Sean Treichler
Highly-scalable, physics-informed GANs for learning solutions of stochastic PDEs
Oct 29, 2019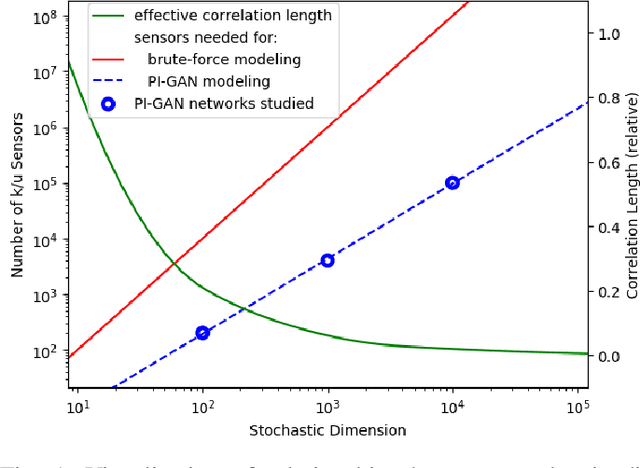
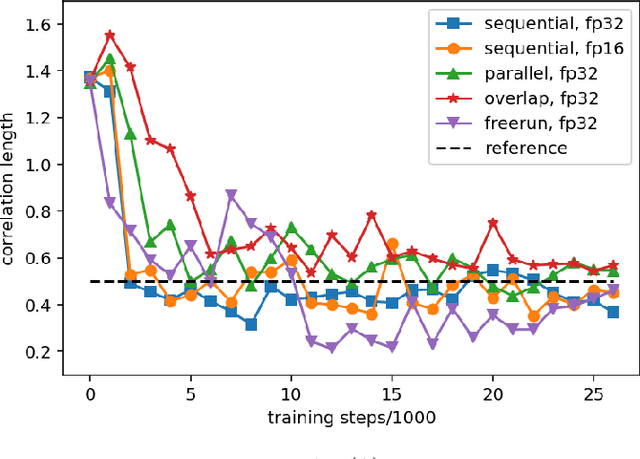
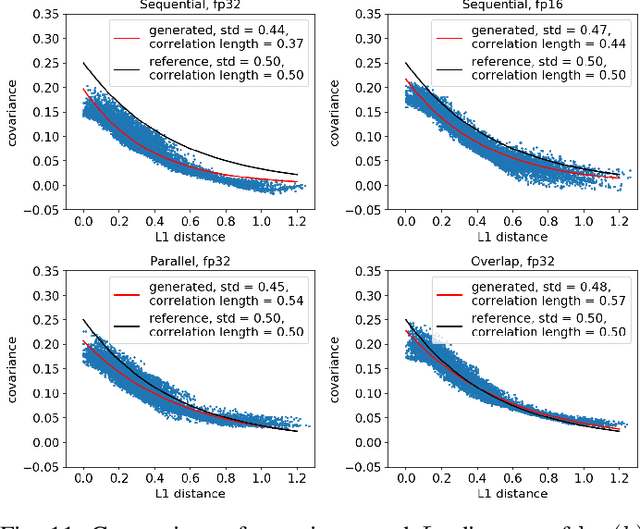
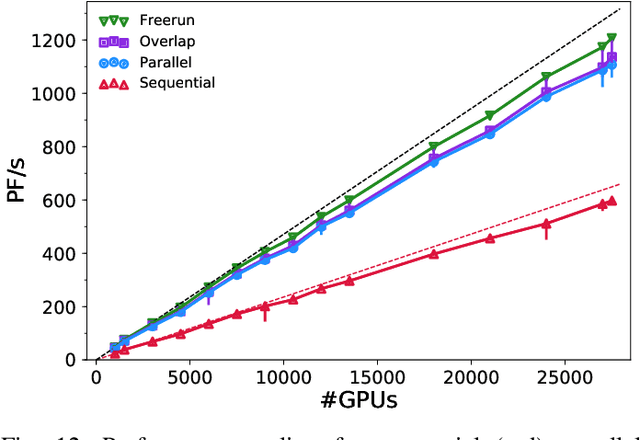
Abstract:Uncertainty quantification for forward and inverse problems is a central challenge across physical and biomedical disciplines. We address this challenge for the problem of modeling subsurface flow at the Hanford Site by combining stochastic computational models with observational data using physics-informed GAN models. The geographic extent, spatial heterogeneity, and multiple correlation length scales of the Hanford Site require training a computationally intensive GAN model to thousands of dimensions. We develop a hierarchical scheme for exploiting domain parallelism, map discriminators and generators to multiple GPUs, and employ efficient communication schemes to ensure training stability and convergence. We developed a highly optimized implementation of this scheme that scales to 27,500 NVIDIA Volta GPUs and 4584 nodes on the Summit supercomputer with a 93.1% scaling efficiency, achieving peak and sustained half-precision rates of 1228 PF/s and 1207 PF/s.
Exascale Deep Learning for Scientific Inverse Problems
Sep 24, 2019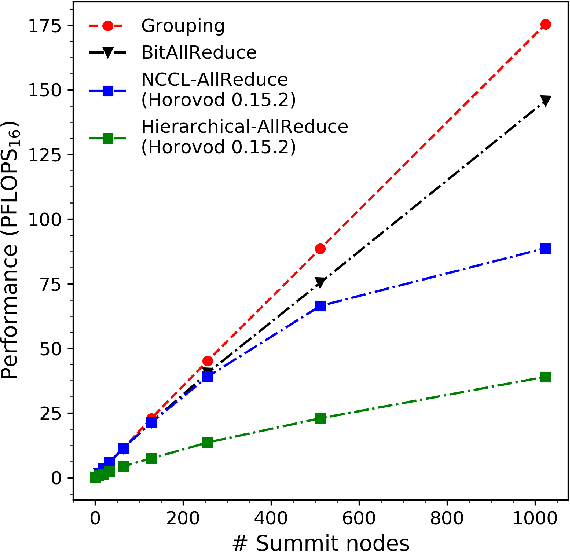
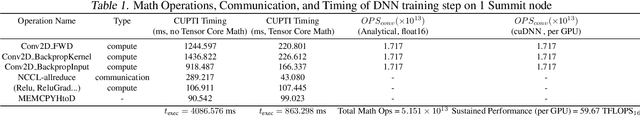
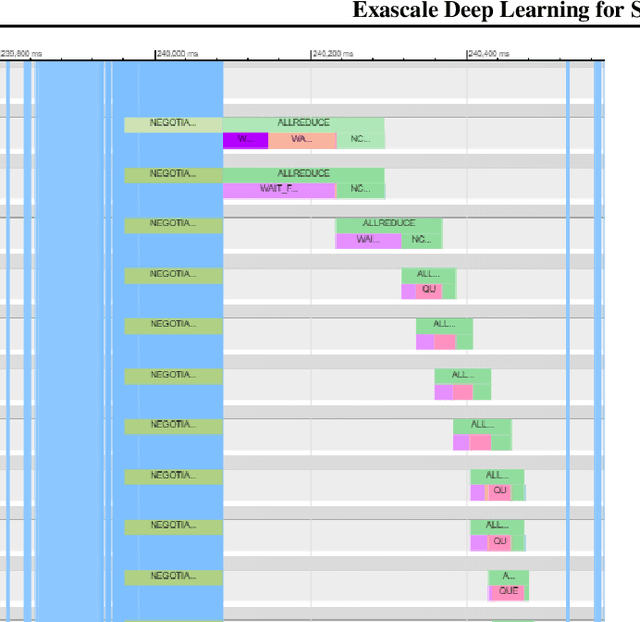

Abstract:We introduce novel communication strategies in synchronous distributed Deep Learning consisting of decentralized gradient reduction orchestration and computational graph-aware grouping of gradient tensors. These new techniques produce an optimal overlap between computation and communication and result in near-linear scaling (0.93) of distributed training up to 27,600 NVIDIA V100 GPUs on the Summit Supercomputer. We demonstrate our gradient reduction techniques in the context of training a Fully Convolutional Neural Network to approximate the solution of a longstanding scientific inverse problem in materials imaging. The efficient distributed training on a dataset size of 0.5 PB, produces a model capable of an atomically-accurate reconstruction of materials, and in the process reaching a peak performance of 2.15(4) EFLOPS$_{16}$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge