Siji Chen
Effects of Exponential Gaussian Distribution on (Double Sampling) Randomized Smoothing
Jun 04, 2024
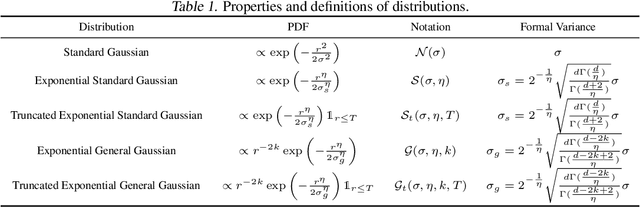
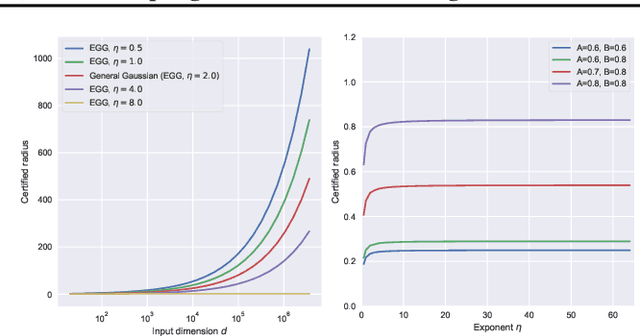
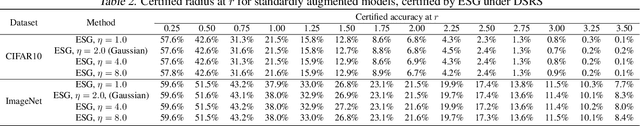
Abstract:Randomized Smoothing (RS) is currently a scalable certified defense method providing robustness certification against adversarial examples. Although significant progress has been achieved in providing defenses against $\ell_p$ adversaries, the interaction between the smoothing distribution and the robustness certification still remains vague. In this work, we comprehensively study the effect of two families of distributions, named Exponential Standard Gaussian (ESG) and Exponential General Gaussian (EGG) distributions, on Randomized Smoothing and Double Sampling Randomized Smoothing (DSRS). We derive an analytic formula for ESG's certified radius, which converges to the origin formula of RS as the dimension $d$ increases. Additionally, we prove that EGG can provide tighter constant factors than DSRS in providing $\Omega(\sqrt{d})$ lower bounds of $\ell_2$ certified radius, and thus further addresses the curse of dimensionality in RS. Our experiments on real-world datasets confirm our theoretical analysis of the ESG distributions, that they provide almost the same certification under different exponents $\eta$ for both RS and DSRS. In addition, EGG
Learning Decentralized Flocking Controllers with Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Network
Oct 02, 2023Abstract:Recently a line of researches has delved the use of graph neural networks (GNNs) for decentralized control in swarm robotics. However, it has been observed that relying solely on the states of immediate neighbors is insufficient to imitate a centralized control policy. To address this limitation, prior studies proposed incorporating $L$-hop delayed states into the computation. While this approach shows promise, it can lead to a lack of consensus among distant flock members and the formation of small clusters, consequently resulting in the failure of cohesive flocking behaviors. Instead, our approach leverages spatiotemporal GNN, named STGNN that encompasses both spatial and temporal expansions. The spatial expansion collects delayed states from distant neighbors, while the temporal expansion incorporates previous states from immediate neighbors. The broader and more comprehensive information gathered from both expansions results in more effective and accurate predictions. We develop an expert algorithm for controlling a swarm of robots and employ imitation learning to train our decentralized STGNN model based on the expert algorithm. We simulate the proposed STGNN approach in various settings, demonstrating its decentralized capacity to emulate the global expert algorithm. Further, we implemented our approach to achieve cohesive flocking, leader following and obstacle avoidance by a group of Crazyflie drones. The performance of STGNN underscores its potential as an effective and reliable approach for achieving cohesive flocking, leader following and obstacle avoidance tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge