Seungyoon Choi
Dynamic Time-aware Continual User Representation Learning
Apr 23, 2025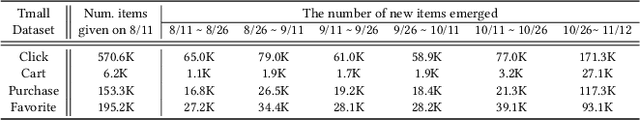
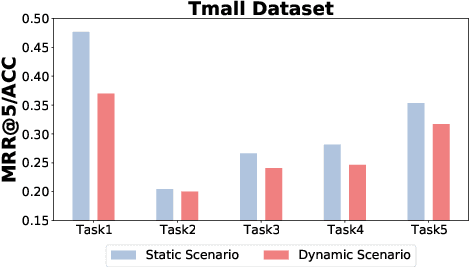
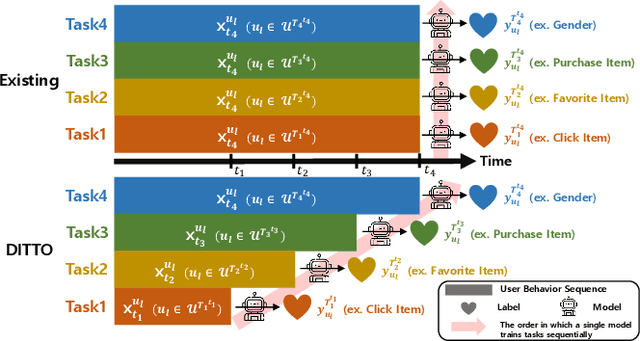
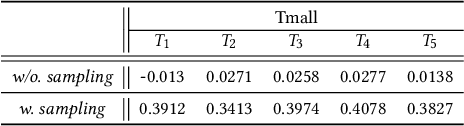
Abstract:Traditional user modeling (UM) approaches have primarily focused on designing models for a single specific task, but they face limitations in generalization and adaptability across various tasks. Recognizing these challenges, recent studies have shifted towards continual learning (CL)-based universal user representation learning aiming to develop a single model capable of handling multiple tasks. Despite advancements, existing methods are in fact evaluated under an unrealistic scenario that does not consider the passage of time as tasks progress, which overlooks newly emerged items that may change the item distribution of previous tasks. In this paper, we introduce a practical evaluation scenario on which CL-based universal user representation learning approaches should be evaluated, which takes into account the passage of time as tasks progress. Then, we propose a novel framework Dynamic Time-aware continual user representation learner, named DITTO, designed to alleviate catastrophic forgetting despite continuous shifts in item distribution, while also allowing the knowledge acquired from previous tasks to adapt to the current shifted item distribution. Through our extensive experiments, we demonstrate the superiority of DITTO over state-of-the-art methods under a practical evaluation scenario. Our source code is available at https://github.com/seungyoon-Choi/DITTO_official.
Large Language Models meet Collaborative Filtering: An Efficient All-round LLM-based Recommender System
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Collaborative filtering recommender systems (CF-RecSys) have shown successive results in enhancing the user experience on social media and e-commerce platforms. However, as CF-RecSys struggles under cold scenarios with sparse user-item interactions, recent strategies have focused on leveraging modality information of user/items (e.g., text or images) based on pre-trained modality encoders and Large Language Models (LLMs). Despite their effectiveness under cold scenarios, we observe that they underperform simple traditional collaborative filtering models under warm scenarios due to the lack of collaborative knowledge. In this work, we propose an efficient All-round LLM-based Recommender system, called A-LLMRec, that excels not only in the cold scenario but also in the warm scenario. Our main idea is to enable an LLM to directly leverage the collaborative knowledge contained in a pre-trained state-of-the-art CF-RecSys so that the emergent ability of the LLM as well as the high-quality user/item embeddings that are already trained by the state-of-the-art CF-RecSys can be jointly exploited. This approach yields two advantages: (1) model-agnostic, allowing for integration with various existing CF-RecSys, and (2) efficiency, eliminating the extensive fine-tuning typically required for LLM-based recommenders. Our extensive experiments on various real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of A-LLMRec in various scenarios, including cold/warm, few-shot, cold user, and cross-domain scenarios. Beyond the recommendation task, we also show the potential of A-LLMRec in generating natural language outputs based on the understanding of the collaborative knowledge by performing a favorite genre prediction task. Our code is available at https://github.com/ghdtjr/A-LLMRec .
DSLR: Diversity Enhancement and Structure Learning for Rehearsal-based Graph Continual Learning
Feb 23, 2024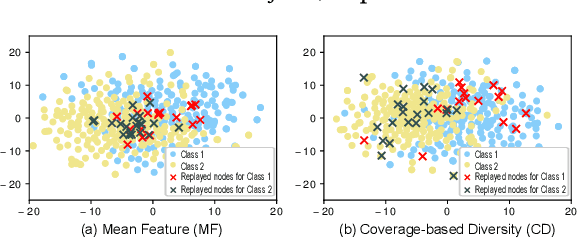
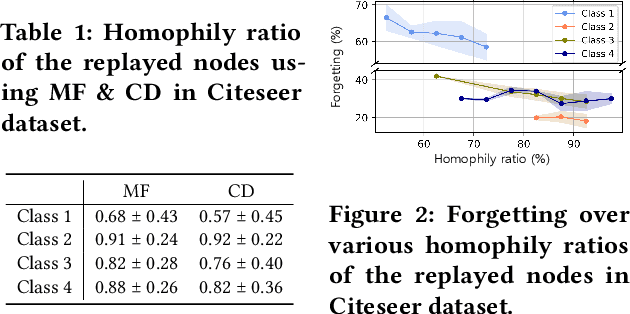

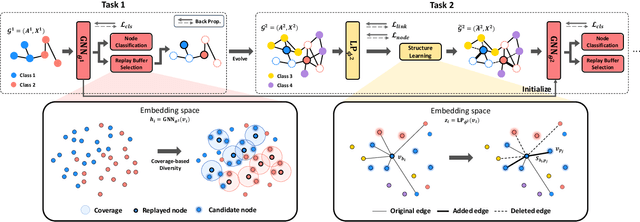
Abstract:We investigate the replay buffer in rehearsal-based approaches for graph continual learning (GCL) methods. Existing rehearsal-based GCL methods select the most representative nodes for each class and store them in a replay buffer for later use in training subsequent tasks. However, we discovered that considering only the class representativeness of each replayed node makes the replayed nodes to be concentrated around the center of each class, incurring a potential risk of overfitting to nodes residing in those regions, which aggravates catastrophic forgetting. Moreover, as the rehearsal-based approach heavily relies on a few replayed nodes to retain knowledge obtained from previous tasks, involving the replayed nodes that have irrelevant neighbors in the model training may have a significant detrimental impact on model performance. In this paper, we propose a GCL model named DSLR, specifically, we devise a coverage-based diversity (CD) approach to consider both the class representativeness and the diversity within each class of the replayed nodes. Moreover, we adopt graph structure learning (GSL) to ensure that the replayed nodes are connected to truly informative neighbors. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of DSLR. Our source code is available at https://github.com/seungyoon-Choi/DSLR_official.
Task-Equivariant Graph Few-shot Learning
Jun 01, 2023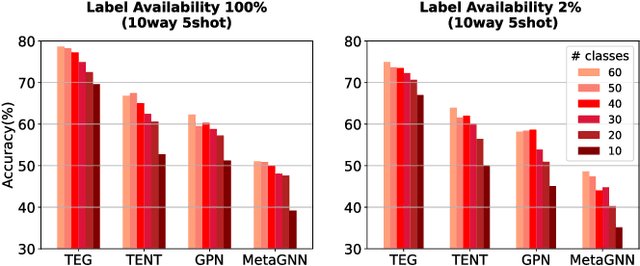
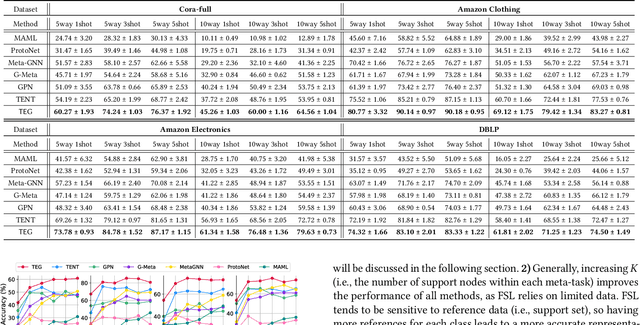
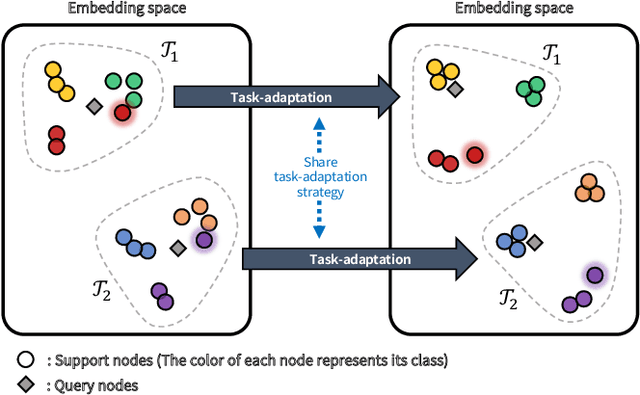
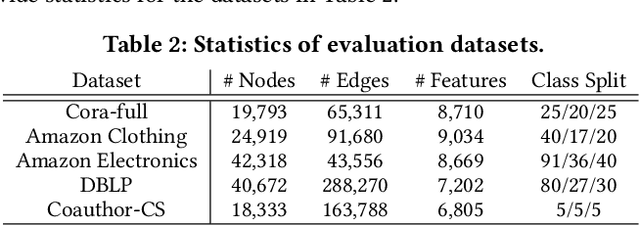
Abstract:Although Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been successful in node classification tasks, their performance heavily relies on the availability of a sufficient number of labeled nodes per class. In real-world situations, not all classes have many labeled nodes and there may be instances where the model needs to classify new classes, making manual labeling difficult. To solve this problem, it is important for GNNs to be able to classify nodes with a limited number of labeled nodes, known as few-shot node classification. Previous episodic meta-learning based methods have demonstrated success in few-shot node classification, but our findings suggest that optimal performance can only be achieved with a substantial amount of diverse training meta-tasks. To address this challenge of meta-learning based few-shot learning (FSL), we propose a new approach, the Task-Equivariant Graph few-shot learning (TEG) framework. Our TEG framework enables the model to learn transferable task-adaptation strategies using a limited number of training meta-tasks, allowing it to acquire meta-knowledge for a wide range of meta-tasks. By incorporating equivariant neural networks, TEG can utilize their strong generalization abilities to learn highly adaptable task-specific strategies. As a result, TEG achieves state-of-the-art performance with limited training meta-tasks. Our experiments on various benchmark datasets demonstrate TEG's superiority in terms of accuracy and generalization ability, even when using minimal meta-training data, highlighting the effectiveness of our proposed approach in addressing the challenges of meta-learning based few-shot node classification. Our code is available at the following link: https://github.com/sung-won-kim/TEG
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge