Shahriar B. Shokouhi
Electrical Engineering Department, Iran University of Science and Technology
Enhancing Vehicle Make and Model Recognition with 3D Attention Modules
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Vehicle make and model recognition (VMMR) is a crucial component of the Intelligent Transport System, garnering significant attention in recent years. VMMR has been widely utilized for detecting suspicious vehicles, monitoring urban traffic, and autonomous driving systems. The complexity of VMMR arises from the subtle visual distinctions among vehicle models and the wide variety of classes produced by manufacturers. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), a prominent type of deep learning model, have been extensively employed in various computer vision tasks, including VMMR, yielding remarkable results. As VMMR is a fine-grained classification problem, it primarily faces inter-class similarity and intra-class variation challenges. In this study, we implement an attention module to address these challenges and enhance the model's focus on critical areas containing distinguishing features. This module, which does not increase the parameters of the original model, generates three-dimensional (3-D) attention weights to refine the feature map. Our proposed model integrates the attention module into two different locations within the middle section of a convolutional model, where the feature maps from these sections offer sufficient information about the input frames without being overly detailed or overly coarse. The performance of our proposed model, along with state-of-the-art (SOTA) convolutional and transformer-based models, was evaluated using the Stanford Cars dataset. Our proposed model achieved the highest accuracy, 90.69\%, among the compared models.
Traffic Sign Recognition Using Local Vision Transformer
Nov 11, 2023Abstract:Recognition of traffic signs is a crucial aspect of self-driving cars and driver assistance systems, and machine vision tasks such as traffic sign recognition have gained significant attention. CNNs have been frequently used in machine vision, but introducing vision transformers has provided an alternative approach to global feature learning. This paper proposes a new novel model that blends the advantages of both convolutional and transformer-based networks for traffic sign recognition. The proposed model includes convolutional blocks for capturing local correlations and transformer-based blocks for learning global dependencies. Additionally, a locality module is incorporated to enhance local perception. The performance of the suggested model is evaluated on the Persian Traffic Sign Dataset and German Traffic Sign Recognition Benchmark and compared with SOTA convolutional and transformer-based models. The experimental evaluations demonstrate that the hybrid network with the locality module outperforms pure transformer-based models and some of the best convolutional networks in accuracy. Specifically, our proposed final model reached 99.66% accuracy in the German traffic sign recognition benchmark and 99.8% in the Persian traffic sign dataset, higher than the best convolutional models. Moreover, it outperforms existing CNNs and ViTs while maintaining fast inference speed. Consequently, the proposed model proves to be significantly faster and more suitable for real-world applications.
MedViT: A Robust Vision Transformer for Generalized Medical Image Classification
Feb 19, 2023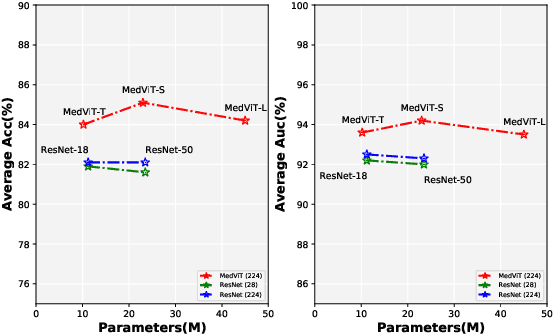
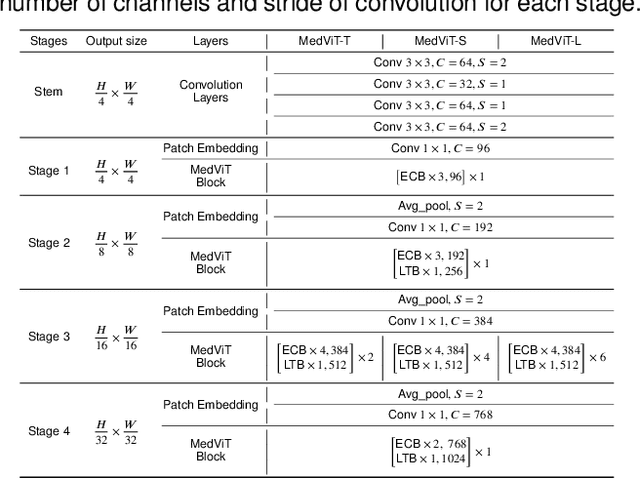
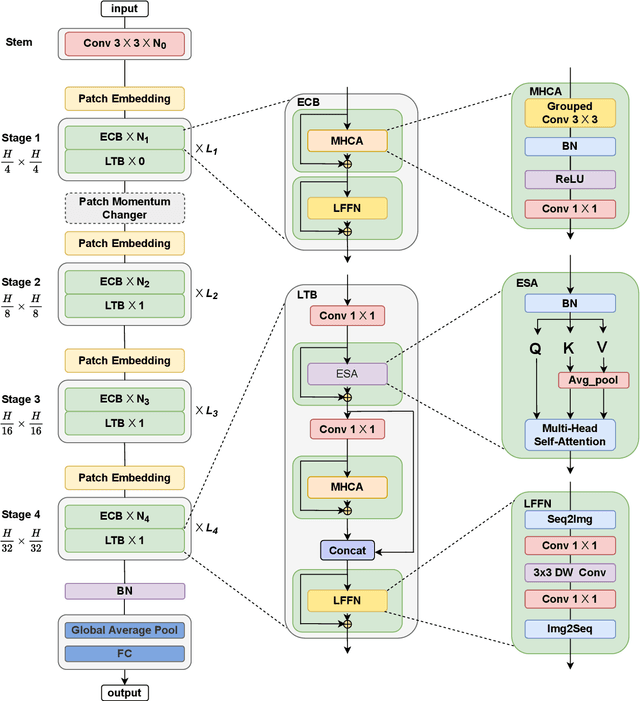
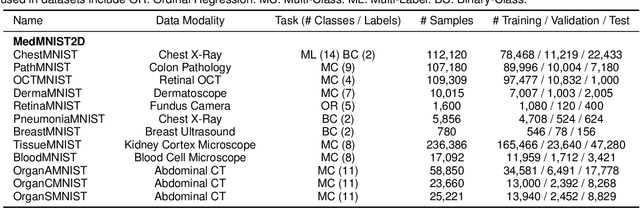
Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have advanced existing medical systems for automatic disease diagnosis. However, there are still concerns about the reliability of deep medical diagnosis systems against the potential threats of adversarial attacks since inaccurate diagnosis could lead to disastrous consequences in the safety realm. In this study, we propose a highly robust yet efficient CNN-Transformer hybrid model which is equipped with the locality of CNNs as well as the global connectivity of vision Transformers. To mitigate the high quadratic complexity of the self-attention mechanism while jointly attending to information in various representation subspaces, we construct our attention mechanism by means of an efficient convolution operation. Moreover, to alleviate the fragility of our Transformer model against adversarial attacks, we attempt to learn smoother decision boundaries. To this end, we augment the shape information of an image in the high-level feature space by permuting the feature mean and variance within mini-batches. With less computational complexity, our proposed hybrid model demonstrates its high robustness and generalization ability compared to the state-of-the-art studies on a large-scale collection of standardized MedMNIST-2D datasets.
Pyramid Transformer for Traffic Sign Detection
Jul 22, 2022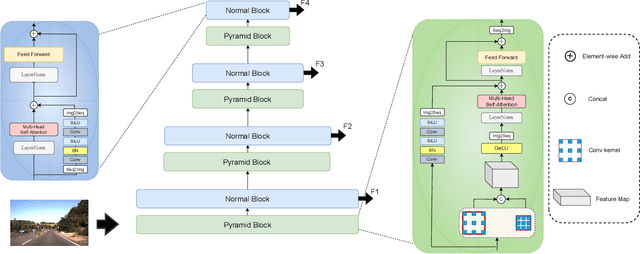
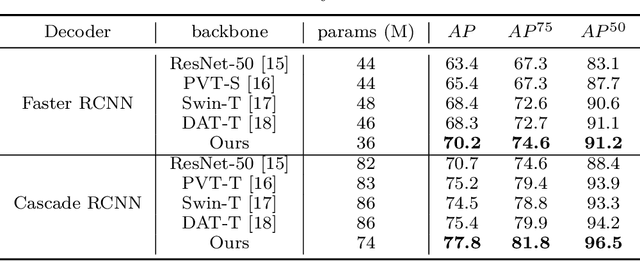
Abstract:Traffic sign detection is a vital task in the visual system of self-driving cars and the automated driving system. Recently, novel Transformer-based models have achieved encouraging results for various computer vision tasks. We still observed that vanilla ViT could not yield satisfactory results in traffic sign detection because the overall size of the datasets is very small and the class distribution of traffic signs is extremely unbalanced. To overcome this problem, a novel Pyramid Transformer with locality mechanisms is proposed in this paper. Specifically, Pyramid Transformer has several spatial pyramid reduction layers to shrink and embed the input image into tokens with rich multi-scale context by using atrous convolutions. Moreover, it inherits an intrinsic scale invariance inductive bias and is able to learn local feature representation for objects at various scales, thereby enhancing the network robustness against the size discrepancy of traffic signs. The experiments are conducted on the German Traffic Sign Detection Benchmark (GTSDB). The results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model in the traffic sign detection tasks. More specifically, Pyramid Transformer achieves 77.8% mAP on GTSDB when applied to the Cascade RCNN as the backbone, which surpasses most well-known and widely-used state-of-the-art models.
Automatic Breast Lesion Detection in Ultrafast DCE-MRI Using Deep Learning
Feb 07, 2021



Abstract:Purpose: We propose a deep learning-based computer-aided detection (CADe) method to detect breast lesions in ultrafast DCE-MRI sequences. This method uses both the three-dimensional spatial information and temporal information obtained from the early-phase of the dynamic acquisition.Methods: The proposed CADe method, based on a modified 3D RetinaNet model, operates on ultrafast T1 weighted sequences, which are preprocessed for motion compensation, temporal normalization, and are cropped before passing into the model. The model is optimized to enable the detection of relatively small breast lesions in a screening setting, focusing on detection of lesions that are harder to differentiate from confounding structures inside the breast.Results: The method was developed based on a dataset consisting of 489 ultrafast MRI studies obtained from 462 patients containing a total of 572 lesions (365 malignant, 207 benign) and achieved a detection rate, sensitivity, and detection rate of benign lesions of 0.90, 0.95, and 0.86 at 4 false positives per normal breast with a 10-fold cross-validation, respectively.Conclusions: The deep learning architecture used for the proposed CADe application can efficiently detect benign and malignant lesions on ultrafast DCE-MRI. Furthermore, utilizing the less visible hard-to detect-lesions in training improves the learning process and, subsequently, detection of malignant breast lesions.
Ensembles of Deep Neural Networks for Action Recognition in Still Images
Mar 22, 2020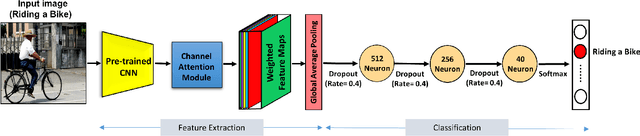
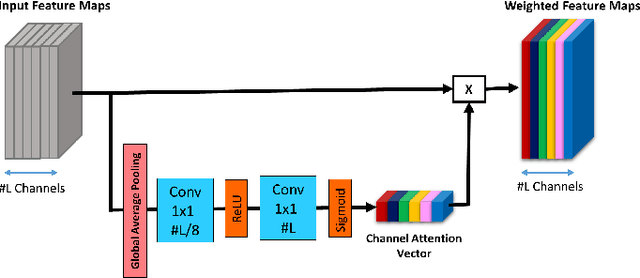
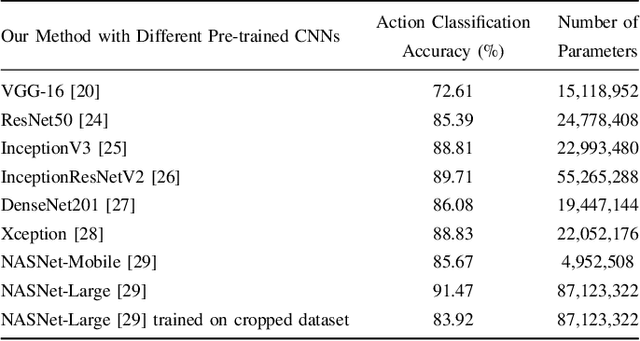

Abstract:Despite the fact that notable improvements have been made recently in the field of feature extraction and classification, human action recognition is still challenging, especially in images, in which, unlike videos, there is no motion. Thus, the methods proposed for recognizing human actions in videos cannot be applied to still images. A big challenge in action recognition in still images is the lack of large enough datasets, which is problematic for training deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) due to the overfitting issue. In this paper, by taking advantage of pre-trained CNNs, we employ the transfer learning technique to tackle the lack of massive labeled action recognition datasets. Furthermore, since the last layer of the CNN has class-specific information, we apply an attention mechanism on the output feature maps of the CNN to extract more discriminative and powerful features for classification of human actions. Moreover, we use eight different pre-trained CNNs in our framework and investigate their performance on Stanford 40 dataset. Finally, we propose using the Ensemble Learning technique to enhance the overall accuracy of action classification by combining the predictions of multiple models. The best setting of our method is able to achieve 93.17$\%$ accuracy on the Stanford 40 dataset.
* 5 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables, Accepted by ICCKE 2019
Visual Object Tracking based on Adaptive Siamese and Motion Estimation Network
Sep 29, 2018



Abstract:Recently, convolutional neural network (CNN) has attracted much attention in different areas of computer vision, due to its powerful abstract feature representation. Visual object tracking is one of the interesting and important areas in computer vision that achieves remarkable improvements in recent years. In this work, we aim to improve both the motion and observation models in visual object tracking by leveraging representation power of CNNs. To this end, a motion estimation network (named MEN) is utilized to seek the most likely locations of the target and prepare a further clue in addition to the previous target position. Hence the motion estimation would be enhanced by generating a small number of candidates near two plausible positions. The generated candidates are then fed into a trained Siamese network to detect the most probable candidate. Each candidate is compared to an adaptable buffer, which is updated under a predefined condition. To take into account the target appearance changes, a weighting CNN (called WCNN) adaptively assigns weights to the final similarity scores of the Siamese network using sequence-specific information. Evaluation results on well-known benchmark datasets (OTB100, OTB50 and OTB2013) prove that the proposed tracker outperforms the state-of-the-art competitors.
Patchwise object tracking via structural local sparse appearance model
Mar 16, 2018


Abstract:In this paper, we propose a robust visual tracking method which exploits the relationships of targets in adjacent frames using patchwise joint sparse representation. Two sets of overlapping patches with different sizes are extracted from target candidates to construct two dictionaries with consideration of joint sparse representation. By applying this representation into structural sparse appearance model, we can take two-fold advantages. First, the correlation of target patches over time is considered. Second, using this local appearance model with different patch sizes takes into account local features of target thoroughly. Furthermore, the position of candidate patches and their occlusion levels are utilized simultaneously to obtain the final likelihood of target candidates. Evaluations on recent challenging benchmark show that our tracking method outperforms the state-of-the-art trackers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge