Shilin Wu
Learning Semantic Abstraction of Shape via 3D Region of Interest
Jan 13, 2022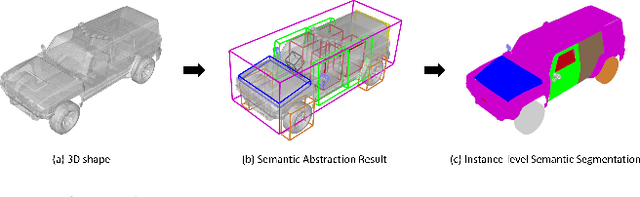
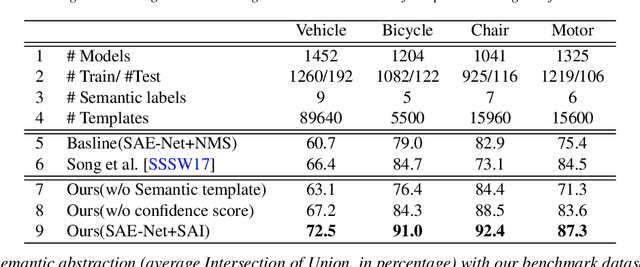
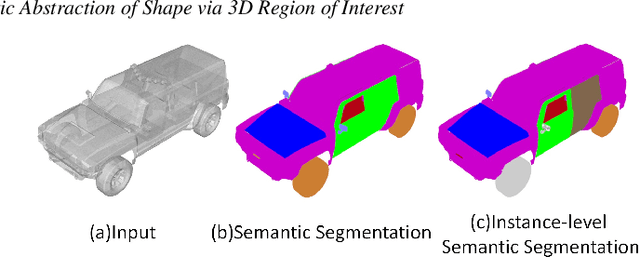
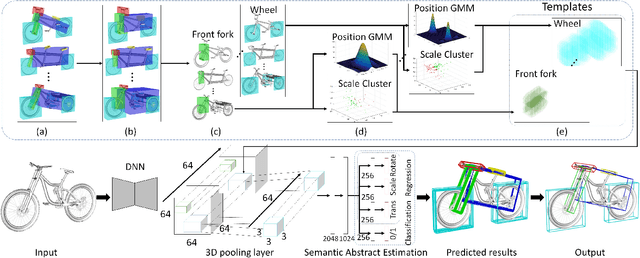
Abstract:In this paper, we focus on the two tasks of 3D shape abstraction and semantic analysis. This is in contrast to current methods, which focus solely on either 3D shape abstraction or semantic analysis. In addition, previous methods have had difficulty producing instance-level semantic results, which has limited their application. We present a novel method for the joint estimation of a 3D shape abstraction and semantic analysis. Our approach first generates a number of 3D semantic candidate regions for a 3D shape; we then employ these candidates to directly predict the semantic categories and refine the parameters of the candidate regions simultaneously using a deep convolutional neural network. Finally, we design an algorithm to fuse the predicted results and obtain the final semantic abstraction, which is shown to be an improvement over a standard non maximum suppression. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach can produce state-of-the-art results. Moreover, we also find that our results can be easily applied to instance-level semantic part segmentation and shape matching.
Region Normalization for Image Inpainting
Nov 23, 2019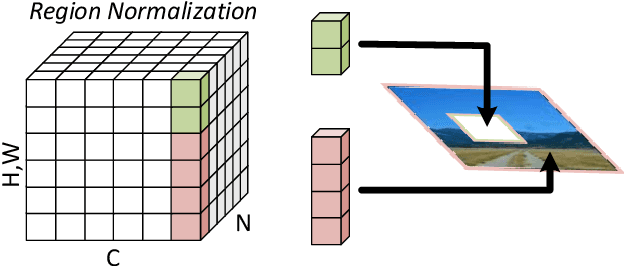
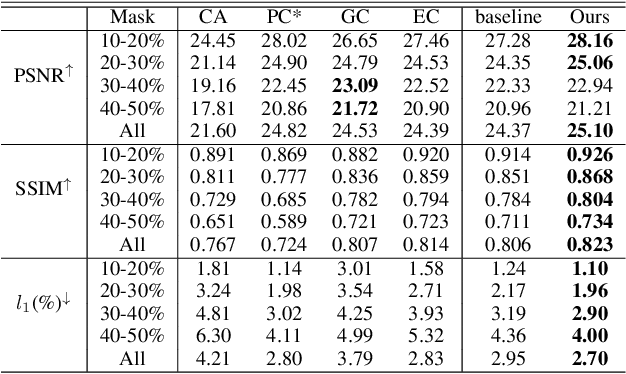
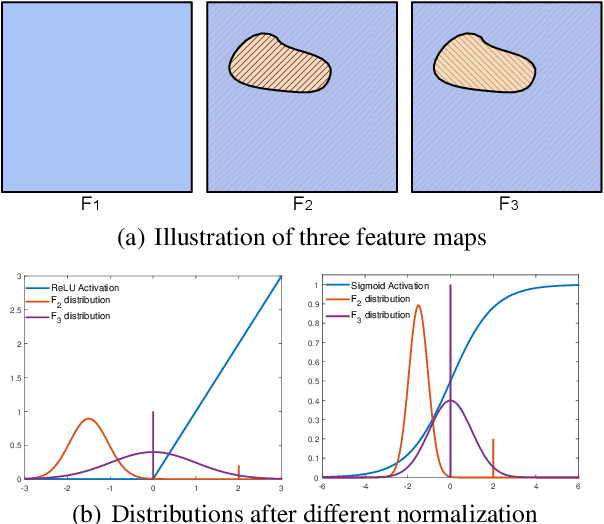
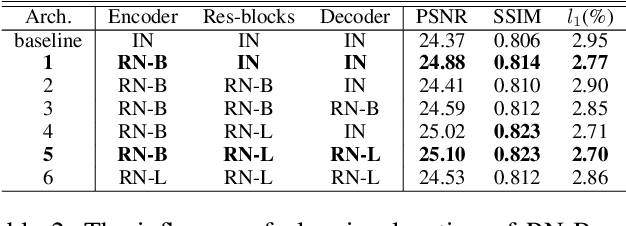
Abstract:Feature Normalization (FN) is an important technique to help neural network training, which typically normalizes features across spatial dimensions. Most previous image inpainting methods apply FN in their networks without considering the impact of the corrupted regions of the input image on normalization, e.g. mean and variance shifts. In this work, we show that the mean and variance shifts caused by full-spatial FN limit the image inpainting network training and we propose a spatial region-wise normalization named Region Normalization (RN) to overcome the limitation. RN divides spatial pixels into different regions according to the input mask, and computes the mean and variance in each region for normalization. We develop two kinds of RN for our image inpainting network: (1) Basic RN (RN-B), which normalizes pixels from the corrupted and uncorrupted regions separately based on the original inpainting mask to solve the mean and variance shift problem; (2) Learnable RN (RN-L), which automatically detects potentially corrupted and uncorrupted regions for separate normalization, and performs global affine transformation to enhance their fusion. We apply RN-B in the early layers and RN-L in the latter layers of the network respectively. Experiments show that our method outperforms current state-of-the-art methods quantitatively and qualitatively. We further generalize RN to other inpainting networks and achieve consistent performance improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge