Sergey Markov
TEncDM: Understanding the Properties of Diffusion Model in the Space of Language Model Encodings
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:Drawing inspiration from the success of diffusion models in various domains, numerous research papers proposed methods for adapting them to text data. Despite these efforts, none of them has managed to achieve the quality of the large language models. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of key components of the text diffusion models and introduce a novel approach named Text Encoding Diffusion Model (TEncDM). Instead of the commonly used token embedding space, we train our model in the space of the language model encodings. Additionally, we propose to use a Transformer-based decoder that utilizes contextual information for text reconstruction. We also analyse self-conditioning and find that it increases the magnitude of the model outputs, allowing the reduction of the number of denoising steps at the inference stage. Evaluation of TEncDM on two downstream text generation tasks, QQP and XSum, demonstrates its superiority over existing non-autoregressive models.
A Family of Pretrained Transformer Language Models for Russian
Sep 19, 2023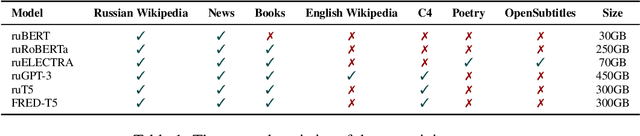
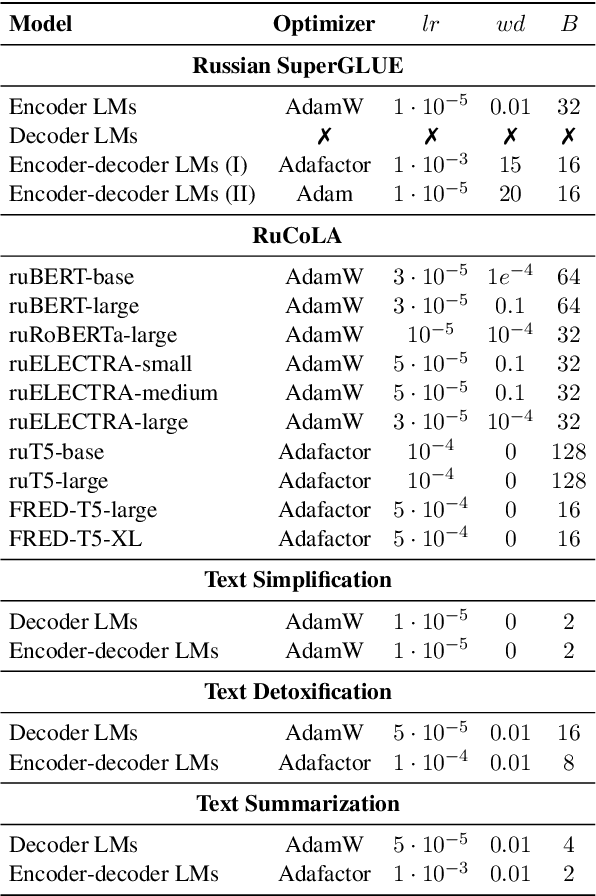
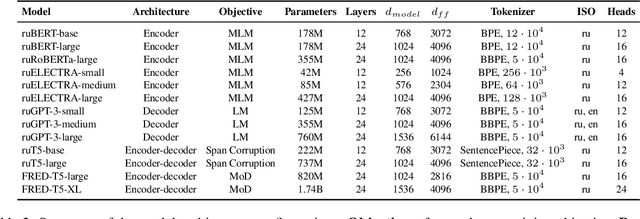
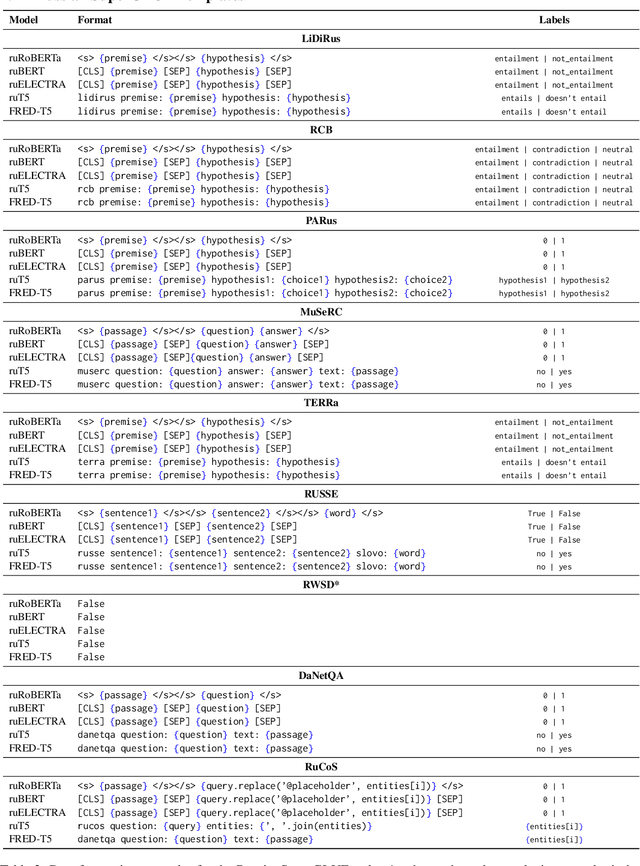
Abstract:Nowadays, Transformer language models (LMs) represent a fundamental component of the NLP research methodologies and applications. However, the development of such models specifically for the Russian language has received little attention. This paper presents a collection of 13 Russian Transformer LMs based on the encoder (ruBERT, ruRoBERTa, ruELECTRA), decoder (ruGPT-3), and encoder-decoder (ruT5, FRED-T5) models in multiple sizes. Access to these models is readily available via the HuggingFace platform. We provide a report of the model architecture design and pretraining, and the results of evaluating their generalization abilities on Russian natural language understanding and generation datasets and benchmarks. By pretraining and releasing these specialized Transformer LMs, we hope to broaden the scope of the NLP research directions and enable the development of industrial solutions for the Russian language.
RuCLIP -- new models and experiments: a technical report
Feb 22, 2022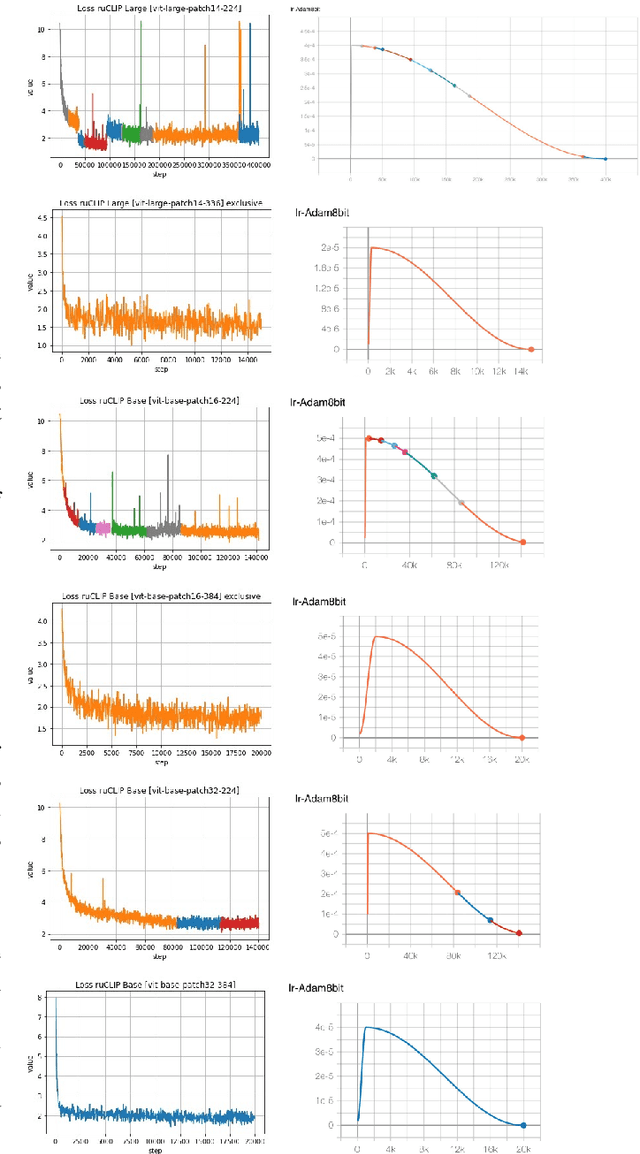
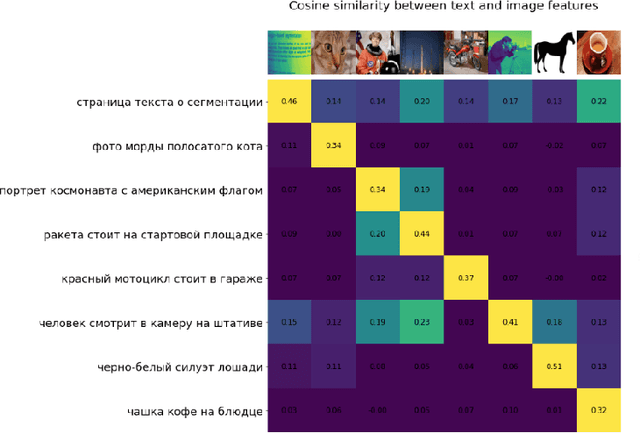
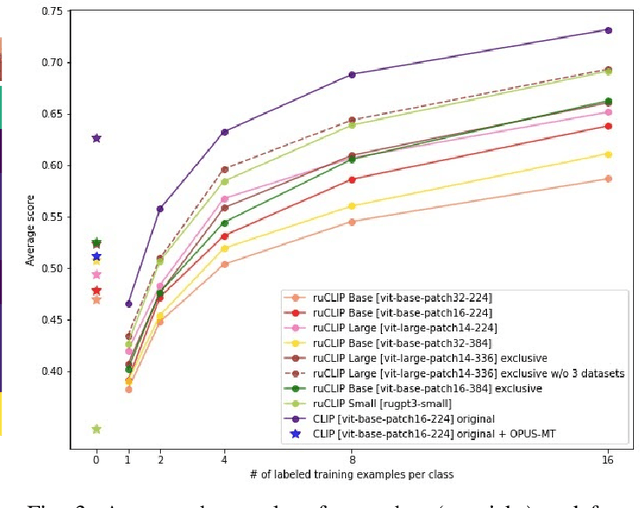
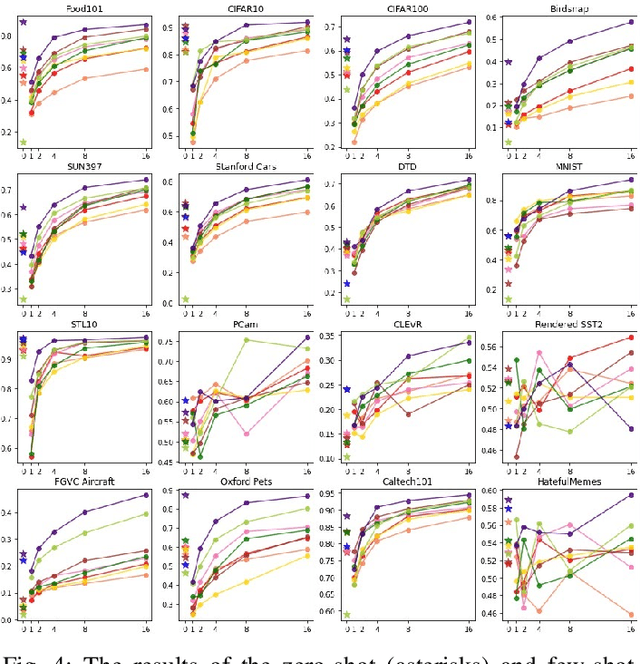
Abstract:In the report we propose six new implementations of ruCLIP model trained on our 240M pairs. The accuracy results are compared with original CLIP model with Ru-En translation (OPUS-MT) on 16 datasets from different domains. Our best implementations outperform CLIP + OPUS-MT solution on most of the datasets in few-show and zero-shot tasks. In the report we briefly describe the implementations and concentrate on the conducted experiments. Inference execution time comparison is also presented in the report.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge