Viacheslav Meshchaninov
Smoothie: Smoothing Diffusion on Token Embeddings for Text Generation
May 24, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved state-of-the-art performance in generating images, audio, and video, but their adaptation to text remains challenging due to its discrete nature. Prior approaches either apply Gaussian diffusion in continuous latent spaces, which inherits semantic structure but struggles with token decoding, or operate in categorical simplex space, which respect discreteness but disregard semantic relation between tokens. In this paper, we propose Smoothing Diffusion on Token Embeddings (Smoothie), a novel diffusion method that combines the strengths of both approaches by progressively smoothing token embeddings based on semantic similarity. This technique enables gradual information removal while maintaining a natural decoding process. Experimental results on several sequence-to-sequence generation tasks demonstrate that Smoothie outperforms existing diffusion-based models in generation quality. Furthermore, ablation studies show that our proposed diffusion space yields better performance than both the standard embedding space and the categorical simplex. Our code is available at https://github.com/ashaba1in/smoothie.
Diffusion on language model embeddings for protein sequence generation
Mar 06, 2024



Abstract:Protein design requires a deep understanding of the inherent complexities of the protein universe. While many efforts lean towards conditional generation or focus on specific families of proteins, the foundational task of unconditional generation remains underexplored and undervalued. Here, we explore this pivotal domain, introducing DiMA, a model that leverages continuous diffusion on embeddings derived from the protein language model, ESM-2, to generate amino acid sequences. DiMA surpasses leading solutions, including autoregressive transformer-based and discrete diffusion models, and we quantitatively illustrate the impact of the design choices that lead to its superior performance. We extensively evaluate the quality, diversity, distribution similarity, and biological relevance of the generated sequences using multiple metrics across various modalities. Our approach consistently produces novel, diverse protein sequences that accurately reflect the inherent structural and functional diversity of the protein space. This work advances the field of protein design and sets the stage for conditional models by providing a robust framework for scalable and high-quality protein sequence generation.
TEncDM: Understanding the Properties of Diffusion Model in the Space of Language Model Encodings
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:Drawing inspiration from the success of diffusion models in various domains, numerous research papers proposed methods for adapting them to text data. Despite these efforts, none of them has managed to achieve the quality of the large language models. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of key components of the text diffusion models and introduce a novel approach named Text Encoding Diffusion Model (TEncDM). Instead of the commonly used token embedding space, we train our model in the space of the language model encodings. Additionally, we propose to use a Transformer-based decoder that utilizes contextual information for text reconstruction. We also analyse self-conditioning and find that it increases the magnitude of the model outputs, allowing the reduction of the number of denoising steps at the inference stage. Evaluation of TEncDM on two downstream text generation tasks, QQP and XSum, demonstrates its superiority over existing non-autoregressive models.
Combining Contrastive and Supervised Learning for Video Super-Resolution Detection
May 20, 2022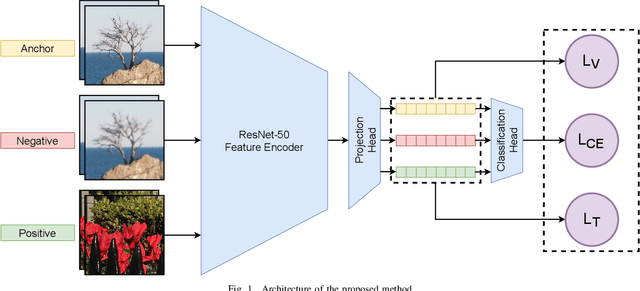
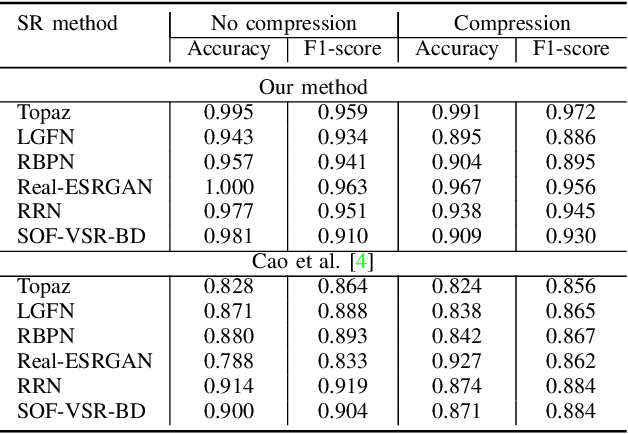
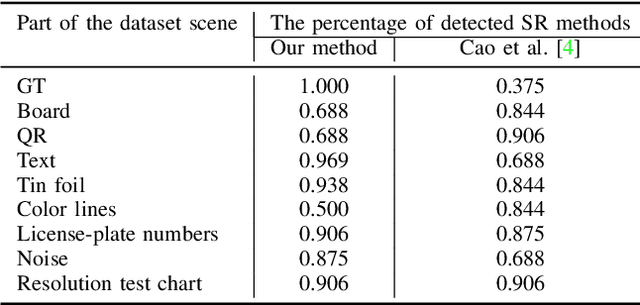
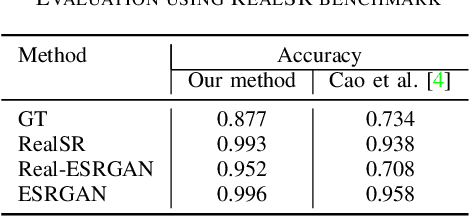
Abstract:Upscaled video detection is a helpful tool in multimedia forensics, but it is a challenging task that involves various upscaling and compression algorithms. There are many resolution-enhancement methods, including interpolation and deep-learning-based super-resolution, and they leave unique traces. In this work, we propose a new upscaled-resolution-detection method based on learning of visual representations using contrastive and cross-entropy losses. To explain how the method detects videos, we systematically review the major components of our framework - in particular, we show that most data-augmentation approaches hinder the learning of the method. Through extensive experiments on various datasets, we demonstrate that our method effectively detects upscaling even in compressed videos and outperforms the state-of-the-art alternatives. The code and models are publicly available at https://github.com/msu-video-group/SRDM
Towards True Detail Restoration for Super-Resolution: A Benchmark and a Quality Metric
Mar 16, 2022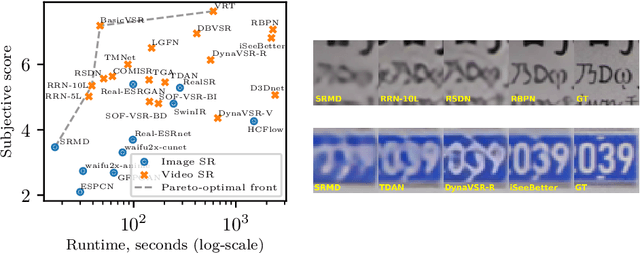



Abstract:Super-resolution (SR) has become a widely researched topic in recent years. SR methods can improve overall image and video quality and create new possibilities for further content analysis. But the SR mainstream focuses primarily on increasing the naturalness of the resulting image despite potentially losing context accuracy. Such methods may produce an incorrect digit, character, face, or other structural object even though they otherwise yield good visual quality. Incorrect detail restoration can cause errors when detecting and identifying objects both manually and automatically. To analyze the detail-restoration capabilities of image and video SR models, we developed a benchmark based on our own video dataset, which contains complex patterns that SR models generally fail to correctly restore. We assessed 32 recent SR models using our benchmark and compared their ability to preserve scene context. We also conducted a crowd-sourced comparison of restored details and developed an objective assessment metric that outperforms other quality metrics by correlation with subjective scores for this task. In conclusion, we provide a deep analysis of benchmark results that yields insights for future SR-based work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge