Shiyi Liu
Hierarchical Multi-Label Contrastive Learning for Protein-Protein Interaction Prediction Across Organisms
Jul 03, 2025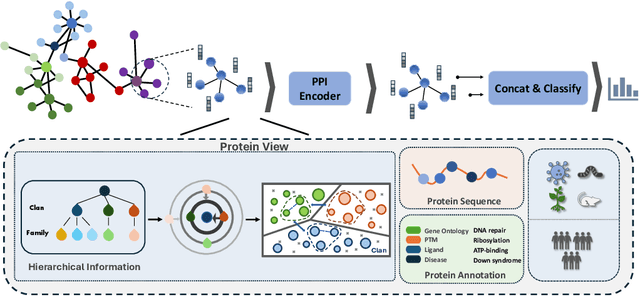
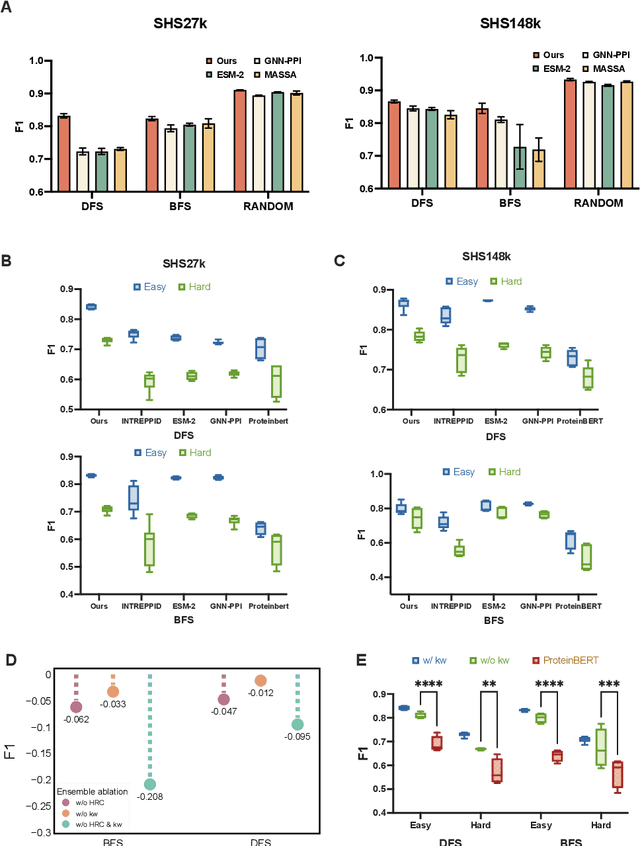
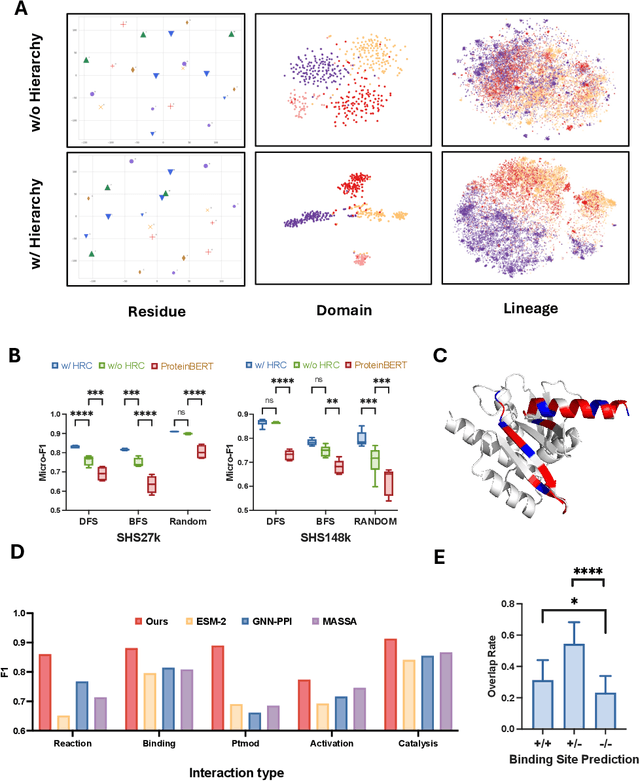
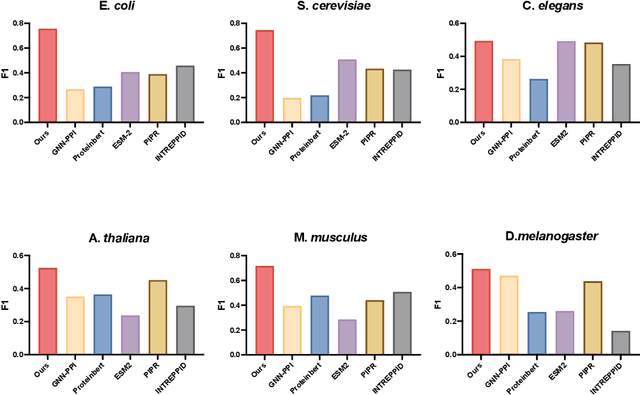
Abstract:Recent advances in AI for science have highlighted the power of contrastive learning in bridging heterogeneous biological data modalities. Building on this paradigm, we propose HIPPO (HIerarchical Protein-Protein interaction prediction across Organisms), a hierarchical contrastive framework for protein-protein interaction(PPI) prediction, where protein sequences and their hierarchical attributes are aligned through multi-tiered biological representation matching. The proposed approach incorporates hierarchical contrastive loss functions that emulate the structured relationship among functional classes of proteins. The framework adaptively incorporates domain and family knowledge through a data-driven penalty mechanism, enforcing consistency between the learned embedding space and the intrinsic hierarchy of protein functions. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that HIPPO achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing methods and showing robustness in low-data regimes. Notably, the model demonstrates strong zero-shot transferability to other species without retraining, enabling reliable PPI prediction and functional inference even in less characterized or rare organisms where experimental data are limited. Further analysis reveals that hierarchical feature fusion is critical for capturing conserved interaction determinants, such as binding motifs and functional annotations. This work advances cross-species PPI prediction and provides a unified framework for interaction prediction in scenarios with sparse or imbalanced multi-species data.
Influence Maximization in Temporal Social Networks with a Cold-Start Problem: A Supervised Approach
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Influence Maximization (IM) in temporal graphs focuses on identifying influential "seeds" that are pivotal for maximizing network expansion. We advocate defining these seeds through Influence Propagation Paths (IPPs), which is essential for scaling up the network. Our focus lies in efficiently labeling IPPs and accurately predicting these seeds, while addressing the often-overlooked cold-start issue prevalent in temporal networks. Our strategy introduces a motif-based labeling method and a tensorized Temporal Graph Network (TGN) tailored for multi-relational temporal graphs, bolstering prediction accuracy and computational efficiency. Moreover, we augment cold-start nodes with new neighbors from historical data sharing similar IPPs. The recommendation system within an online team-based gaming environment presents subtle impact on the social network, forming multi-relational (i.e., weak and strong) temporal graphs for our empirical IM study. We conduct offline experiments to assess prediction accuracy and model training efficiency, complemented by online A/B testing to validate practical network growth and the effectiveness in addressing the cold-start issue.
HERA: Hybrid Edge-cloud Resource Allocation for Cost-Efficient AI Agents
Apr 01, 2025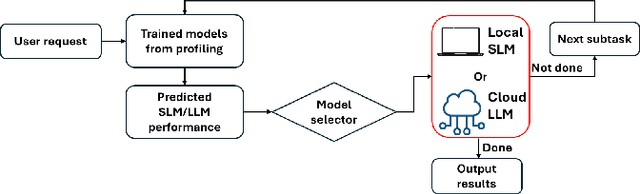

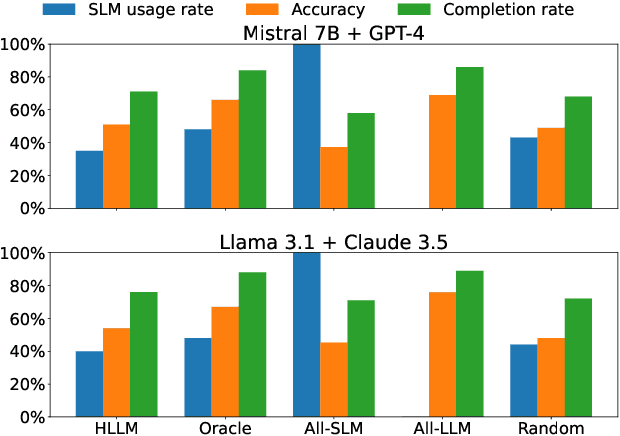
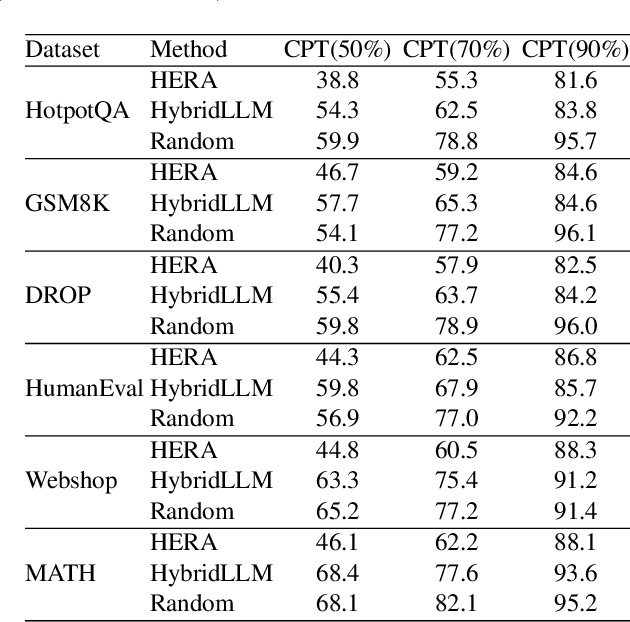
Abstract:In the realm of AI, large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, central to the operation of AI agents, predominantly operate in the cloud, incurring high operational costs. With local-based small language models (SLMs) becoming more accurate, the necessity of cloud-exclusive processing is being reconsidered. An AI agent's response to a user's request comprises a series of subtasks or iterations. Existing approaches only allocate a single request between SLM and LLM to ensure their outputs are similar, but adopting this approach in the AI agent scenario for assigning each subtask is not effective since SLM will output a different subsequent subtask, which affects the accuracy of the final output. In this paper, we first conduct experimental analysis to understand the features of AI agent operations. Leveraging our findings, we propose the Adaptive Iteration-level Model Selector (AIMS), a lightweight scheduler to automatically partition AI agent's subtasks between local-based SLM and cloud-based LLM. AIMS considers the varying subtask features and strategically decides the location for each subtask in order to use SLM as much as possible while attaining the accuracy level. Our experimental results demonstrate that AIMS increases accuracy by up to 9.1% and SLM usage by up to 10.8% compared to HybridLLM. It offloads 45.67% of subtasks to a local SLM while attaining similar accuracy on average compared with the cloud-only LLM approach.
JailbreakHunter: A Visual Analytics Approach for Jailbreak Prompts Discovery from Large-Scale Human-LLM Conversational Datasets
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained significant attention but also raised concerns due to the risk of misuse. Jailbreak prompts, a popular type of adversarial attack towards LLMs, have appeared and constantly evolved to breach the safety protocols of LLMs. To address this issue, LLMs are regularly updated with safety patches based on reported jailbreak prompts. However, malicious users often keep their successful jailbreak prompts private to exploit LLMs. To uncover these private jailbreak prompts, extensive analysis of large-scale conversational datasets is necessary to identify prompts that still manage to bypass the system's defenses. This task is highly challenging due to the immense volume of conversation data, diverse characteristics of jailbreak prompts, and their presence in complex multi-turn conversations. To tackle these challenges, we introduce JailbreakHunter, a visual analytics approach for identifying jailbreak prompts in large-scale human-LLM conversational datasets. We have designed a workflow with three analysis levels: group-level, conversation-level, and turn-level. Group-level analysis enables users to grasp the distribution of conversations and identify suspicious conversations using multiple criteria, such as similarity with reported jailbreak prompts in previous research and attack success rates. Conversation-level analysis facilitates the understanding of the progress of conversations and helps discover jailbreak prompts within their conversation contexts. Turn-level analysis allows users to explore the semantic similarity and token overlap between a singleturn prompt and the reported jailbreak prompts, aiding in the identification of new jailbreak strategies. The effectiveness and usability of the system were verified through multiple case studies and expert interviews.
POEM: Interactive Prompt Optimization for Enhancing Multimodal Reasoning of Large Language Models
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have exhibited impressive abilities for multimodal content comprehension and reasoning with proper prompting in zero- or few-shot settings. Despite the proliferation of interactive systems developed to support prompt engineering for LLMs across various tasks, most have primarily focused on textual or visual inputs, thus neglecting the complex interplay between modalities within multimodal inputs. This oversight hinders the development of effective prompts that guide model multimodal reasoning processes by fully exploiting the rich context provided by multiple modalities. In this paper, we present POEM, a visual analytics system to facilitate efficient prompt engineering for enhancing the multimodal reasoning performance of LLMs. The system enables users to explore the interaction patterns across modalities at varying levels of detail for a comprehensive understanding of the multimodal knowledge elicited by various prompts. Through diverse recommendations of demonstration examples and instructional principles, POEM supports users in iteratively crafting and refining prompts to better align and enhance model knowledge with human insights. The effectiveness and efficiency of our system are validated through two case studies and interviews with experts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge