Shuangli Li
Multi-Temporal Relationship Inference in Urban Areas
Jun 15, 2023Abstract:Finding multiple temporal relationships among locations can benefit a bunch of urban applications, such as dynamic offline advertising and smart public transport planning. While some efforts have been made on finding static relationships among locations, little attention is focused on studying time-aware location relationships. Indeed, abundant location-based human activities are time-varying and the availability of these data enables a new paradigm for understanding the dynamic relationships in a period among connective locations. To this end, we propose to study a new problem, namely multi-Temporal relationship inference among locations (Trial for short), where the major challenge is how to integrate dynamic and geographical influence under the relationship sparsity constraint. Specifically, we propose a solution to Trial with a graph learning scheme, which includes a spatially evolving graph neural network (SEENet) with two collaborative components: spatially evolving graph convolution module (SEConv) and spatially evolving self-supervised learning strategy (SE-SSL). SEConv performs the intra-time aggregation and inter-time propagation to capture the multifaceted spatially evolving contexts from the view of location message passing. In addition, SE-SSL designs time-aware self-supervised learning tasks in a global-local manner with additional evolving constraint to enhance the location representation learning and further handle the relationship sparsity. Finally, experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method over several state-of-the-art approaches.
GeomGCL: Geometric Graph Contrastive Learning for Molecular Property Prediction
Sep 24, 2021



Abstract:Recently many efforts have been devoted to applying graph neural networks (GNNs) to molecular property prediction which is a fundamental task for computational drug and material discovery. One of major obstacles to hinder the successful prediction of molecule property by GNNs is the scarcity of labeled data. Though graph contrastive learning (GCL) methods have achieved extraordinary performance with insufficient labeled data, most focused on designing data augmentation schemes for general graphs. However, the fundamental property of a molecule could be altered with the augmentation method (like random perturbation) on molecular graphs. Whereas, the critical geometric information of molecules remains rarely explored under the current GNN and GCL architectures. To this end, we propose a novel graph contrastive learning method utilizing the geometry of the molecule across 2D and 3D views, which is named GeomGCL. Specifically, we first devise a dual-view geometric message passing network (GeomMPNN) to adaptively leverage the rich information of both 2D and 3D graphs of a molecule. The incorporation of geometric properties at different levels can greatly facilitate the molecular representation learning. Then a novel geometric graph contrastive scheme is designed to make both geometric views collaboratively supervise each other to improve the generalization ability of GeomMPNN. We evaluate GeomGCL on various downstream property prediction tasks via a finetune process. Experimental results on seven real-life molecular datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed GeomGCL against state-of-the-art baselines.
Structure-aware Interactive Graph Neural Networks for the Prediction of Protein-Ligand Binding Affinity
Jul 21, 2021



Abstract:Drug discovery often relies on the successful prediction of protein-ligand binding affinity. Recent advances have shown great promise in applying graph neural networks (GNNs) for better affinity prediction by learning the representations of protein-ligand complexes. However, existing solutions usually treat protein-ligand complexes as topological graph data, thus the biomolecular structural information is not fully utilized. The essential long-range interactions among atoms are also neglected in GNN models. To this end, we propose a structure-aware interactive graph neural network (SIGN) which consists of two components: polar-inspired graph attention layers (PGAL) and pairwise interactive pooling (PiPool). Specifically, PGAL iteratively performs the node-edge aggregation process to update embeddings of nodes and edges while preserving the distance and angle information among atoms. Then, PiPool is adopted to gather interactive edges with a subsequent reconstruction loss to reflect the global interactions. Exhaustive experimental study on two benchmarks verifies the superiority of SIGN.
Spatial Object Recommendation with Hints: When Spatial Granularity Matters
Jan 08, 2021

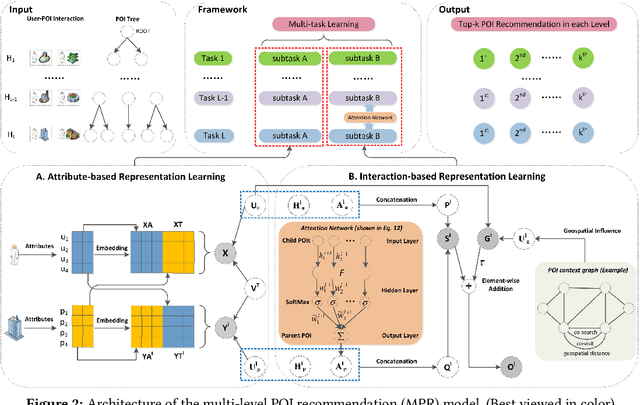

Abstract:Existing spatial object recommendation algorithms generally treat objects identically when ranking them. However, spatial objects often cover different levels of spatial granularity and thereby are heterogeneous. For example, one user may prefer to be recommended a region (say Manhattan), while another user might prefer a venue (say a restaurant). Even for the same user, preferences can change at different stages of data exploration. In this paper, we study how to support top-k spatial object recommendations at varying levels of spatial granularity, enabling spatial objects at varying granularity, such as a city, suburb, or building, as a Point of Interest (POI). To solve this problem, we propose the use of a POI tree, which captures spatial containment relationships between POIs. We design a novel multi-task learning model called MPR (short for Multi-level POI Recommendation), where each task aims to return the top-k POIs at a certain spatial granularity level. Each task consists of two subtasks: (i) attribute-based representation learning; (ii) interaction-based representation learning. The first subtask learns the feature representations for both users and POIs, capturing attributes directly from their profiles. The second subtask incorporates user-POI interactions into the model. Additionally, MPR can provide insights into why certain recommendations are being made to a user based on three types of hints: user-aspect, POI-aspect, and interaction-aspect. We empirically validate our approach using two real-life datasets, and show promising performance improvements over several state-of-the-art methods.
Distance-aware Molecule Graph Attention Network for Drug-Target Binding Affinity Prediction
Dec 17, 2020



Abstract:Accurately predicting the binding affinity between drugs and proteins is an essential step for computational drug discovery. Since graph neural networks (GNNs) have demonstrated remarkable success in various graph-related tasks, GNNs have been considered as a promising tool to improve the binding affinity prediction in recent years. However, most of the existing GNN architectures can only encode the topological graph structure of drugs and proteins without considering the relative spatial information among their atoms. Whereas, different from other graph datasets such as social networks and commonsense knowledge graphs, the relative spatial position and chemical bonds among atoms have significant impacts on the binding affinity. To this end, in this paper, we propose a diStance-aware Molecule graph Attention Network (S-MAN) tailored to drug-target binding affinity prediction. As a dedicated solution, we first propose a position encoding mechanism to integrate the topological structure and spatial position information into the constructed pocket-ligand graph. Moreover, we propose a novel edge-node hierarchical attentive aggregation structure which has edge-level aggregation and node-level aggregation. The hierarchical attentive aggregation can capture spatial dependencies among atoms, as well as fuse the position-enhanced information with the capability of discriminating multiple spatial relations among atoms. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on two standard datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness of S-MAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge