Shrey Satapara
Fighting Fire with Fire: Adversarial Prompting to Generate a Misinformation Detection Dataset
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:The recent success in language generation capabilities of large language models (LLMs), such as GPT, Bard, Llama etc., can potentially lead to concerns about their possible misuse in inducing mass agitation and communal hatred via generating fake news and spreading misinformation. Traditional means of developing a misinformation ground-truth dataset does not scale well because of the extensive manual effort required to annotate the data. In this paper, we propose an LLM-based approach of creating silver-standard ground-truth datasets for identifying misinformation. Specifically speaking, given a trusted news article, our proposed approach involves prompting LLMs to automatically generate a summarised version of the original article. The prompts in our proposed approach act as a controlling mechanism to generate specific types of factual incorrectness in the generated summaries, e.g., incorrect quantities, false attributions etc. To investigate the usefulness of this dataset, we conduct a set of experiments where we train a range of supervised models for the task of misinformation detection.
Overview of the HASOC Subtrack at FIRE 2021: Hate Speech and Offensive Content Identification in English and Indo-Aryan Languages
Dec 17, 2021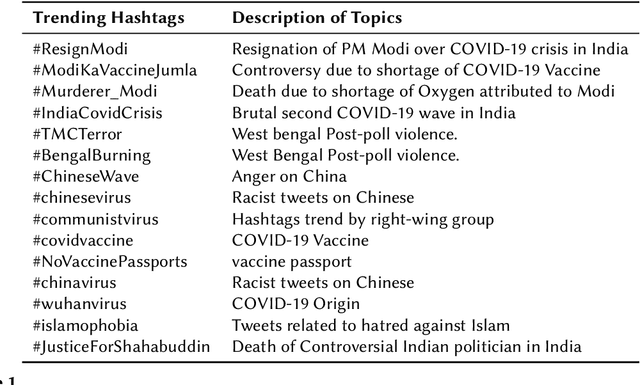
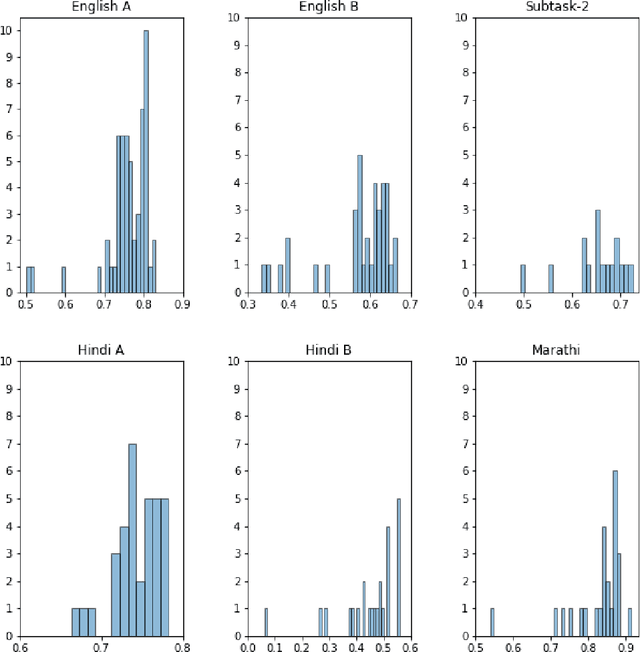
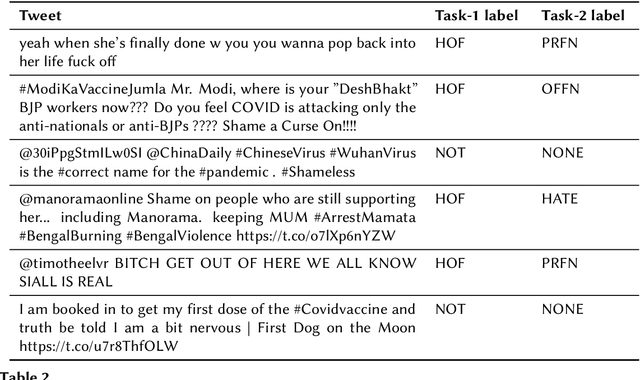
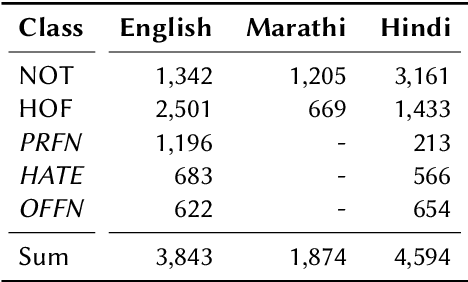
Abstract:The widespread of offensive content online such as hate speech poses a growing societal problem. AI tools are necessary for supporting the moderation process at online platforms. For the evaluation of these identification tools, continuous experimentation with data sets in different languages are necessary. The HASOC track (Hate Speech and Offensive Content Identification) is dedicated to develop benchmark data for this purpose. This paper presents the HASOC subtrack for English, Hindi, and Marathi. The data set was assembled from Twitter. This subtrack has two sub-tasks. Task A is a binary classification problem (Hate and Not Offensive) offered for all three languages. Task B is a fine-grained classification problem for three classes (HATE) Hate speech, OFFENSIVE and PROFANITY offered for English and Hindi. Overall, 652 runs were submitted by 65 teams. The performance of the best classification algorithms for task A are F1 measures 0.91, 0.78 and 0.83 for Marathi, Hindi and English, respectively. This overview presents the tasks and the data development as well as the detailed results. The systems submitted to the competition applied a variety of technologies. The best performing algorithms were mainly variants of transformer architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge