Sangah Lee
KoBALT: Korean Benchmark For Advanced Linguistic Tasks
May 22, 2025Abstract:We introduce KoBALT (Korean Benchmark for Advanced Linguistic Tasks), a comprehensive linguistically-motivated benchmark comprising 700 multiple-choice questions spanning 24 phenomena across five linguistic domains: syntax, semantics, pragmatics, phonetics/phonology, and morphology. KoBALT is designed to advance the evaluation of large language models (LLMs) in Korean, a morphologically rich language, by addressing the limitations of conventional benchmarks that often lack linguistic depth and typological grounding. It introduces a suite of expert-curated, linguistically motivated questions with minimal n-gram overlap with standard Korean corpora, substantially mitigating the risk of data contamination and allowing a more robust assessment of true language understanding. Our evaluation of 20 contemporary LLMs reveals significant performance disparities, with the highest-performing model achieving 61\% general accuracy but showing substantial variation across linguistic domains - from stronger performance in semantics (66\%) to considerable weaknesses in phonology (31\%) and morphology (36\%). Through human preference evaluation with 95 annotators, we demonstrate a strong correlation between KoBALT scores and human judgments, validating our benchmark's effectiveness as a discriminative measure of Korean language understanding. KoBALT addresses critical gaps in linguistic evaluation for typologically diverse languages and provides a robust framework for assessing genuine linguistic competence in Korean language models.
ManWav: The First Manchu ASR Model
Jun 19, 2024
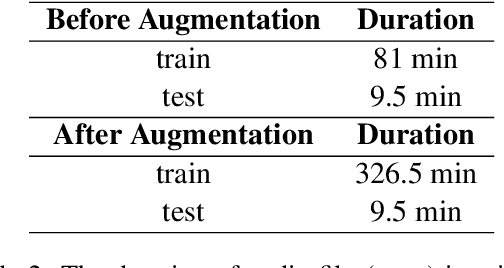
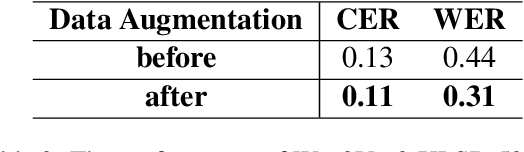

Abstract:This study addresses the widening gap in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) research between high resource and extremely low resource languages, with a particular focus on Manchu, a critically endangered language. Manchu exemplifies the challenges faced by marginalized linguistic communities in accessing state-of-the-art technologies. In a pioneering effort, we introduce the first-ever Manchu ASR model ManWav, leveraging Wav2Vec2-XLSR-53. The results of the first Manchu ASR is promising, especially when trained with our augmented data. Wav2Vec2-XLSR-53 fine-tuned with augmented data demonstrates a 0.02 drop in CER and 0.13 drop in WER compared to the same base model fine-tuned with original data.
KoCoNovel: Annotated Dataset of Character Coreference in Korean Novels
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we present KoCoNovel, a novel character coreference dataset derived from Korean literary texts, complete with detailed annotation guidelines. Comprising 178K tokens from 50 modern and contemporary novels, KoCoNovel stands as one of the largest public coreference resolution corpora in Korean, and the first to be based on literary texts. KoCoNovel offers four distinct versions to accommodate a wide range of literary coreference analysis needs. These versions are designed to support perspectives of the omniscient author or readers, and to manage multiple entities as either separate or overlapping, thereby broadening its applicability. One of KoCoNovel's distinctive features is that 24% of all character mentions are single common nouns, lacking possessive markers or articles. This feature is particularly influenced by the nuances of Korean address term culture, which favors the use of terms denoting social relationships and kinship over personal names. In experiments with a BERT-based coreference model, we observe notable performance enhancements with KoCoNovel in character coreference tasks within literary texts, compared to a larger non-literary coreference dataset. Such findings underscore KoCoNovel's potential to significantly enhance coreference resolution models through the integration of Korean cultural and linguistic dynamics.
K-Act2Emo: Korean Commonsense Knowledge Graph for Indirect Emotional Expression
Mar 23, 2024Abstract:In many literary texts, emotions are indirectly conveyed through descriptions of actions, facial expressions, and appearances, necessitating emotion inference for narrative understanding. In this paper, we introduce K-Act2Emo, a Korean commonsense knowledge graph (CSKG) comprising 1,900 indirect emotional expressions and the emotions inferable from them. We categorize reasoning types into inferences in positive situations, inferences in negative situations, and inferences when expressions do not serve as emotional cues. Unlike existing CSKGs, K-Act2Emo specializes in emotional contexts, and experimental results validate its effectiveness for training emotion inference models. Significantly, the BART-based knowledge model fine-tuned with K-Act2Emo outperforms various existing Korean large language models, achieving performance levels comparable to GPT-4 Turbo.
Mergen: The First Manchu-Korean Machine Translation Model Trained on Augmented Data
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:The Manchu language, with its roots in the historical Manchurian region of Northeast China, is now facing a critical threat of extinction, as there are very few speakers left. In our efforts to safeguard the Manchu language, we introduce Mergen, the first-ever attempt at a Manchu-Korean Machine Translation (MT) model. To develop this model, we utilize valuable resources such as the Manwen Laodang(a historical book) and a Manchu-Korean dictionary. Due to the scarcity of a Manchu-Korean parallel dataset, we expand our data by employing word replacement guided by GloVe embeddings, trained on both monolingual and parallel texts. Our approach is built around an encoder-decoder neural machine translation model, incorporating a bi-directional Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) layer. The experiments have yielded promising results, showcasing a significant enhancement in Manchu-Korean translation, with a remarkable 20-30 point increase in the BLEU score.
DaG LLM ver 1.0: Pioneering Instruction-Tuned Language Modeling for Korean NLP
Nov 23, 2023Abstract:This paper presents the DaG LLM (David and Goliath Large Language Model), a language model specialized for Korean and fine-tuned through Instruction Tuning across 41 tasks within 13 distinct categories.
KR-BERT: A Small-Scale Korean-Specific Language Model
Aug 11, 2020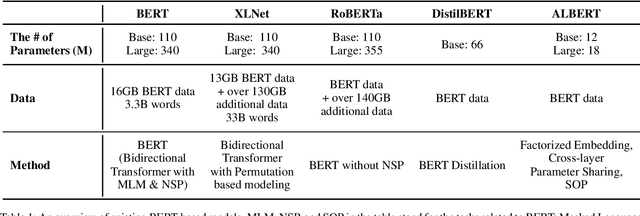


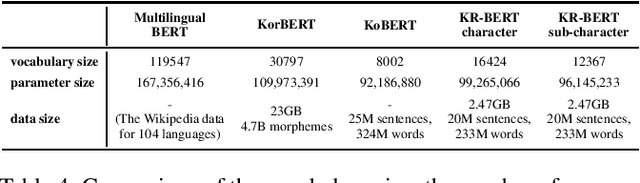
Abstract:Since the appearance of BERT, recent works including XLNet and RoBERTa utilize sentence embedding models pre-trained by large corpora and a large number of parameters. Because such models have large hardware and a huge amount of data, they take a long time to pre-train. Therefore it is important to attempt to make smaller models that perform comparatively. In this paper, we trained a Korean-specific model KR-BERT, utilizing a smaller vocabulary and dataset. Since Korean is one of the morphologically rich languages with poor resources using non-Latin alphabets, it is also important to capture language-specific linguistic phenomena that the Multilingual BERT model missed. We tested several tokenizers including our BidirectionalWordPiece Tokenizer and adjusted the minimal span of tokens for tokenization ranging from sub-character level to character-level to construct a better vocabulary for our model. With those adjustments, our KR-BERT model performed comparably and even better than other existing pre-trained models using a corpus about 1/10 of the size.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge