Shuran Zhou
Pronunciation Assessment with Multi-modal Large Language Models
Jul 12, 2024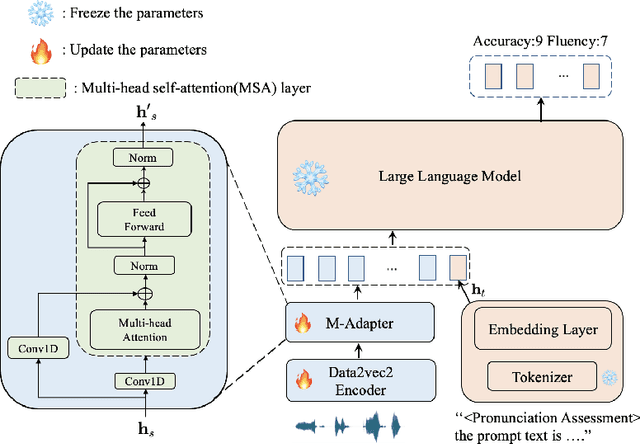

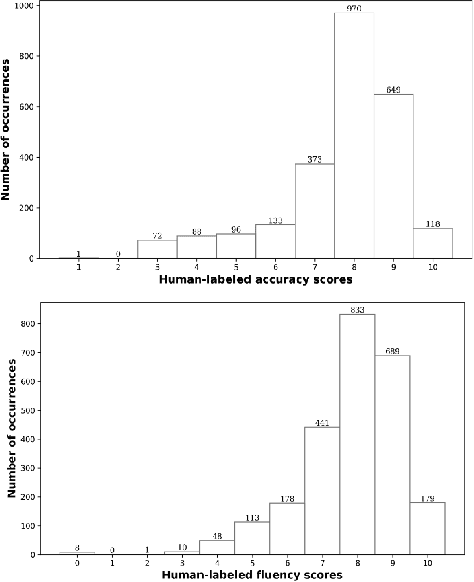
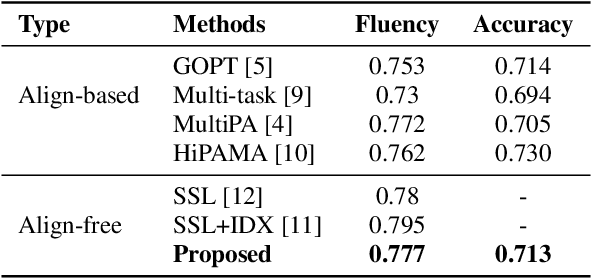
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), renowned for their powerful conversational abilities, are widely recognized as exceptional tools in the field of education, particularly in the context of automated intelligent instruction systems for language learning. In this paper, we propose a scoring system based on LLMs, motivated by their positive impact on text-related scoring tasks. Specifically, the speech encoder first maps the learner's speech into contextual features. The adapter layer then transforms these features to align with the text embedding in latent space. The assessment task-specific prefix and prompt text are embedded and concatenated with the features generated by the modality adapter layer, enabling the LLMs to predict accuracy and fluency scores. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed scoring systems achieve competitive results compared to the baselines on the Speechocean762 datasets. Moreover, we also conducted an ablation study to better understand the contributions of the prompt text and training strategy in the proposed scoring system.
Audio-Visual Wake Word Spotting System For MISP Challenge 2021
Apr 20, 2022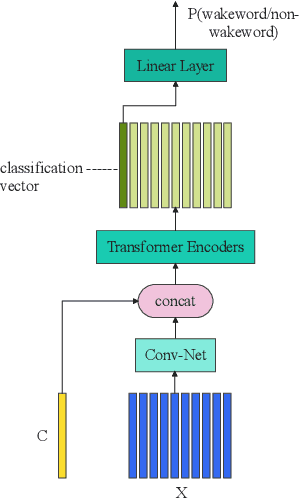
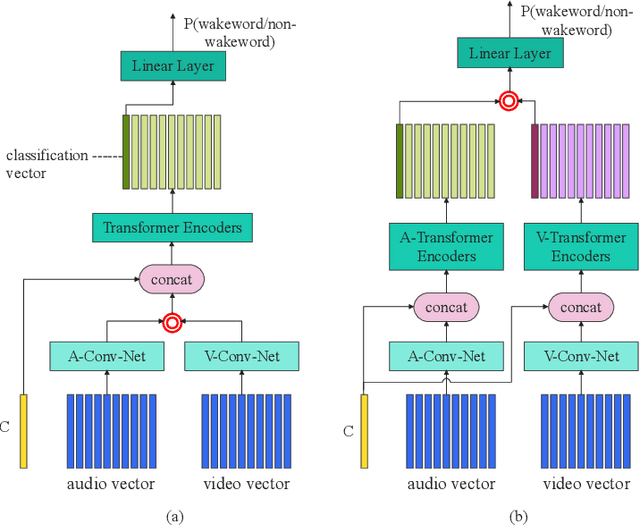
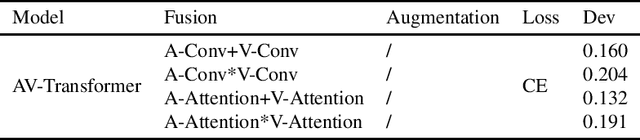
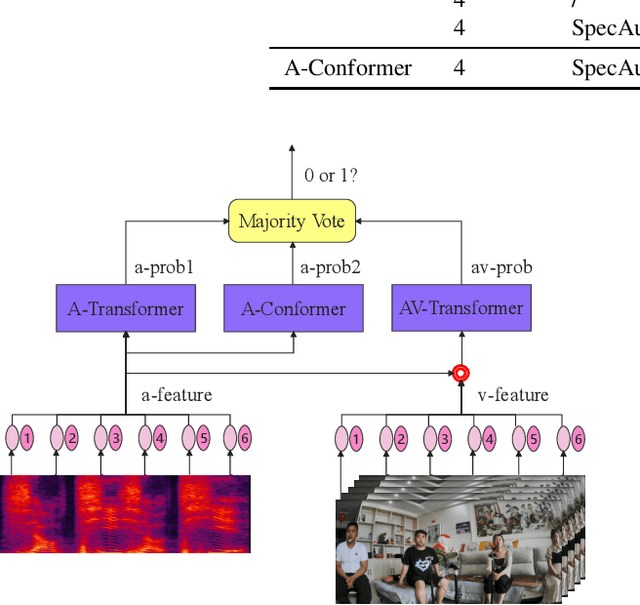
Abstract:This paper presents the details of our system designed for the Task 1 of Multimodal Information Based Speech Processing (MISP) Challenge 2021. The purpose of Task 1 is to leverage both audio and video information to improve the environmental robustness of far-field wake word spotting. In the proposed system, firstly, we take advantage of speech enhancement algorithms such as beamforming and weighted prediction error (WPE) to address the multi-microphone conversational audio. Secondly, several data augmentation techniques are applied to simulate a more realistic far-field scenario. For the video information, the provided region of interest (ROI) is used to obtain visual representation. Then the multi-layer CNN is proposed to learn audio and visual representations, and these representations are fed into our two-branch attention-based network which can be employed for fusion, such as transformer and conformed. The focal loss is used to fine-tune the model and improve the performance significantly. Finally, multiple trained models are integrated by casting vote to achieve our final 0.091 score.
Time Domain Adversarial Voice Conversion for ADD 2022
Apr 20, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we describe our speech generation system for the first Audio Deep Synthesis Detection Challenge (ADD 2022). Firstly, we build an any-to-many voice conversion (VC) system to convert source speech with arbitrary language content into the target speaker%u2019s fake speech. Then the converted speech generated from VC is post-processed in the time domain to improve the deception ability. The experimental results show that our system has adversarial ability against anti-spoofing detectors with a little compromise in audio quality and speaker similarity. This system ranks top in Track 3.1 in the ADD 2022, showing that our method could also gain good generalization ability against different detectors.
Audio Deep Fake Detection System with Neural Stitching for ADD 2022
Apr 20, 2022

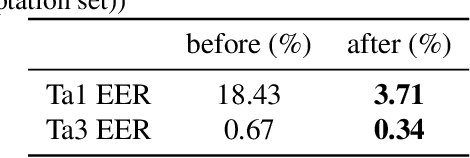
Abstract:This paper describes our best system and methodology for ADD 2022: The First Audio Deep Synthesis Detection Challenge\cite{Yi2022ADD}. The very same system was used for both two rounds of evaluation in Track 3.2 with a similar training methodology. The first round of Track 3.2 data is generated from Text-to-Speech(TTS) or voice conversion (VC) algorithms, while the second round of data consists of generated fake audio from other participants in Track 3.1, aiming to spoof our systems. Our systems use a standard 34-layer ResNet, with multi-head attention pooling \cite{india2019self} to learn the discriminative embedding for fake audio and spoof detection. We further utilize neural stitching to boost the model's generalization capability in order to perform equally well in different tasks, and more details will be explained in the following sessions. The experiments show that our proposed method outperforms all other systems with a 10.1% equal error rate(EER) in Track 3.2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge