Stamatis Outsios
GreekBART: The First Pretrained Greek Sequence-to-Sequence Model
Apr 03, 2023



Abstract:The era of transfer learning has revolutionized the fields of Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing, bringing powerful pretrained models with exceptional performance across a variety of tasks. Specifically, Natural Language Processing tasks have been dominated by transformer-based language models. In Natural Language Inference and Natural Language Generation tasks, the BERT model and its variants, as well as the GPT model and its successors, demonstrated exemplary performance. However, the majority of these models are pretrained and assessed primarily for the English language or on a multilingual corpus. In this paper, we introduce GreekBART, the first Seq2Seq model based on BART-base architecture and pretrained on a large-scale Greek corpus. We evaluate and compare GreekBART against BART-random, Greek-BERT, and XLM-R on a variety of discriminative tasks. In addition, we examine its performance on two NLG tasks from GreekSUM, a newly introduced summarization dataset for the Greek language. The model, the code, and the new summarization dataset will be publicly available.
NLP Research and Resources at DaSciM, Ecole Polytechnique
Dec 01, 2021Abstract:DaSciM (Data Science and Mining) part of LIX at Ecole Polytechnique, established in 2013 and since then producing research results in the area of large scale data analysis via methods of machine and deep learning. The group has been specifically active in the area of NLP and text mining with interesting results at methodological and resources level. Here follow our different contributions of interest to the AFIA community.
An Ensemble Method for Producing Word Representations for the Greek Language
Dec 10, 2019



Abstract:In this paper we present a new ensemble method, Continuous Bag-of-Skip-grams (CBOS), that produces high-quality word representations for the Greek language. The CBOS method combines the pioneering approaches for learning word representations: Continuous Bag-of-Words (CBOW) and Continuous Skip-gram. These methods are compared through a word analogy task on three different sources of data: the English Wikipedia corpus, the Greek Wikipedia corpus, and the Greek Web Content corpus. By comparing these methods across different datasets, it is evident that the CBOS method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Evaluation of Greek Word Embeddings
Apr 08, 2019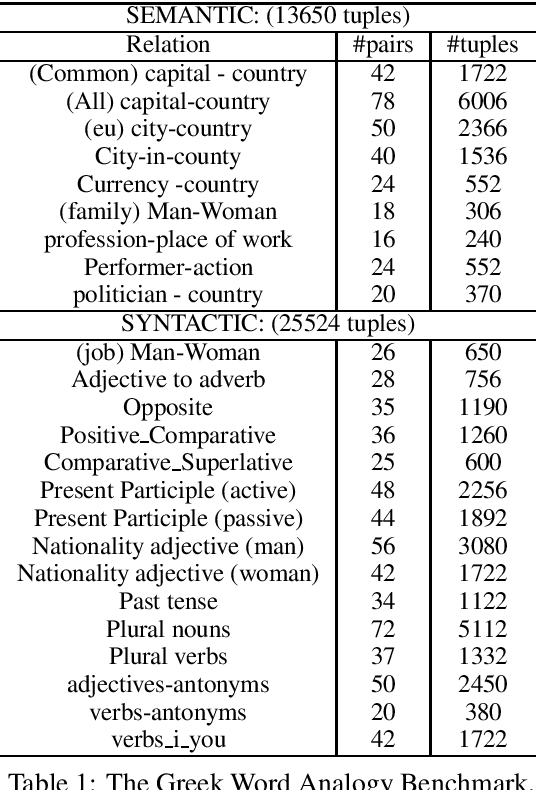

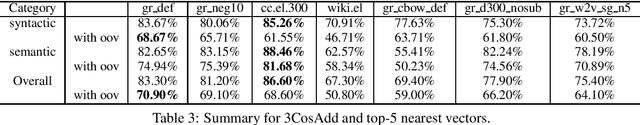

Abstract:Since word embeddings have been the most popular input for many NLP tasks, evaluating their quality is of critical importance. Most research efforts are focusing on English word embeddings. This paper addresses the problem of constructing and evaluating such models for the Greek language. We created a new word analogy corpus considering the original English Word2vec word analogy corpus and some specific linguistic aspects of the Greek language as well. Moreover, we created a Greek version of WordSim353 corpora for a basic evaluation of word similarities. We tested seven word vector models and our evaluation showed that we are able to create meaningful representations. Last, we discovered that the morphological complexity of the Greek language and polysemy can influence the quality of the resulting word embeddings.
Word Embeddings from Large-Scale Greek Web Content
Oct 26, 2018Abstract:Word embeddings are undoubtedly very useful components in many NLP tasks. In this paper, we present word embeddings and other linguistic resources trained on the largest to date digital Greek language corpus. We also present a live web tool for testing the Greek word embeddings, by offering "analogy", "similarity score" and "most similar words" functions. Through our explorer, one could interact with the Greek word vectors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge