Seungji Lee
Large-Scale Multilingual Speech Recognition with a Streaming End-to-End Model
Sep 11, 2019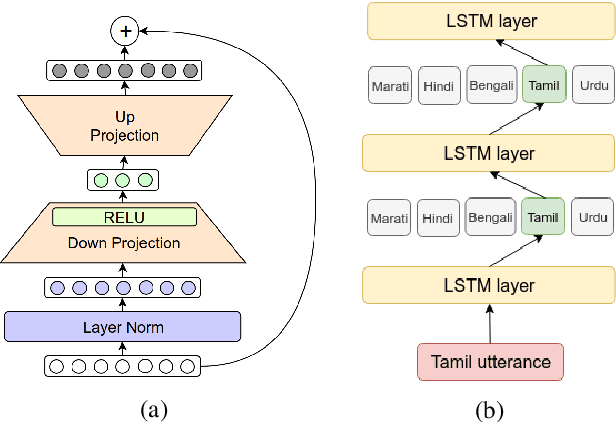
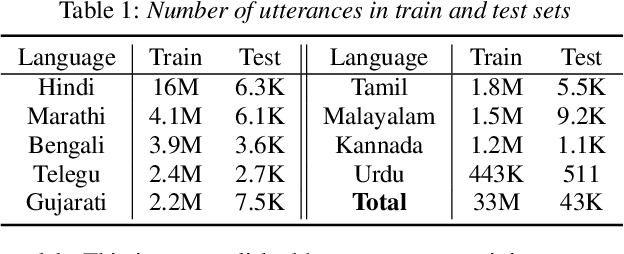
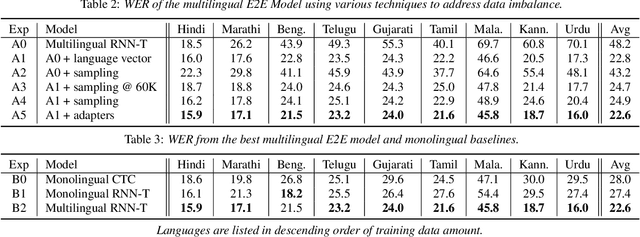
Abstract:Multilingual end-to-end (E2E) models have shown great promise in expansion of automatic speech recognition (ASR) coverage of the world's languages. They have shown improvement over monolingual systems, and have simplified training and serving by eliminating language-specific acoustic, pronunciation, and language models. This work presents an E2E multilingual system which is equipped to operate in low-latency interactive applications, as well as handle a key challenge of real world data: the imbalance in training data across languages. Using nine Indic languages, we compare a variety of techniques, and find that a combination of conditioning on a language vector and training language-specific adapter layers produces the best model. The resulting E2E multilingual model achieves a lower word error rate (WER) than both monolingual E2E models (eight of nine languages) and monolingual conventional systems (all nine languages).
No Need for a Lexicon? Evaluating the Value of the Pronunciation Lexica in End-to-End Models
Dec 05, 2017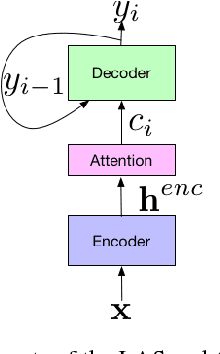

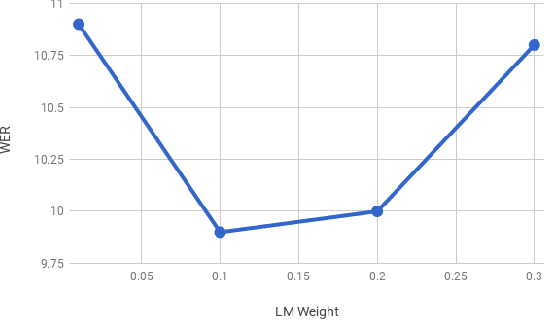
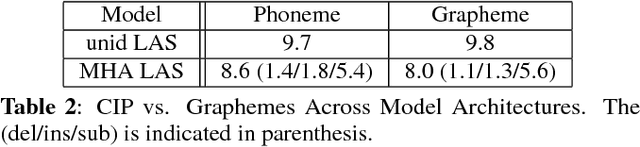
Abstract:For decades, context-dependent phonemes have been the dominant sub-word unit for conventional acoustic modeling systems. This status quo has begun to be challenged recently by end-to-end models which seek to combine acoustic, pronunciation, and language model components into a single neural network. Such systems, which typically predict graphemes or words, simplify the recognition process since they remove the need for a separate expert-curated pronunciation lexicon to map from phoneme-based units to words. However, there has been little previous work comparing phoneme-based versus grapheme-based sub-word units in the end-to-end modeling framework, to determine whether the gains from such approaches are primarily due to the new probabilistic model, or from the joint learning of the various components with grapheme-based units. In this work, we conduct detailed experiments which are aimed at quantifying the value of phoneme-based pronunciation lexica in the context of end-to-end models. We examine phoneme-based end-to-end models, which are contrasted against grapheme-based ones on a large vocabulary English Voice-search task, where we find that graphemes do indeed outperform phonemes. We also compare grapheme and phoneme-based approaches on a multi-dialect English task, which once again confirm the superiority of graphemes, greatly simplifying the system for recognizing multiple dialects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge