Shuyang Zhao
A Robust Probability-based Joint Registration Method of Multiple Point Clouds Considering Local Consistency
Sep 15, 2024



Abstract:In robotic inspection, joint registration of multiple point clouds is an essential technique for estimating the transformation relationships between measured parts, such as multiple blades in a propeller. However, the presence of noise and outliers in the data can significantly impair the registration performance by affecting the correctness of correspondences. To address this issue, we incorporate local consistency property into the probability-based joint registration method. Specifically, each measured point set is treated as a sample from an unknown Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), and the registration problem is framed as estimating the probability model. By incorporating local consistency into the optimization process, we enhance the robustness and accuracy of the posterior distributions, which represent the one-to-all correspondences that directly determine the registration results. Effective closed-form solution for transformation and probability parameters are derived with Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms the existing methods, achieving high accuracy and robustness with the existence of noise and outliers. The code will be available at https://github.com/sulingjie/JPRLC_registration.
Active Learning for Sound Event Detection
Feb 12, 2020

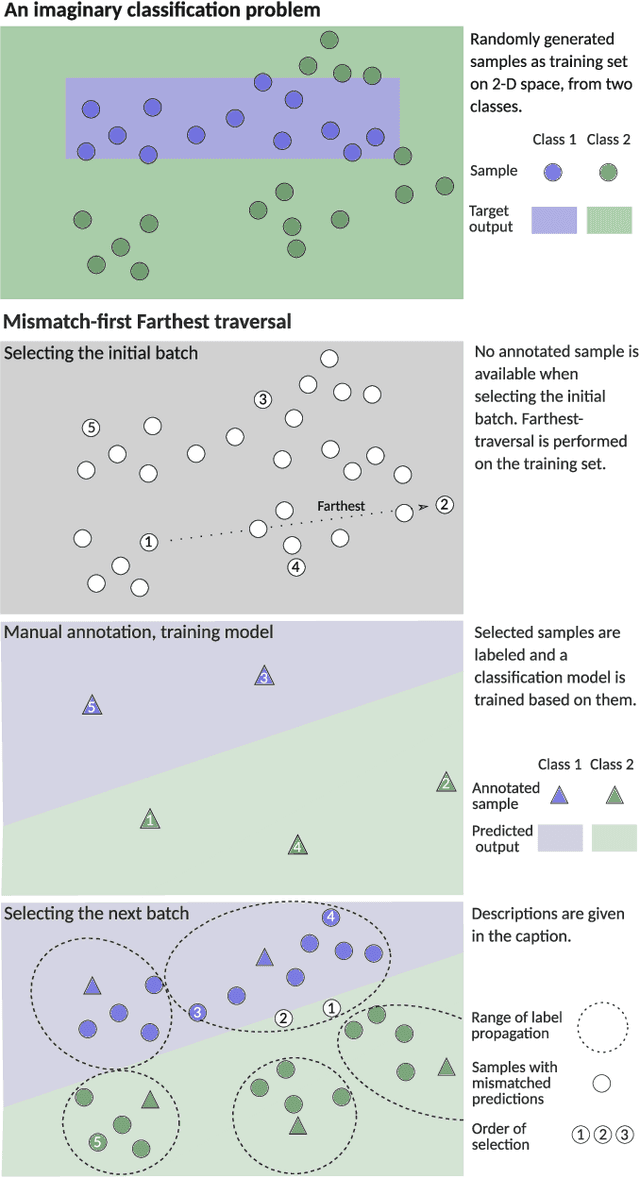
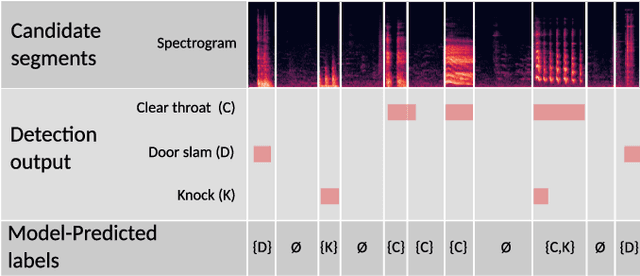
Abstract:This paper proposes an active learning system for sound event detection (SED). It aims at maximizing the accuracy of a learned SED model with limited annotation effort. The proposed system analyzes an initially unlabeled audio dataset, from which it selects sound segments for manual annotation. The candidate segments are generated based on a proposed change point detection approach, and the selection is based on the principle of mismatch-first farthest-traversal. During the training of SED models, recordings are used as training inputs, preserving the long-term context for annotated segments. The proposed system clearly outperforms reference methods in the two datasets used for evaluation (TUT Rare Sound 2017 and TAU Spatial Sound 2019). Training with recordings as context outperforms training with only annotated segments. Mismatch-first farthest-traversal outperforms reference sample selection methods based on random sampling and uncertainty sampling. Remarkably, the required annotation effort can be greatly reduced on the dataset where target sound events are rare: by annotating only 2% of the training data, the achieved SED performance is similar to annotating all the training data.
Tag Recommendation by Word-Level Tag Sequence Modeling
Nov 30, 2019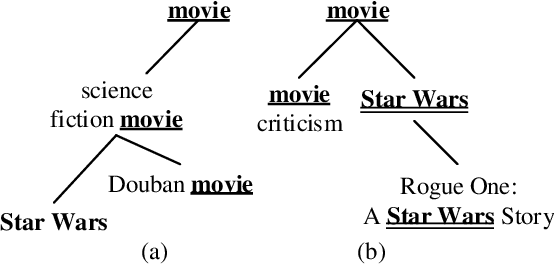
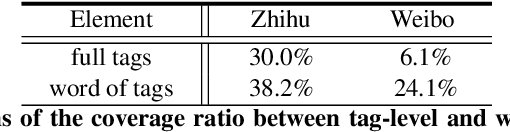
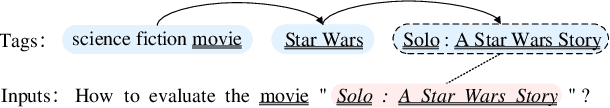

Abstract:In this paper, we transform tag recommendation into a word-based text generation problem and introduce a sequence-to-sequence model. The model inherits the advantages of LSTM-based encoder for sequential modeling and attention-based decoder with local positional encodings for learning relations globally. Experimental results on Zhihu datasets illustrate the proposed model outperforms other state-of-the-art text classification based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge