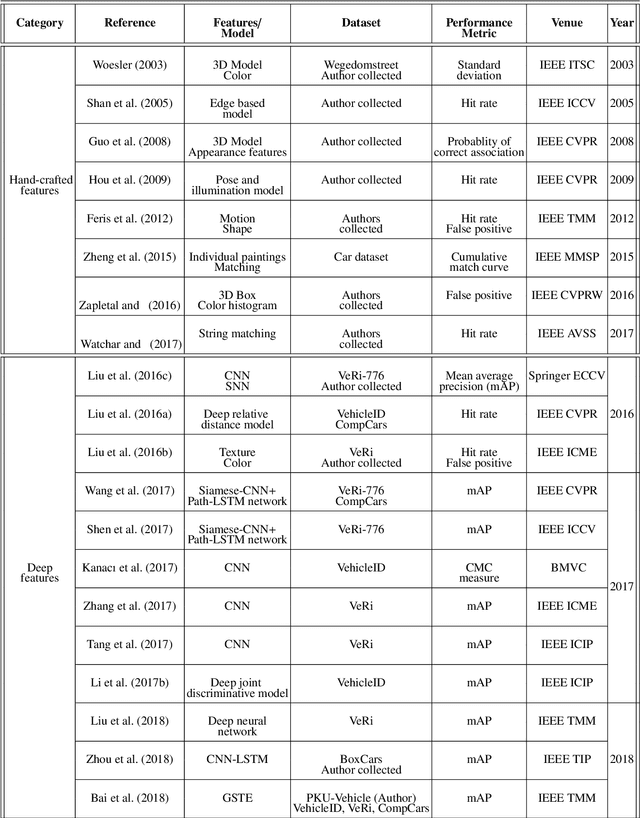
Abstract:Vehicle re-identification (V-reID) has become significantly popular in the community due to its applications and research significance. In particular, the V-reID is an important problem that still faces numerous open challenges. This paper reviews different V-reID methods including sensor based methods, hybrid methods, and vision based methods which are further categorized into hand-crafted feature based methods and deep feature based methods. The vision based methods make the V-reID problem particularly interesting, and our review systematically addresses and evaluates these methods for the first time. We conduct experiments on four comprehensive benchmark datasets and compare the performances of recent hand-crafted feature based methods and deep feature based methods. We present the detail analysis of these methods in terms of mean average precision (mAP) and cumulative matching curve (CMC). These analyses provide objective insight into the strengths and weaknesses of these methods. We also provide the details of different V-reID datasets and critically discuss the challenges and future trends of V-reID methods.
* 17 pages; 21 figures; journal paper
Towards a Crowd Analytic Framework For Crowd Management in Majid-al-Haram
Sep 14, 2017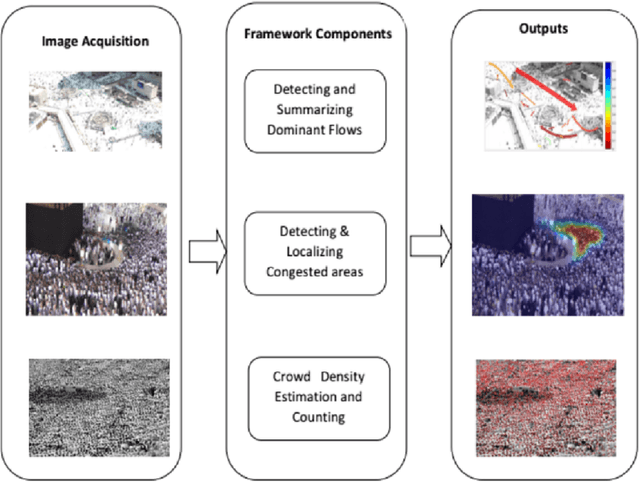

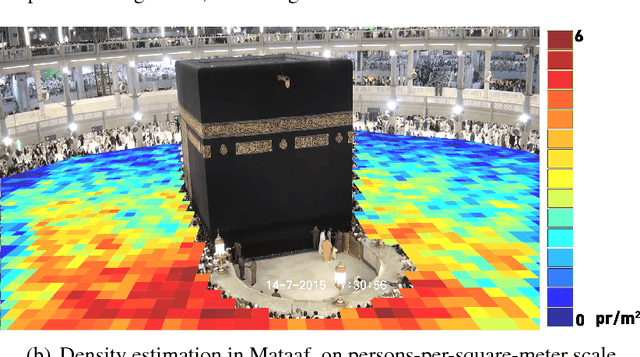
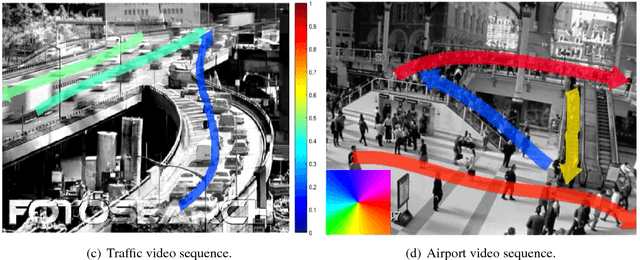
Abstract:The scared cities of Makkah Al Mukarramah and Madina Al Munawarah host millions of pilgrims every year. During Hajj, the movement of large number of people has a unique spatial and temporal constraints, which makes Hajj one of toughest challenges for crowd management. In this paper, we propose a computer vision based framework that automatically analyses video sequence and computes important measurements which include estimation of crowd density, identification of dominant patterns, detection and localization of congestion. In addition, we analyze helpful statistics of the crowd like speed, and direction, that could provide support to crowd management personnel. The framework presented in this paper indicate that new advances in computer vision and machine learning can be leveraged effectively for challenging and high density crowd management applications. However, significant customization of existing approaches is required to apply them to the challenging crowd management situations in Masjid Al Haram. Our results paint a promising picture for deployment of computer vision technologies to assist in quantitative measurement of crowd size, density and congestion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge