Solange Rossato
Pantagruel: Unified Self-Supervised Encoders for French Text and Speech
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:We release Pantagruel models, a new family of self-supervised encoder models for French text and speech. Instead of predicting modality-tailored targets such as textual tokens or speech units, Pantagruel learns contextualized target representations in the feature space, allowing modality-specific encoders to capture linguistic and acoustic regularities more effectively. Separate models are pre-trained on large-scale French corpora, including Wikipedia, OSCAR and CroissantLLM for text, together with MultilingualLibriSpeech, LeBenchmark, and INA-100k for speech. INA-100k is a newly introduced 100,000-hour corpus of French audio derived from the archives of the Institut National de l'Audiovisuel (INA), the national repository of French radio and television broadcasts, providing highly diverse audio data. We evaluate Pantagruel across a broad range of downstream tasks spanning both modalities, including those from the standard French benchmarks such as FLUE or LeBenchmark. Across these tasks, Pantagruel models show competitive or superior performance compared to strong French baselines such as CamemBERT, FlauBERT, and LeBenchmark2.0, while maintaining a shared architecture that can seamlessly handle either speech or text inputs. These results confirm the effectiveness of feature-space self-supervised objectives for French representation learning and highlight Pantagruel as a robust foundation for multimodal speech-text understanding.
LeBenchmark 2.0: a Standardized, Replicable and Enhanced Framework for Self-supervised Representations of French Speech
Sep 11, 2023Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) is at the origin of unprecedented improvements in many different domains including computer vision and natural language processing. Speech processing drastically benefitted from SSL as most of the current domain-related tasks are now being approached with pre-trained models. This work introduces LeBenchmark 2.0 an open-source framework for assessing and building SSL-equipped French speech technologies. It includes documented, large-scale and heterogeneous corpora with up to 14,000 hours of heterogeneous speech, ten pre-trained SSL wav2vec 2.0 models containing from 26 million to one billion learnable parameters shared with the community, and an evaluation protocol made of six downstream tasks to complement existing benchmarks. LeBenchmark 2.0 also presents unique perspectives on pre-trained SSL models for speech with the investigation of frozen versus fine-tuned downstream models, task-agnostic versus task-specific pre-trained models as well as a discussion on the carbon footprint of large-scale model training.
LeBenchmark: A Reproducible Framework for Assessing Self-Supervised Representation Learning from Speech
Apr 23, 2021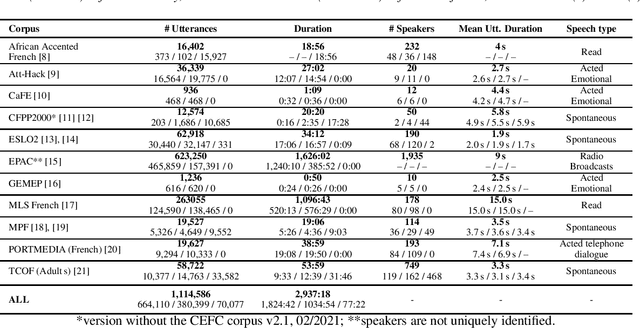
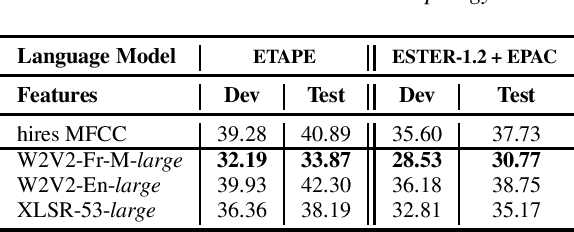
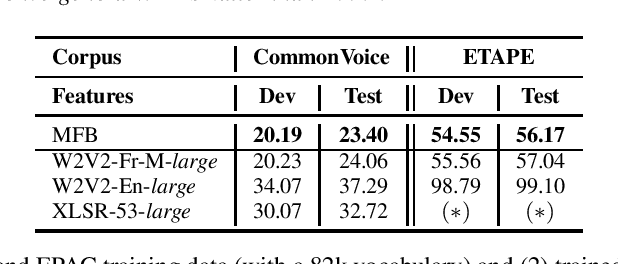
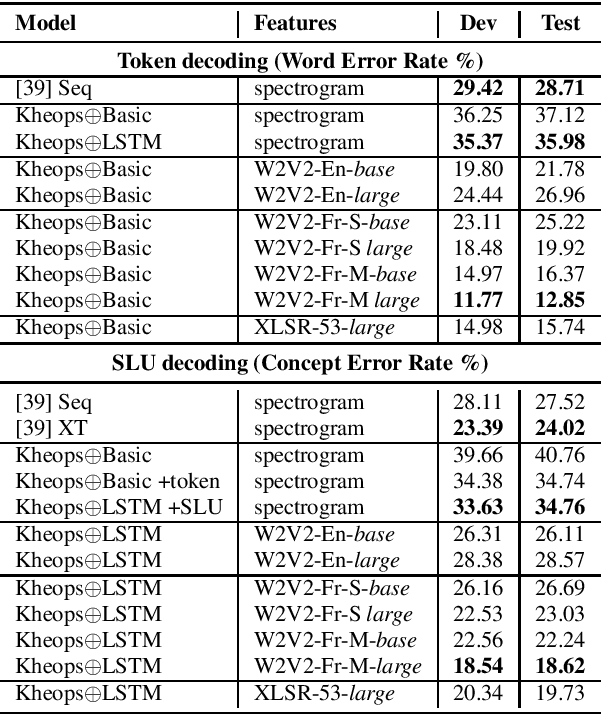
Abstract:Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) using huge unlabeled data has been successfully explored for image and natural language processing. Recent works also investigated SSL from speech. They were notably successful to improve performance on downstream tasks such as automatic speech recognition (ASR). While these works suggest it is possible to reduce dependence on labeled data for building efficient speech systems, their evaluation was mostly made on ASR and using multiple and heterogeneous experimental settings (most of them for English). This renders difficult the objective comparison between SSL approaches and the evaluation of their impact on building speech systems. In this paper, we propose LeBenchmark: a reproducible framework for assessing SSL from speech. It not only includes ASR (high and low resource) tasks but also spoken language understanding, speech translation and emotion recognition. We also target speech technologies in a language different than English: French. SSL models of different sizes are trained from carefully sourced and documented datasets. Experiments show that SSL is beneficial for most but not all tasks which confirms the need for exhaustive and reliable benchmarks to evaluate its real impact. LeBenchmark is shared with the scientific community for reproducible research in SSL from speech.
Gender Representation in Open Source Speech Resources
Mar 18, 2020



Abstract:With the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and the growing use of deep-learning architectures, the question of ethics, transparency and fairness of AI systems has become a central concern within the research community. We address transparency and fairness in spoken language systems by proposing a study about gender representation in speech resources available through the Open Speech and Language Resource platform. We show that finding gender information in open source corpora is not straightforward and that gender balance depends on other corpus characteristics (elicited/non elicited speech, low/high resource language, speech task targeted). The paper ends with recommendations about metadata and gender information for researchers in order to assure better transparency of the speech systems built using such corpora.
Gender Representation in French Broadcast Corpora and Its Impact on ASR Performance
Aug 23, 2019
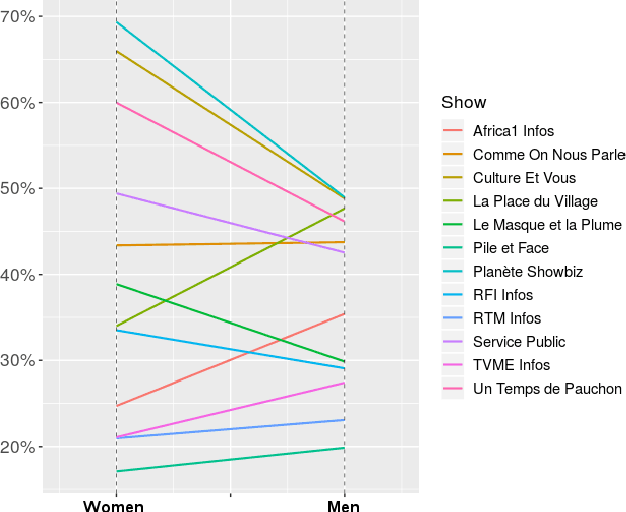


Abstract:This paper analyzes the gender representation in four major corpora of French broadcast. These corpora being widely used within the speech processing community, they are a primary material for training automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. As gender bias has been highlighted in numerous natural language processing (NLP) applications, we study the impact of the gender imbalance in TV and radio broadcast on the performance of an ASR system. This analysis shows that women are under-represented in our data in terms of speakers and speech turns. We introduce the notion of speaker role to refine our analysis and find that women are even fewer within the Anchor category corresponding to prominent speakers. The disparity of available data for both gender causes performance to decrease on women. However this global trend can be counterbalanced for speaker who are used to speak in the media when sufficient amount of data is available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge