Sidra Aleem
Test-Time Adaptation with SaLIP: A Cascade of SAM and CLIP for Zero shot Medical Image Segmentation
Apr 09, 2024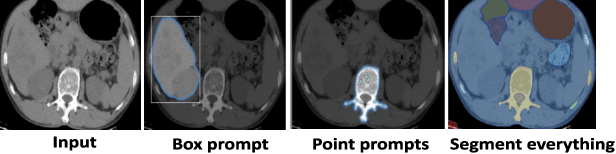
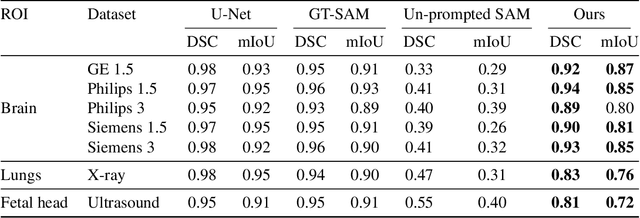
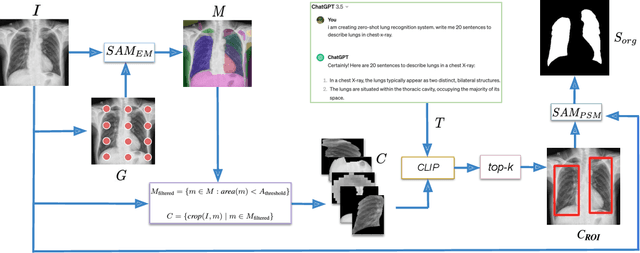
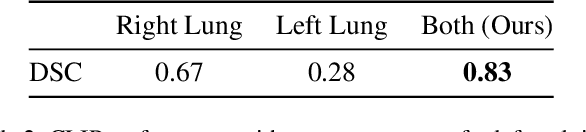
Abstract:The Segment Anything Model (SAM) and CLIP are remarkable vision foundation models (VFMs). SAM, a prompt driven segmentation model, excels in segmentation tasks across diverse domains, while CLIP is renowned for its zero shot recognition capabilities. However, their unified potential has not yet been explored in medical image segmentation. To adapt SAM to medical imaging, existing methods primarily rely on tuning strategies that require extensive data or prior prompts tailored to the specific task, making it particularly challenging when only a limited number of data samples are available. This work presents an in depth exploration of integrating SAM and CLIP into a unified framework for medical image segmentation. Specifically, we propose a simple unified framework, SaLIP, for organ segmentation. Initially, SAM is used for part based segmentation within the image, followed by CLIP to retrieve the mask corresponding to the region of interest (ROI) from the pool of SAM generated masks. Finally, SAM is prompted by the retrieved ROI to segment a specific organ. Thus, SaLIP is training and fine tuning free and does not rely on domain expertise or labeled data for prompt engineering. Our method shows substantial enhancements in zero shot segmentation, showcasing notable improvements in DICE scores across diverse segmentation tasks like brain (63.46%), lung (50.11%), and fetal head (30.82%), when compared to un prompted SAM. Code and text prompts will be available online.
ConvLoRA and AdaBN based Domain Adaptation via Self-Training
Feb 07, 2024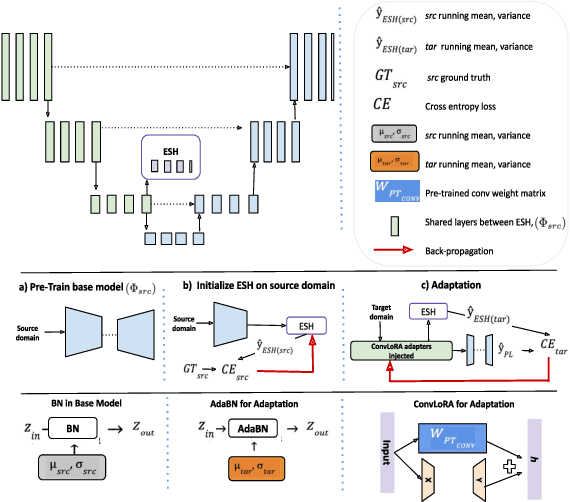
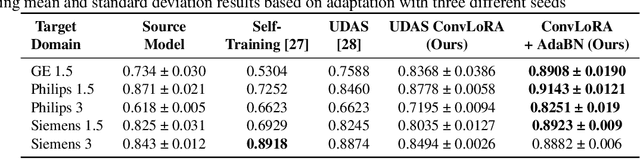
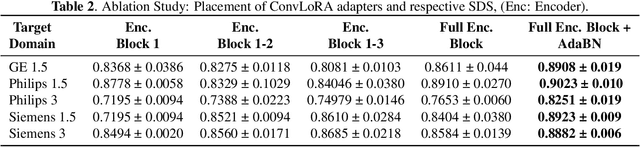
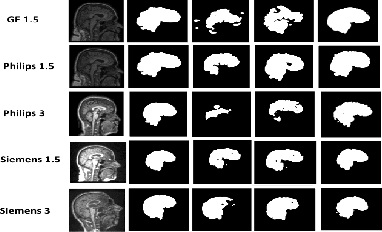
Abstract:Existing domain adaptation (DA) methods often involve pre-training on the source domain and fine-tuning on the target domain. For multi-target domain adaptation, having a dedicated/separate fine-tuned network for each target domain, that retain all the pre-trained model parameters, is prohibitively expensive. To address this limitation, we propose Convolutional Low-Rank Adaptation (ConvLoRA). ConvLoRA freezes pre-trained model weights, adds trainable low-rank decomposition matrices to convolutional layers, and backpropagates the gradient through these matrices thus greatly reducing the number of trainable parameters. To further boost adaptation, we utilize Adaptive Batch Normalization (AdaBN) which computes target-specific running statistics and use it along with ConvLoRA. Our method has fewer trainable parameters and performs better or on-par with large independent fine-tuned networks (with less than 0.9% trainable parameters of the total base model) when tested on the segmentation of Calgary-Campinas dataset containing brain MRI images. Our approach is simple, yet effective and can be applied to any deep learning-based architecture which uses convolutional and batch normalization layers. Code is available at: https://github.com/aleemsidra/ConvLoRA.
An Ensemble Deep Learning Approach for COVID-19 Severity Prediction Using Chest CT Scans
May 17, 2023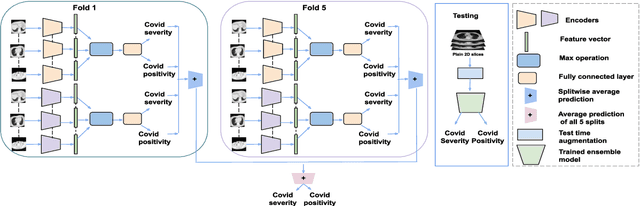
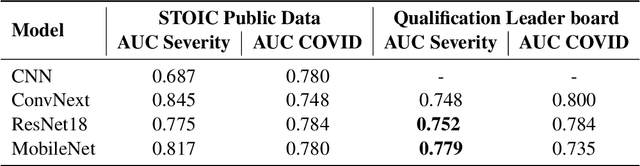
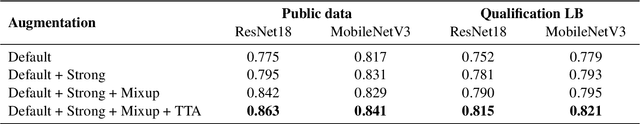
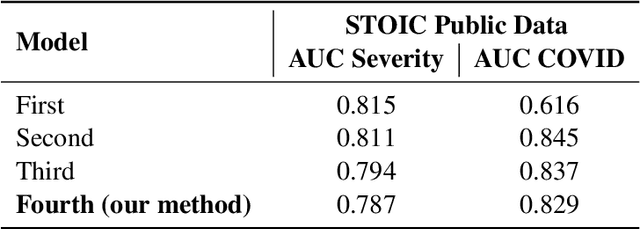
Abstract:Chest X-rays have been widely used for COVID-19 screening; however, 3D computed tomography (CT) is a more effective modality. We present our findings on COVID-19 severity prediction from chest CT scans using the STOIC dataset. We developed an ensemble deep learning based model that incorporates multiple neural networks to improve predictions. To address data imbalance, we used slicing functions and data augmentation. We further improved performance using test time data augmentation. Our approach which employs a simple yet effective ensemble of deep learning-based models with strong test time augmentations, achieved results comparable to more complex methods and secured the fourth position in the STOIC2021 COVID-19 AI Challenge. Our code is available on online: at: https://github.com/aleemsidra/stoic2021- baseline-finalphase-main.
Random Data Augmentation based Enhancement: A Generalized Enhancement Approach for Medical Datasets
Oct 03, 2022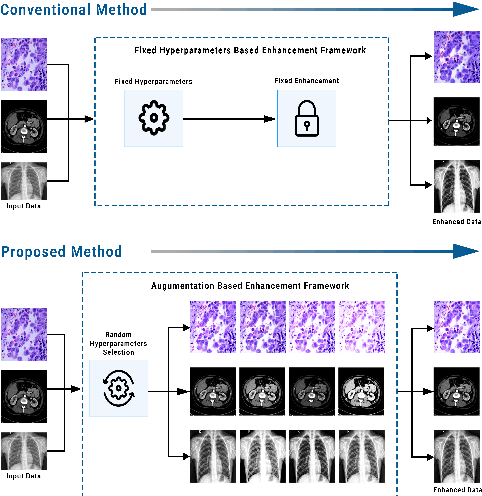
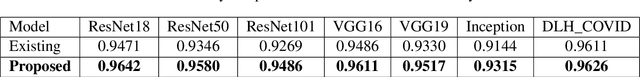
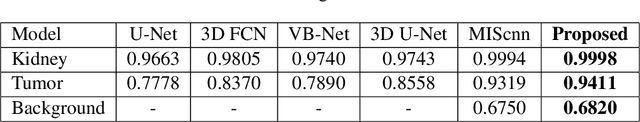
Abstract:Over the years, the paradigm of medical image analysis has shifted from manual expertise to automated systems, often using deep learning (DL) systems. The performance of deep learning algorithms is highly dependent on data quality. Particularly for the medical domain, it is an important aspect as medical data is very sensitive to quality and poor quality can lead to misdiagnosis. To improve the diagnostic performance, research has been done both in complex DL architectures and in improving data quality using dataset dependent static hyperparameters. However, the performance is still constrained due to data quality and overfitting of hyperparameters to a specific dataset. To overcome these issues, this paper proposes random data augmentation based enhancement. The main objective is to develop a generalized, data-independent and computationally efficient enhancement approach to improve medical data quality for DL. The quality is enhanced by improving the brightness and contrast of images. In contrast to the existing methods, our method generates enhancement hyperparameters randomly within a defined range, which makes it robust and prevents overfitting to a specific dataset. To evaluate the generalization of the proposed method, we use four medical datasets and compare its performance with state-of-the-art methods for both classification and segmentation tasks. For grayscale imagery, experiments have been performed with: COVID-19 chest X-ray, KiTS19, and for RGB imagery with: LC25000 datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that with the proposed enhancement methodology, DL architectures outperform other existing methods. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/aleemsidra/Augmentation-Based-Generalized-Enhancement
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge