Shaoyuan Li
RRT*former: Environment-Aware Sampling-Based Motion Planning using Transformer
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:We investigate the sampling-based optimal path planning problem for robotics in complex and dynamic environments. Most existing sampling-based algorithms neglect environmental information or the information from previous samples. Yet, these pieces of information are highly informative, as leveraging them can provide better heuristics when sampling the next state. In this paper, we propose a novel sampling-based planning algorithm, called \emph{RRT*former}, which integrates the standard RRT* algorithm with a Transformer network in a novel way. Specifically, the Transformer is used to extract features from the environment and leverage information from previous samples to better guide the sampling process. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that, compared to existing sampling-based approaches such as RRT*, Neural RRT*, and their variants, our algorithm achieves considerable improvements in both the optimality of the path and sampling efficiency. The code for our implementation is available on https://github.com/fengmingyang666/RRTformer.
Online Synthesis of Control Barrier Functions with Local Occupancy Grid Maps for Safe Navigation in Unknown Environments
May 17, 2025Abstract:Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) have emerged as an effective and non-invasive safety filter for ensuring the safety of autonomous systems in dynamic environments with formal guarantees. However, most existing works on CBF synthesis focus on fully known settings. Synthesizing CBFs online based on perception data in unknown environments poses particular challenges. Specifically, this requires the construction of CBFs from high-dimensional data efficiently in real time. This paper proposes a new approach for online synthesis of CBFs directly from local Occupancy Grid Maps (OGMs). Inspired by steady-state thermal fields, we show that the smoothness requirement of CBFs corresponds to the solution of the steady-state heat conduction equation with suitably chosen boundary conditions. By leveraging the sparsity of the coefficient matrix in Laplace's equation, our approach allows for efficient computation of safety values for each grid cell in the map. Simulation and real-world experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Specifically, the results show that our CBFs can be synthesized in an average of milliseconds on a 200 * 200 grid map, highlighting its real-time applicability.
Forgetting, Ignorance or Myopia: Revisiting Key Challenges in Online Continual Learning
Sep 28, 2024Abstract:Online continual learning requires the models to learn from constant, endless streams of data. While significant efforts have been made in this field, most were focused on mitigating the catastrophic forgetting issue to achieve better classification ability, at the cost of a much heavier training workload. They overlooked that in real-world scenarios, e.g., in high-speed data stream environments, data do not pause to accommodate slow models. In this paper, we emphasize that model throughput -- defined as the maximum number of training samples that a model can process within a unit of time -- is equally important. It directly limits how much data a model can utilize and presents a challenging dilemma for current methods. With this understanding, we revisit key challenges in OCL from both empirical and theoretical perspectives, highlighting two critical issues beyond the well-documented catastrophic forgetting: Model's ignorance: the single-pass nature of OCL challenges models to learn effective features within constrained training time and storage capacity, leading to a trade-off between effective learning and model throughput; Model's myopia: the local learning nature of OCL on the current task leads the model to adopt overly simplified, task-specific features and excessively sparse classifier, resulting in the gap between the optimal solution for the current task and the global objective. To tackle these issues, we propose the Non-sparse Classifier Evolution framework (NsCE) to facilitate effective global discriminative feature learning with minimal time cost. NsCE integrates non-sparse maximum separation regularization and targeted experience replay techniques with the help of pre-trained models, enabling rapid acquisition of new globally discriminative features.
Terrain-adaptive Central Pattern Generators with Reinforcement Learning for Hexapod Locomotion
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:Inspired by biological motion generation, central pattern generators (CPGs) is frequently employed in legged robot locomotion control to produce natural gait pattern with low-dimensional control signals. However, the limited adaptability and stability over complex terrains hinder its application. To address this issue, this paper proposes a terrain-adaptive locomotion control method that incorporates deep reinforcement learning (DRL) framework into CPG, where the CPG model is responsible for the generation of synchronized signals, providing basic locomotion gait, while DRL is integrated to enhance the adaptability of robot towards uneven terrains by adjusting the parameters of CPG mapping functions. The experiments conducted on the hexapod robot in Isaac Gym simulation environment demonstrated the superiority of the proposed method in terrain-adaptability, convergence rate and reward design complexity.
Unlocking the Power of Open Set : A New Perspective for Open-set Noisy Label Learning
May 07, 2023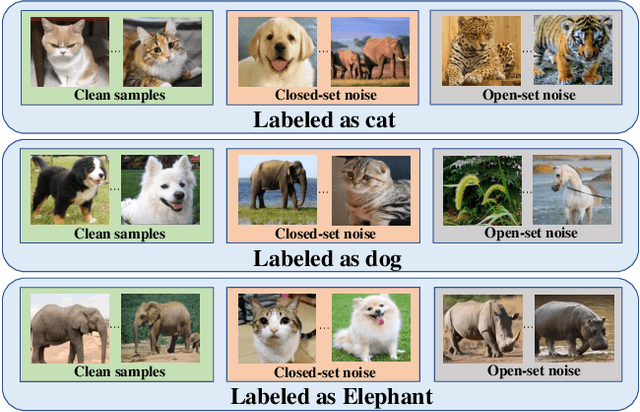
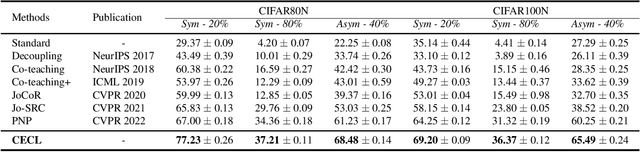
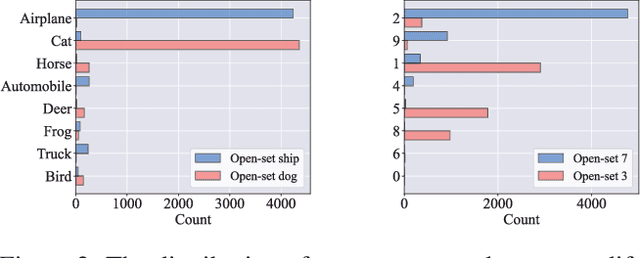
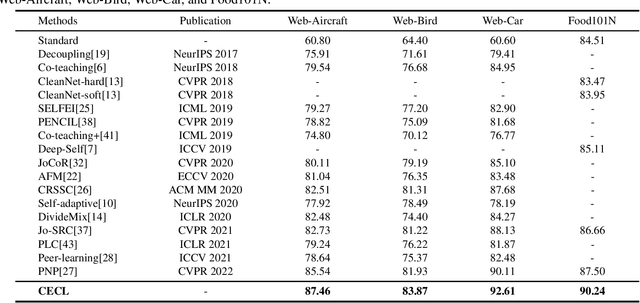
Abstract:Learning from noisy data has attracted much attention, where most methods focus on closed-set label noise. However, a more common scenario in the real world is the presence of both open-set and closed-set noise. Existing methods typically identify and handle these two types of label noise separately by designing a specific strategy for each type. However, in many real-world scenarios, it would be challenging to identify open-set examples, especially when the dataset has been severely corrupted. Unlike the previous works, we explore how models behave when faced open-set examples, and find that a part of open-set examples gradually get integrated into certain known classes, which is beneficial for the seperation among known classes. Motivated by the phenomenon, in this paper, we propose a novel two-step contrastive learning method called CECL, which aims to deal with both types of label noise by exploiting the useful information of open-set examples. Specifically, we incorporate some open-set examples into closed-set classes to enhance performance while treating others as delimiters to improve representative ability. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets with diverse label noise demonstrate that CECL can outperform state-of-the-art methods.
To Explore or Not to Explore: Regret-Based LTL Planning in Partially-Known Environments
Apr 01, 2022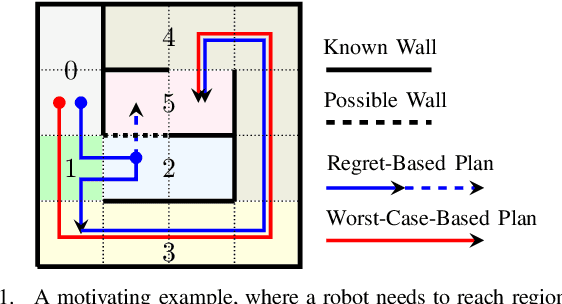
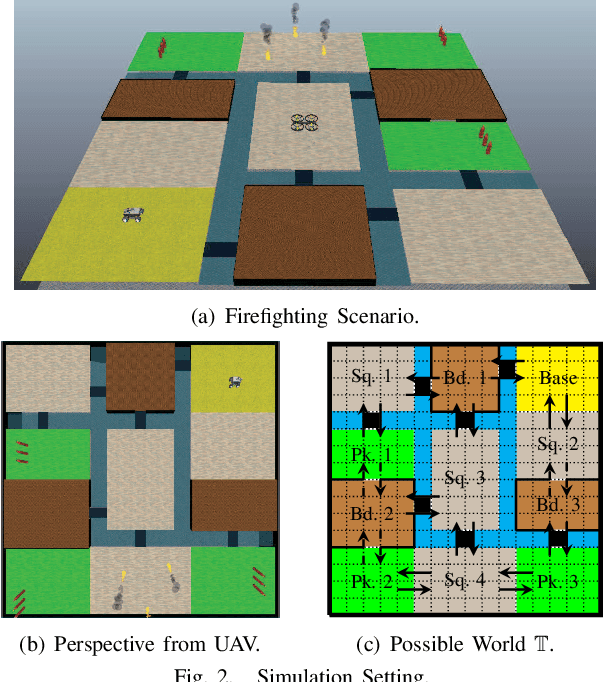
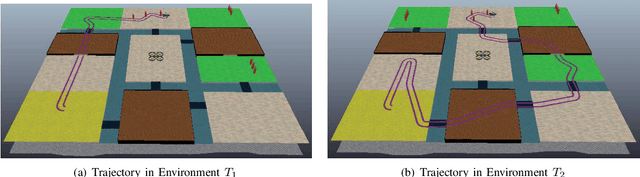
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the optimal robot path planning problem for high-level specifications described by co-safe linear temporal logic (LTL) formulae. We consider the scenario where the map geometry of the workspace is partially-known. Specifically, we assume that there are some unknown regions, for which the robot does not know their successor regions a priori unless it reaches these regions physically. In contrast to the standard game-based approach that optimizes the worst-case cost, in the paper, we propose to use regret as a new metric for planning in such a partially-known environment. The regret of a plan under a fixed but unknown environment is the difference between the actual cost incurred and the best-response cost the robot could have achieved if it realizes the actual environment with hindsight. We provide an effective algorithm for finding an optimal plan that satisfies the LTL specification while minimizing its regret. A case study on firefighting robots is provided to illustrate the proposed framework. We argue that the new metric is more suitable for the scenario of partially-known environment since it captures the trade-off between the actual cost spent and the potential benefit one may obtain for exploring an unknown region.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge