Shirly Wang
University of Toronto
Confounding Feature Acquisition for Causal Effect Estimation
Nov 17, 2020
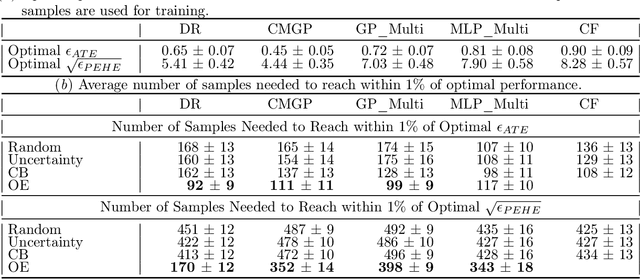
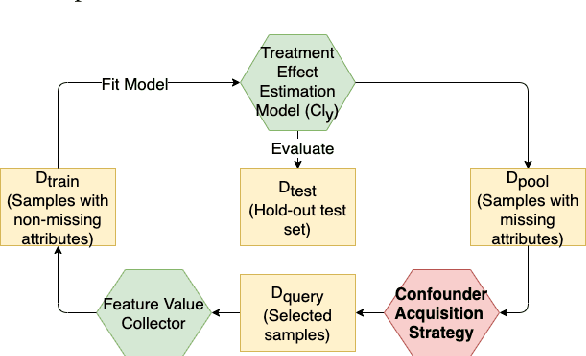
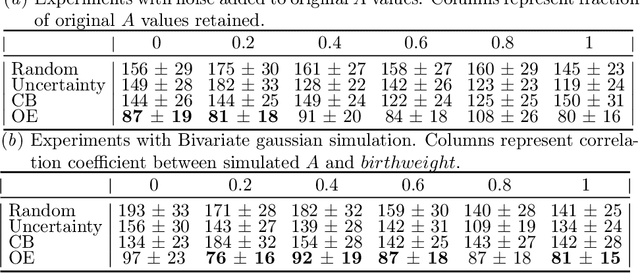
Abstract:Reliable treatment effect estimation from observational data depends on the availability of all confounding information. While much work has targeted treatment effect estimation from observational data, there is relatively little work in the setting of confounding variable missingness, where collecting more information on confounders is often costly or time-consuming. In this work, we frame this challenge as a problem of feature acquisition of confounding features for causal inference. Our goal is to prioritize acquiring values for a fixed and known subset of missing confounders in samples that lead to efficient average treatment effect estimation. We propose two acquisition strategies based on i) covariate balancing (CB), and ii) reducing statistical estimation error on observed factual outcome error (OE). We compare CB and OE on five common causal effect estimation methods, and demonstrate improved sample efficiency of OE over baseline methods under various settings. We also provide visualizations for further analysis on the difference between our proposed methods.
MIMIC-Extract: A Data Extraction, Preprocessing, and Representation Pipeline for MIMIC-III
Jul 19, 2019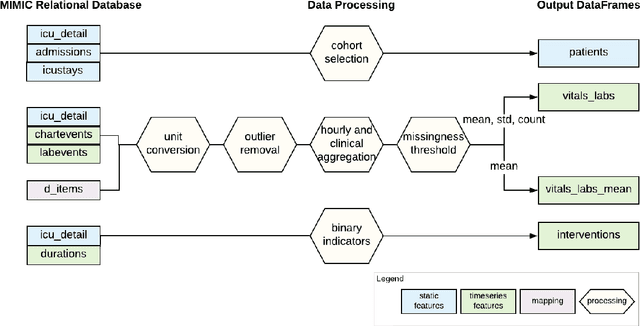
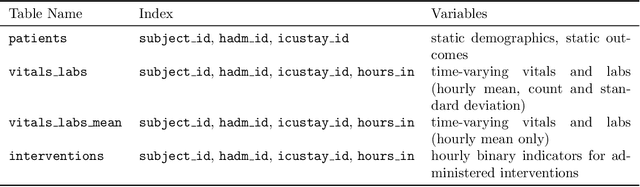
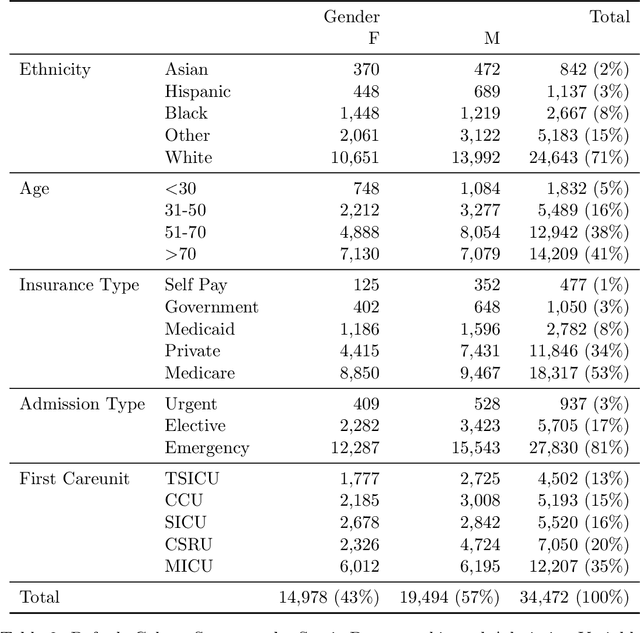
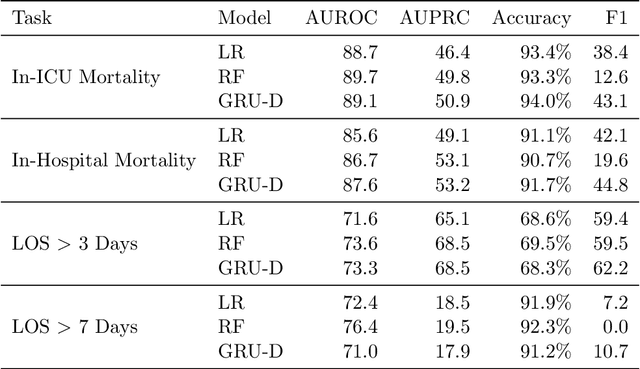
Abstract:Robust machine learning relies on access to data that can be used with standardized frameworks in important tasks and the ability to develop models whose performance can be reasonably reproduced. In machine learning for healthcare, the community faces reproducibility challenges due to a lack of publicly accessible data and a lack of standardized data processing frameworks. We present MIMIC-Extract, an open-source pipeline for transforming raw electronic health record (EHR) data for critical care patients contained in the publicly-available MIMIC-III database into dataframes that are directly usable in common machine learning pipelines. MIMIC-Extract addresses three primary challenges in making complex health records data accessible to the broader machine learning community. First, it provides standardized data processing functions, including unit conversion, outlier detection, and aggregating semantically equivalent features, thus accounting for duplication and reducing missingness. Second, it preserves the time series nature of clinical data and can be easily integrated into clinically actionable prediction tasks in machine learning for health. Finally, it is highly extensible so that other researchers with related questions can easily use the same pipeline. We demonstrate the utility of this pipeline by showcasing several benchmark tasks and baseline results.
Reproducibility in Machine Learning for Health
Jul 02, 2019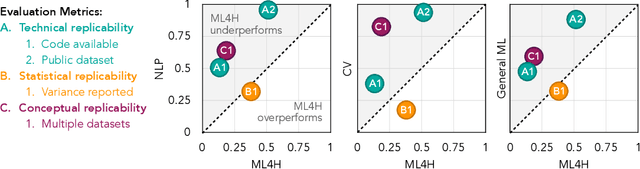
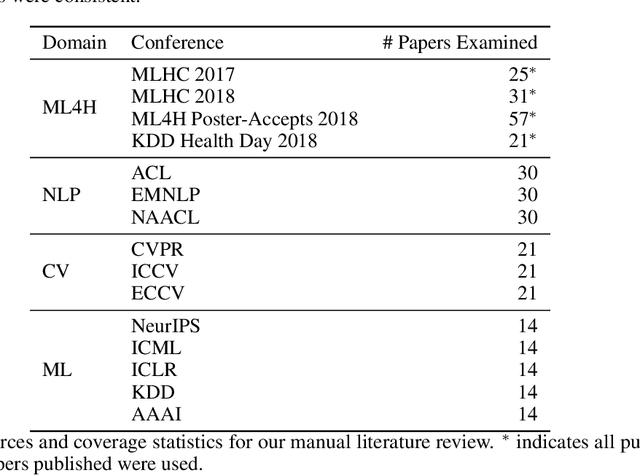
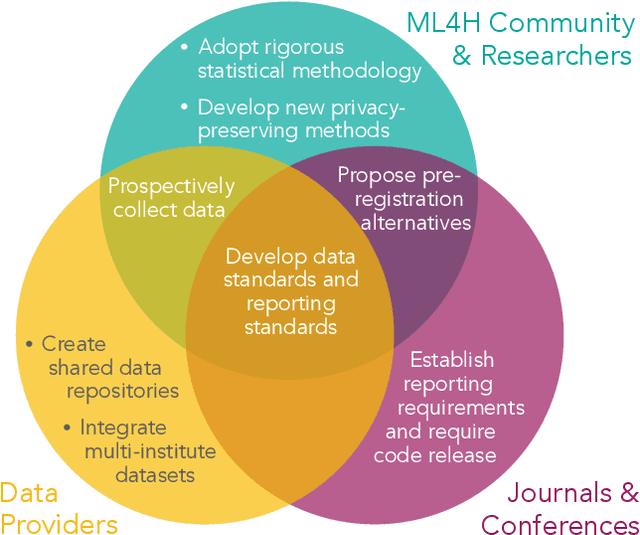
Abstract:Machine learning algorithms designed to characterize, monitor, and intervene on human health (ML4H) are expected to perform safely and reliably when operating at scale, potentially outside strict human supervision. This requirement warrants a stricter attention to issues of reproducibility than other fields of machine learning. In this work, we conduct a systematic evaluation of over 100 recently published ML4H research papers along several dimensions related to reproducibility. We find that the field of ML4H compares poorly to more established machine learning fields, particularly concerning data and code accessibility. Finally, drawing from success in other fields of science, we propose recommendations to data providers, academic publishers, and the ML4H research community in order to promote reproducible research moving forward.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge