Shijie Sun
FSD-CAP: Fractional Subgraph Diffusion with Class-Aware Propagation for Graph Feature Imputation
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Imputing missing node features in graphs is challenging, particularly under high missing rates. Existing methods based on latent representations or global diffusion often fail to produce reliable estimates, and may propagate errors across the graph. We propose FSD-CAP, a two-stage framework designed to improve imputation quality under extreme sparsity. In the first stage, a graph-distance-guided subgraph expansion localizes the diffusion process. A fractional diffusion operator adjusts propagation sharpness based on local structure. In the second stage, imputed features are refined using class-aware propagation, which incorporates pseudo-labels and neighborhood entropy to promote consistency. We evaluated FSD-CAP on multiple datasets. With $99.5\%$ of features missing across five benchmark datasets, FSD-CAP achieves average accuracies of $80.06\%$ (structural) and $81.01\%$ (uniform) in node classification, close to the $81.31\%$ achieved by a standard GCN with full features. For link prediction under the same setting, it reaches AUC scores of $91.65\%$ (structural) and $92.41\%$ (uniform), compared to $95.06\%$ for the fully observed case. Furthermore, FSD-CAP demonstrates superior performance on both large-scale and heterophily datasets when compared to other models.
Beyond Skeletons: Integrative Latent Mapping for Coherent 4D Sequence Generation
Mar 20, 2024



Abstract:Directly learning to model 4D content, including shape, color and motion, is challenging. Existing methods depend on skeleton-based motion control and offer limited continuity in detail. To address this, we propose a novel framework that generates coherent 4D sequences with animation of 3D shapes under given conditions with dynamic evolution of shape and color over time through integrative latent mapping. We first employ an integrative latent unified representation to encode shape and color information of each detailed 3D geometry frame. The proposed skeleton-free latent 4D sequence joint representation allows us to leverage diffusion models in a low-dimensional space to control the generation of 4D sequences. Finally, temporally coherent 4D sequences are generated conforming well to the input images and text prompts. Extensive experiments on the ShapeNet, 3DBiCar and DeformingThings4D datasets for several tasks demonstrate that our method effectively learns to generate quality 3D shapes with color and 4D mesh animations, improving over the current state-of-the-art. Source code will be released.
Simultaneous Multiple Object Detection and Pose Estimation using 3D Model Infusion with Monocular Vision
Nov 22, 2022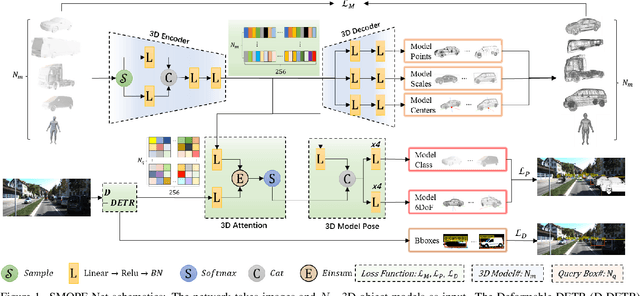

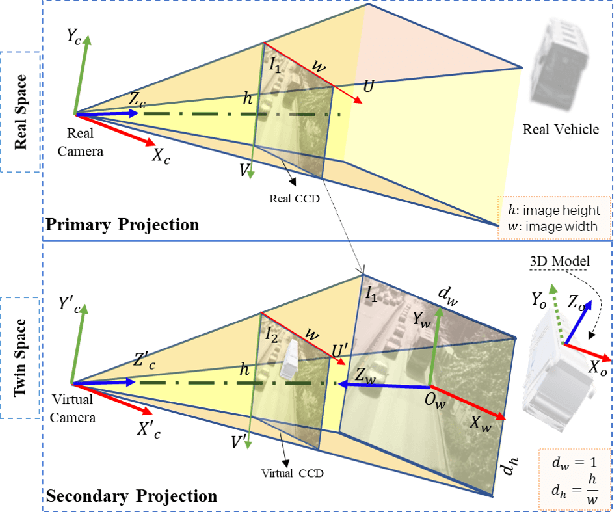
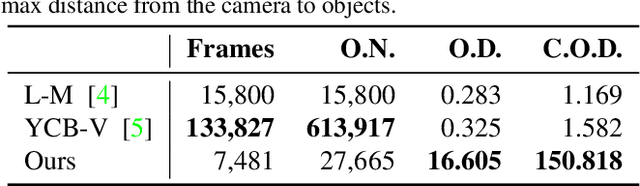
Abstract:Multiple object detection and pose estimation are vital computer vision tasks. The latter relates to the former as a downstream problem in applications such as robotics and autonomous driving. However, due to the high complexity of both tasks, existing methods generally treat them independently, which is sub-optimal. We propose simultaneous neural modeling of both using monocular vision and 3D model infusion. Our Simultaneous Multiple Object detection and Pose Estimation network (SMOPE-Net) is an end-to-end trainable multitasking network with a composite loss that also provides the advantages of anchor-free detections for efficient downstream pose estimation. To enable the annotation of training data for our learning objective, we develop a Twin-Space object labeling method and demonstrate its correctness analytically and empirically. Using the labeling method, we provide the KITTI-6DoF dataset with $\sim7.5$K annotated frames. Extensive experiments on KITTI-6DoF and the popular LineMod datasets show a consistent performance gain with SMOPE-Net over existing pose estimation methods. Here are links to our proposed SMOPE-Net, KITTI-6DoF dataset, and LabelImg3D labeling tool.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge