Amin Boudesh
TransfoRhythm: A Transformer Architecture Conductive to Blood Pressure Estimation via Solo PPG Signal Capturing
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:Recent statistics indicate that approximately 1.3 billion individuals worldwide suffer from hypertension, a leading cause of premature death globally. Blood pressure (BP) serves as a critical health indicator for accurate and timely diagnosis and/or treatment of hypertension. Driven by recent advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), there has been a surge of interest in developing data-driven and cuff-less BP estimation solutions. In this context, current literature predominantly focuses on coupling Electrocardiography (ECG) and Photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors, though this approach is constrained by reliance on multiple sensor types. An alternative, utilizing standalone PPG signals, presents challenges due to the absence of auxiliary sensors (ECG), requiring the use of morphological features while addressing motion artifacts and high-frequency noise. To address these issues, the paper introduces the TransfoRhythm framework, a Transformer-based DNN architecture built upon the recently released physiological database, MIMIC-IV. Leveraging Multi-Head Attention (MHA) mechanism, TransfoRhythm identifies dependencies and similarities across data segments, forming a robust framework for cuff-less BP estimation solely using PPG signals. To our knowledge, this paper represents the first study to apply the MIMIC IV dataset for cuff-less BP estimation, and TransfoRhythm is the first MHA-based model trained via MIMIC IV for BP prediction. Performance evaluation through comprehensive experiments demonstrates TransfoRhythm's superiority over its state-of-the-art counterparts. Specifically, TransfoRhythm achieves highly accurate results with Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of [1.84, 1.42] and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of [1.50, 1.17] for systolic and diastolic blood pressures, respectively.
Pyramid Transformer for Traffic Sign Detection
Jul 22, 2022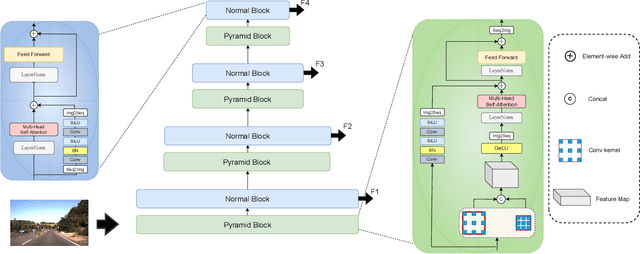
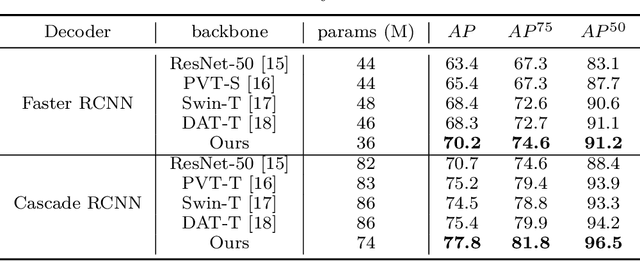
Abstract:Traffic sign detection is a vital task in the visual system of self-driving cars and the automated driving system. Recently, novel Transformer-based models have achieved encouraging results for various computer vision tasks. We still observed that vanilla ViT could not yield satisfactory results in traffic sign detection because the overall size of the datasets is very small and the class distribution of traffic signs is extremely unbalanced. To overcome this problem, a novel Pyramid Transformer with locality mechanisms is proposed in this paper. Specifically, Pyramid Transformer has several spatial pyramid reduction layers to shrink and embed the input image into tokens with rich multi-scale context by using atrous convolutions. Moreover, it inherits an intrinsic scale invariance inductive bias and is able to learn local feature representation for objects at various scales, thereby enhancing the network robustness against the size discrepancy of traffic signs. The experiments are conducted on the German Traffic Sign Detection Benchmark (GTSDB). The results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model in the traffic sign detection tasks. More specifically, Pyramid Transformer achieves 77.8% mAP on GTSDB when applied to the Cascade RCNN as the backbone, which surpasses most well-known and widely-used state-of-the-art models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge