Siyang Jiang
Tibetan Language and AI: A Comprehensive Survey of Resources, Methods and Challenges
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Tibetan, one of the major low-resource languages in Asia, presents unique linguistic and sociocultural characteristics that pose both challenges and opportunities for AI research. Despite increasing interest in developing AI systems for underrepresented languages, Tibetan has received limited attention due to a lack of accessible data resources, standardized benchmarks, and dedicated tools. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of the current state of Tibetan AI in the AI domain, covering textual and speech data resources, NLP tasks, machine translation, speech recognition, and recent developments in LLMs. We systematically categorize existing datasets and tools, evaluate methods used across different tasks, and compare performance where possible. We also identify persistent bottlenecks such as data sparsity, orthographic variation, and the lack of unified evaluation metrics. Additionally, we discuss the potential of cross-lingual transfer, multi-modal learning, and community-driven resource creation. This survey aims to serve as a foundational reference for future work on Tibetan AI research and encourages collaborative efforts to build an inclusive and sustainable AI ecosystem for low-resource languages.
ContextAgent: Context-Aware Proactive LLM Agents with Open-World Sensory Perceptions
May 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have propelled intelligent agents from reactive responses to proactive support. While promising, existing proactive agents either rely exclusively on observations from enclosed environments (e.g., desktop UIs) with direct LLM inference or employ rule-based proactive notifications, leading to suboptimal user intent understanding and limited functionality for proactive service. In this paper, we introduce ContextAgent, the first context-aware proactive agent that incorporates extensive sensory contexts to enhance the proactive capabilities of LLM agents. ContextAgent first extracts multi-dimensional contexts from massive sensory perceptions on wearables (e.g., video and audio) to understand user intentions. ContextAgent then leverages the sensory contexts and the persona contexts from historical data to predict the necessity for proactive services. When proactive assistance is needed, ContextAgent further automatically calls the necessary tools to assist users unobtrusively. To evaluate this new task, we curate ContextAgentBench, the first benchmark for evaluating context-aware proactive LLM agents, covering 1,000 samples across nine daily scenarios and twenty tools. Experiments on ContextAgentBench show that ContextAgent outperforms baselines by achieving up to 8.5% and 6.0% higher accuracy in proactive predictions and tool calling, respectively. We hope our research can inspire the development of more advanced, human-centric, proactive AI assistants.
An LLM-Empowered Low-Resolution Vision System for On-Device Human Behavior Understanding
May 03, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancements in Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) offer the potential to surpass conventional labeling by generating richer, more detailed descriptions of on-device human behavior understanding (HBU) in low-resolution vision systems, such as depth, thermal, and infrared. However, existing large vision language model (LVLM) approaches are unable to understand low-resolution data well as they are primarily designed for high-resolution data, such as RGB images. A quick fixing approach is to caption a large amount of low-resolution data, but it requires a significant amount of labor-intensive annotation efforts. In this paper, we propose a novel, labor-saving system, Llambda, designed to support low-resolution HBU. The core idea is to leverage limited labeled data and a large amount of unlabeled data to guide LLMs in generating informative captions, which can be combined with raw data to effectively fine-tune LVLM models for understanding low-resolution videos in HBU. First, we propose a Contrastive-Oriented Data Labeler, which can capture behavior-relevant information from long, low-resolution videos and generate high-quality pseudo labels for unlabeled data via contrastive learning. Second, we propose a Physical-Knowledge Guided Captioner, which utilizes spatial and temporal consistency checks to mitigate errors in pseudo labels. Therefore, it can improve LLMs' understanding of sequential data and then generate high-quality video captions. Finally, to ensure on-device deployability, we employ LoRA-based efficient fine-tuning to adapt LVLMs for low-resolution data. We evaluate Llambda using a region-scale real-world testbed and three distinct low-resolution datasets, and the experiments show that Llambda outperforms several state-of-the-art LVLM systems up to $40.03\%$ on average Bert-Score.
DrHouse: An LLM-empowered Diagnostic Reasoning System through Harnessing Outcomes from Sensor Data and Expert Knowledge
May 21, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have the potential to transform digital healthcare, as evidenced by recent advances in LLM-based virtual doctors. However, current approaches rely on patient's subjective descriptions of symptoms, causing increased misdiagnosis. Recognizing the value of daily data from smart devices, we introduce a novel LLM-based multi-turn consultation virtual doctor system, DrHouse, which incorporates three significant contributions: 1) It utilizes sensor data from smart devices in the diagnosis process, enhancing accuracy and reliability. 2) DrHouse leverages continuously updating medical databases such as Up-to-Date and PubMed to ensure our model remains at diagnostic standard's forefront. 3) DrHouse introduces a novel diagnostic algorithm that concurrently evaluates potential diseases and their likelihood, facilitating more nuanced and informed medical assessments. Through multi-turn interactions, DrHouse determines the next steps, such as accessing daily data from smart devices or requesting in-lab tests, and progressively refines its diagnoses. Evaluations on three public datasets and our self-collected datasets show that DrHouse can achieve up to an 18.8% increase in diagnosis accuracy over the state-of-the-art baselines. The results of a 32-participant user study show that 75% medical experts and 91.7% patients are willing to use DrHouse.
Dual Adversarial Alignment for Realistic Support-Query Shift Few-shot Learning
Sep 05, 2023Abstract:Support-query shift few-shot learning aims to classify unseen examples (query set) to labeled data (support set) based on the learned embedding in a low-dimensional space under a distribution shift between the support set and the query set. However, in real-world scenarios the shifts are usually unknown and varied, making it difficult to estimate in advance. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a novel but more difficult challenge, RSQS, focusing on Realistic Support-Query Shift few-shot learning. The key feature of RSQS is that the individual samples in a meta-task are subjected to multiple distribution shifts in each meta-task. In addition, we propose a unified adversarial feature alignment method called DUal adversarial ALignment framework (DuaL) to relieve RSQS from two aspects, i.e., inter-domain bias and intra-domain variance. On the one hand, for the inter-domain bias, we corrupt the original data in advance and use the synthesized perturbed inputs to train the repairer network by minimizing distance in the feature level. On the other hand, for intra-domain variance, we proposed a generator network to synthesize hard, i.e., less similar, examples from the support set in a self-supervised manner and introduce regularized optimal transportation to derive a smooth optimal transportation plan. Lastly, a benchmark of RSQS is built with several state-of-the-art baselines among three datasets (CIFAR100, mini-ImageNet, and Tiered-Imagenet). Experiment results show that DuaL significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in our benchmark.
PGADA: Perturbation-Guided Adversarial Alignment for Few-shot Learning Under the Support-Query Shift
May 08, 2022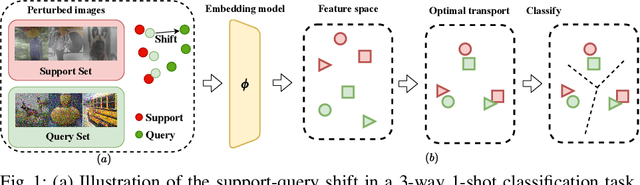
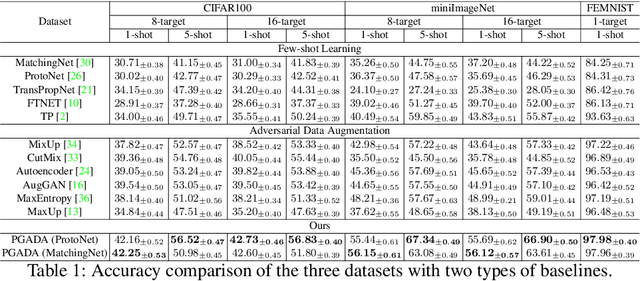
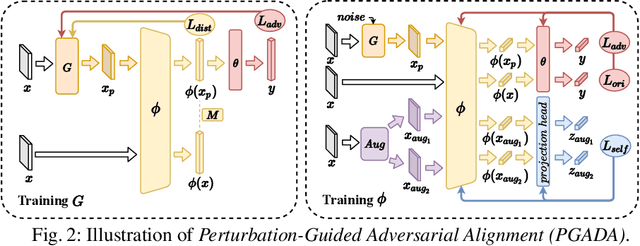

Abstract:Few-shot learning methods aim to embed the data to a low-dimensional embedding space and then classify the unseen query data to the seen support set. While these works assume that the support set and the query set lie in the same embedding space, a distribution shift usually occurs between the support set and the query set, i.e., the Support-Query Shift, in the real world. Though optimal transportation has shown convincing results in aligning different distributions, we find that the small perturbations in the images would significantly misguide the optimal transportation and thus degrade the model performance. To relieve the misalignment, we first propose a novel adversarial data augmentation method, namely Perturbation-Guided Adversarial Alignment (PGADA), which generates the hard examples in a self-supervised manner. In addition, we introduce Regularized Optimal Transportation to derive a smooth optimal transportation plan. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets manifest that our framework significantly outperforms the eleven state-of-the-art methods on three datasets.
RIIT: Rethinking the Importance of Implementation Tricks in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Mar 01, 2021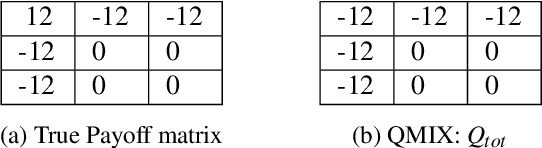
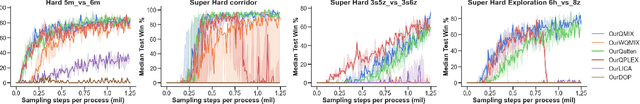

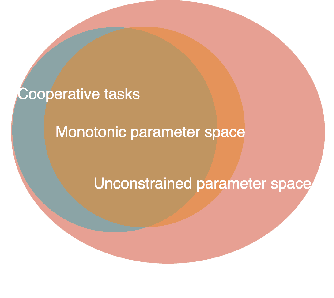
Abstract:In recent years, Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning (MADRL) has been successfully applied to various complex scenarios such as computer games and robot swarms. We investigate the impact of "implementation tricks" of state-of-the-art (SOTA) QMIX-based algorithms. Firstly, we find that such tricks, described as auxiliary details to the core algorithm, seemingly of secondary importance, have a major impact. Our finding demonstrates that, after minimal tuning, QMIX attains extraordinarily high win rates and achieves SOTA in the StarCraft Multi-Agent Challenge (SMAC). Furthermore, we find QMIX's monotonicity condition helps improve sample efficiency in some cooperative tasks, and we propose a new policy-based algorithm, called: RIIT, to prove the importance of the monotonicity condition. RIIT also achieves SOTA in policy-based algorithms. At last, we propose a hypothesis to explain the monotonicity condition. We open-sourced the code at \url{https://github.com/hijkzzz/pymarl2}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge