Anastasia Maltseva
Kandinsky 5.0: A Family of Foundation Models for Image and Video Generation
Nov 19, 2025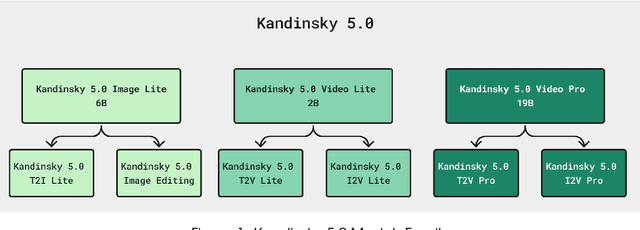
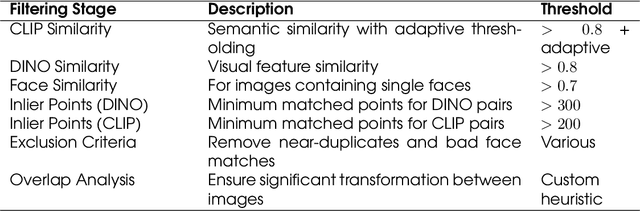
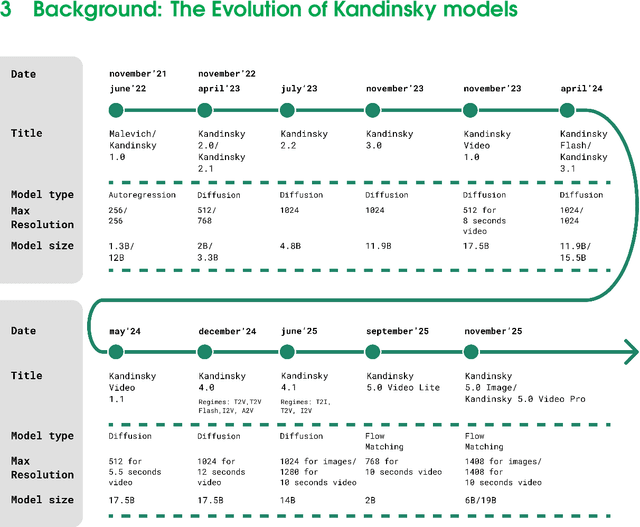
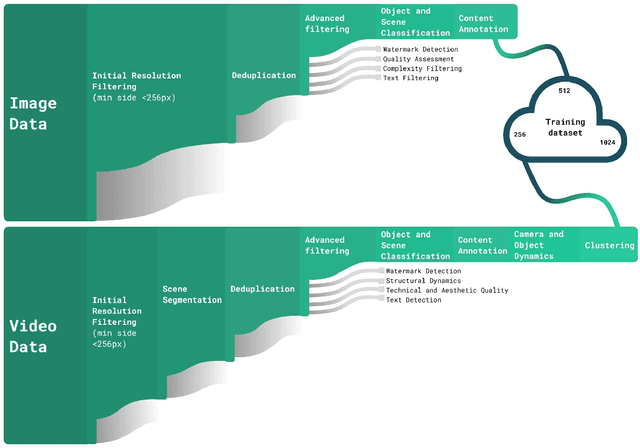
Abstract:This report introduces Kandinsky 5.0, a family of state-of-the-art foundation models for high-resolution image and 10-second video synthesis. The framework comprises three core line-up of models: Kandinsky 5.0 Image Lite - a line-up of 6B parameter image generation models, Kandinsky 5.0 Video Lite - a fast and lightweight 2B parameter text-to-video and image-to-video models, and Kandinsky 5.0 Video Pro - 19B parameter models that achieves superior video generation quality. We provide a comprehensive review of the data curation lifecycle - including collection, processing, filtering and clustering - for the multi-stage training pipeline that involves extensive pre-training and incorporates quality-enhancement techniques such as self-supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL)-based post-training. We also present novel architectural, training, and inference optimizations that enable Kandinsky 5.0 to achieve high generation speeds and state-of-the-art performance across various tasks, as demonstrated by human evaluation. As a large-scale, publicly available generative framework, Kandinsky 5.0 leverages the full potential of its pre-training and subsequent stages to be adapted for a wide range of generative applications. We hope that this report, together with the release of our open-source code and training checkpoints, will substantially advance the development and accessibility of high-quality generative models for the research community.
Kandinsky 3.0 Technical Report
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:We present Kandinsky 3.0, a large-scale text-to-image generation model based on latent diffusion, continuing the series of text-to-image Kandinsky models and reflecting our progress to achieve higher quality and realism of image generation. Compared to previous versions of Kandinsky 2.x, Kandinsky 3.0 leverages a two times larger U-Net backbone, a ten times larger text encoder and removes diffusion mapping. We describe the architecture of the model, the data collection procedure, the training technique, and the production system of user interaction. We focus on the key components that, as we have identified as a result of a large number of experiments, had the most significant impact on improving the quality of our model compared to the others. By our side-by-side comparisons, Kandinsky becomes better in text understanding and works better on specific domains. Project page: https://ai-forever.github.io/Kandinsky-3
Kandinsky: an Improved Text-to-Image Synthesis with Image Prior and Latent Diffusion
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Text-to-image generation is a significant domain in modern computer vision and has achieved substantial improvements through the evolution of generative architectures. Among these, there are diffusion-based models that have demonstrated essential quality enhancements. These models are generally split into two categories: pixel-level and latent-level approaches. We present Kandinsky1, a novel exploration of latent diffusion architecture, combining the principles of the image prior models with latent diffusion techniques. The image prior model is trained separately to map text embeddings to image embeddings of CLIP. Another distinct feature of the proposed model is the modified MoVQ implementation, which serves as the image autoencoder component. Overall, the designed model contains 3.3B parameters. We also deployed a user-friendly demo system that supports diverse generative modes such as text-to-image generation, image fusion, text and image fusion, image variations generation, and text-guided inpainting/outpainting. Additionally, we released the source code and checkpoints for the Kandinsky models. Experimental evaluations demonstrate a FID score of 8.03 on the COCO-30K dataset, marking our model as the top open-source performer in terms of measurable image generation quality.
RuCLIP -- new models and experiments: a technical report
Feb 22, 2022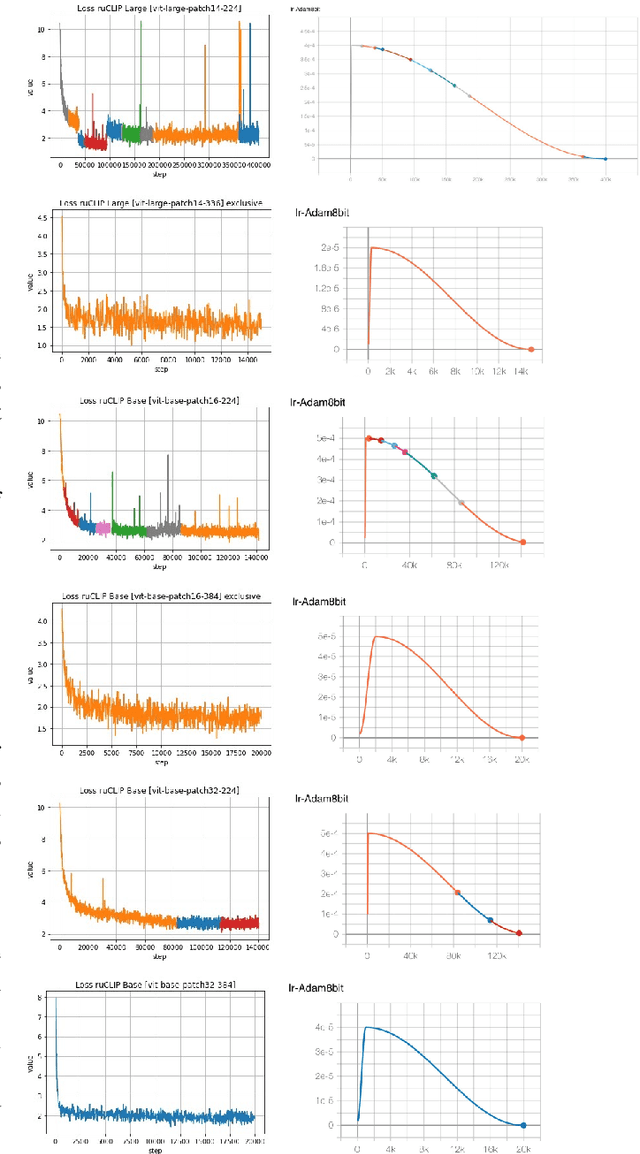
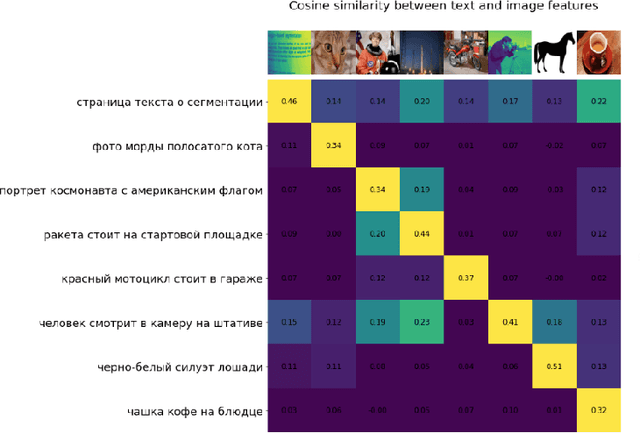
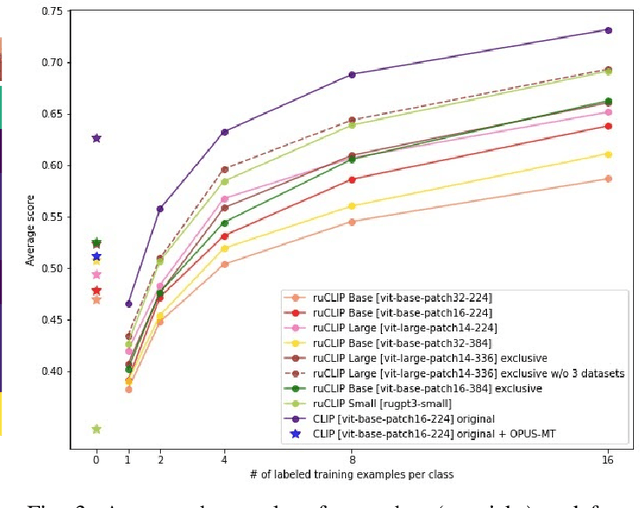
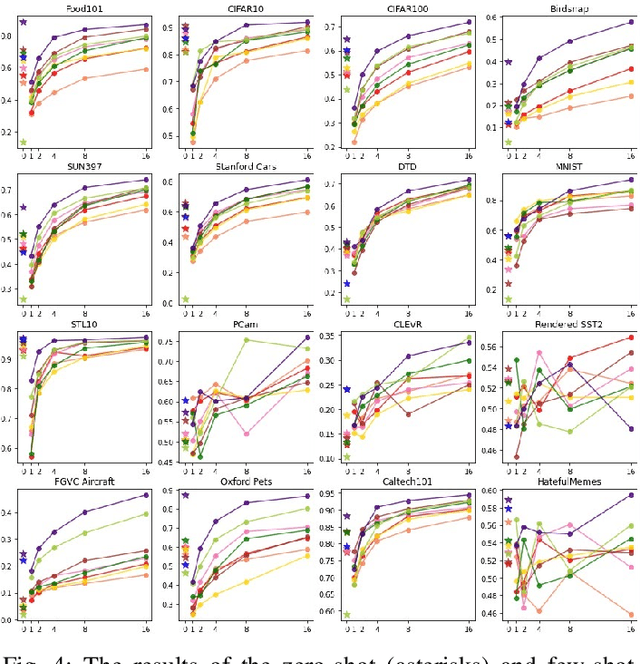
Abstract:In the report we propose six new implementations of ruCLIP model trained on our 240M pairs. The accuracy results are compared with original CLIP model with Ru-En translation (OPUS-MT) on 16 datasets from different domains. Our best implementations outperform CLIP + OPUS-MT solution on most of the datasets in few-show and zero-shot tasks. In the report we briefly describe the implementations and concentrate on the conducted experiments. Inference execution time comparison is also presented in the report.
A new face swap method for image and video domains: a technical report
Feb 07, 2022



Abstract:Deep fake technology became a hot field of research in the last few years. Researchers investigate sophisticated Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), autoencoders, and other approaches to establish precise and robust algorithms for face swapping. Achieved results show that the deep fake unsupervised synthesis task has problems in terms of the visual quality of generated data. These problems usually lead to high fake detection accuracy when an expert analyzes them. The first problem is that existing image-to-image approaches do not consider video domain specificity and frame-by-frame processing leads to face jittering and other clearly visible distortions. Another problem is the generated data resolution, which is low for many existing methods due to high computational complexity. The third problem appears when the source face has larger proportions (like bigger cheeks), and after replacement it becomes visible on the face border. Our main goal was to develop such an approach that could solve these problems and outperform existing solutions on a number of clue metrics. We introduce a new face swap pipeline that is based on FaceShifter architecture and fixes the problems stated above. With a new eye loss function, super-resolution block, and Gaussian-based face mask generation leads to improvements in quality which is confirmed during evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge