Samia Ainouz
Physically-admissible polarimetric data augmentation for road-scene analysis
Jun 15, 2022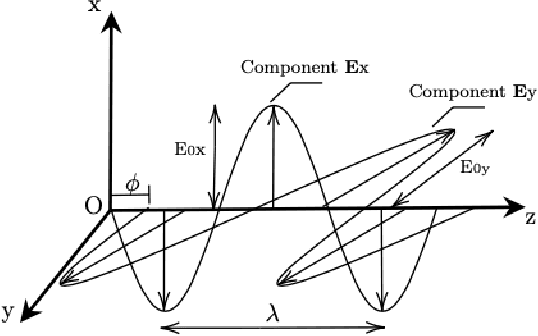
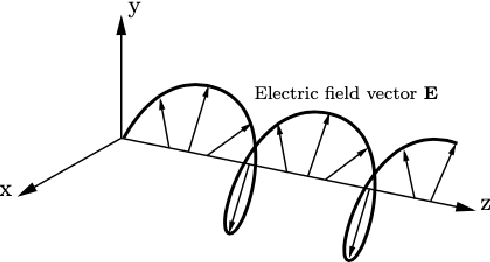
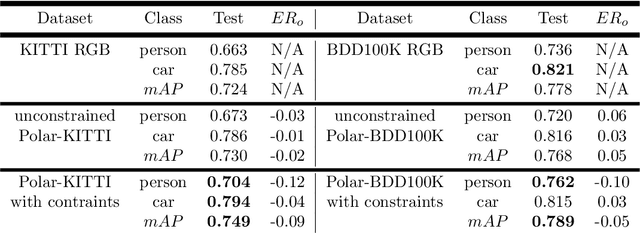
Abstract:Polarimetric imaging, along with deep learning, has shown improved performances on different tasks including scene analysis. However, its robustness may be questioned because of the small size of the training datasets. Though the issue could be solved by data augmentation, polarization modalities are subject to physical feasibility constraints unaddressed by classical data augmentation techniques. To address this issue, we propose to use CycleGAN, an image translation technique based on deep generative models that solely relies on unpaired data, to transfer large labeled road scene datasets to the polarimetric domain. We design several auxiliary loss terms that, alongside the CycleGAN losses, deal with the physical constraints of polarimetric images. The efficiency of this solution is demonstrated on road scene object detection tasks where generated realistic polarimetric images allow to improve performances on cars and pedestrian detection up to 9%. The resulting constrained CycleGAN is publicly released, allowing anyone to generate their own polarimetric images.
A formal approach to good practices in Pseudo-Labeling for Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Re-Identification
Dec 28, 2021

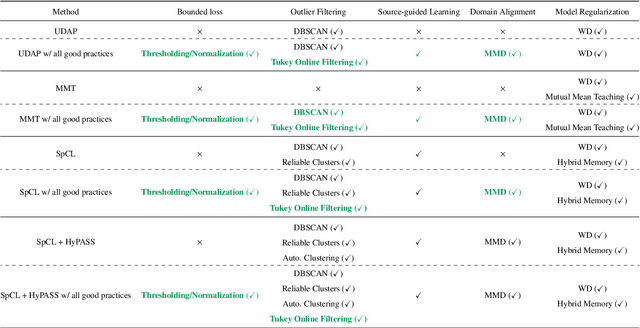
Abstract:The use of pseudo-labels prevails in order to tackle Unsupervised Domain Adaptive (UDA) Re-Identification (re-ID) with the best performance. Indeed, this family of approaches has given rise to several UDA re-ID specific frameworks, which are effective. In these works, research directions to improve Pseudo-Labeling UDA re-ID performance are varied and mostly based on intuition and experiments: refining pseudo-labels, reducing the impact of errors in pseudo-labels... It can be hard to deduce from them general good practices, which can be implemented in any Pseudo-Labeling method, to consistently improve its performance. To address this key question, a new theoretical view on Pseudo-Labeling UDA re-ID is proposed. The contributions are threefold: (i) A novel theoretical framework for Pseudo-Labeling UDA re-ID, formalized through a new general learning upper-bound on the UDA re-ID performance. (ii) General good practices for Pseudo-Labeling, directly deduced from the interpretation of the proposed theoretical framework, in order to improve the target re-ID performance. (iii) Extensive experiments on challenging person and vehicle cross-dataset re-ID tasks, showing consistent performance improvements for various state-of-the-art methods and various proposed implementations of good practices.
Improving Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Re-Identification via Source-Guided Selection of Pseudo-Labeling Hyperparameters
Nov 04, 2021
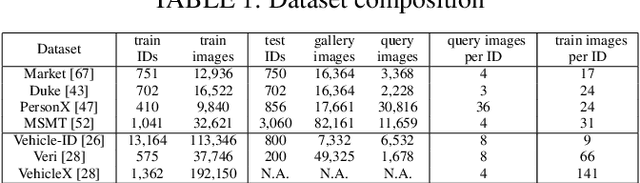
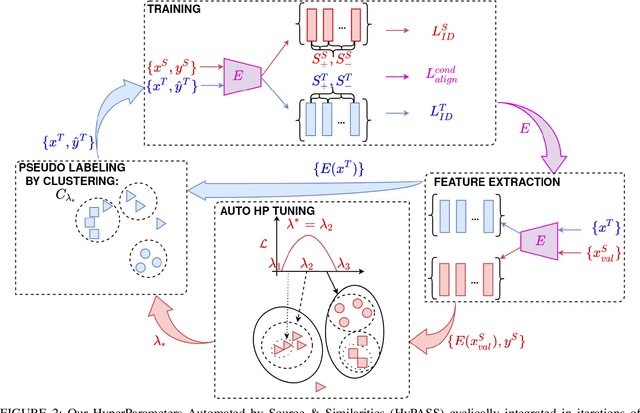

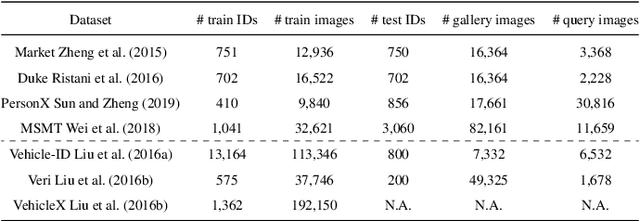
Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) for re-identification (re-ID) is a challenging task: to avoid a costly annotation of additional data, it aims at transferring knowledge from a domain with annotated data to a domain of interest with only unlabeled data. Pseudo-labeling approaches have proven to be effective for UDA re-ID. However, the effectiveness of these approaches heavily depends on the choice of some hyperparameters (HP) that affect the generation of pseudo-labels by clustering. The lack of annotation in the domain of interest makes this choice non-trivial. Current approaches simply reuse the same empirical value for all adaptation tasks and regardless of the target data representation that changes through pseudo-labeling training phases. As this simplistic choice may limit their performance, we aim at addressing this issue. We propose new theoretical grounds on HP selection for clustering UDA re-ID as well as method of automatic and cyclic HP tuning for pseudo-labeling UDA clustering: HyPASS. HyPASS consists in incorporating two modules in pseudo-labeling methods: (i) HP selection based on a labeled source validation set and (ii) conditional domain alignment of feature discriminativeness to improve HP selection based on source samples. Experiments on commonly used person re-ID and vehicle re-ID datasets show that our proposed HyPASS consistently improves the best state-of-the-art methods in re-ID compared to the commonly used empirical HP setting.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Person Re-Identification through Source-Guided Pseudo-Labeling
Sep 20, 2020



Abstract:Person Re-Identification (re-ID) aims at retrieving images of the same person taken by different cameras. A challenge for re-ID is the performance preservation when a model is used on data of interest (target data) which belong to a different domain from the training data domain (source data). Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) is an interesting research direction for this challenge as it avoids a costly annotation of the target data. Pseudo-labeling methods achieve the best results in UDA-based re-ID. Surprisingly, labeled source data are discarded after this initialization step. However, we believe that pseudo-labeling could further leverage the labeled source data in order to improve the post-initialization training steps. In order to improve robustness against erroneous pseudo-labels, we advocate the exploitation of both labeled source data and pseudo-labeled target data during all training iterations. To support our guideline, we introduce a framework which relies on a two-branch architecture optimizing classification and triplet loss based metric learning in source and target domains, respectively, in order to allow \emph{adaptability to the target domain} while ensuring \emph{robustness to noisy pseudo-labels}. Indeed, shared low and mid-level parameters benefit from the source classification and triplet loss signal while high-level parameters of the target branch learn domain-specific features. Our method is simple enough to be easily combined with existing pseudo-labeling UDA approaches. We show experimentally that it is efficient and improves performance when the base method has no mechanism to deal with pseudo-label noise or for hard adaptation tasks. Our approach reaches state-of-the-art performance when evaluated on commonly used datasets, Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID, and outperforms the state of the art when targeting the bigger and more challenging dataset MSMT.
Road scenes analysis in adverse weather conditions by polarization-encoded images and adapted deep learning
Oct 02, 2019



Abstract:Object detection in road scenes is necessary to develop both autonomous vehicles and driving assistance systems. Even if deep neural networks for recognition task have shown great performances using conventional images, they fail to detect objects in road scenes in complex acquisition situations. In contrast, polarization images, characterizing the light wave, can robustly describe important physical properties of the object even under poor illumination or strong reflections. This paper shows how non-conventional polarimetric imaging modality overcomes the classical methods for object detection especially in adverse weather conditions. The efficiency of the proposed method is mostly due to the high power of the polarimetry to discriminate any object by its reflective properties and on the use of deep neural networks for object detection. Our goal by this work, is to prove that polarimetry brings a real added value compared with RGB images for object detection. Experimental results on our own dataset composed of road scene images taken during adverse weather conditions show that polarimetry together with deep learning can improve the state-of-the-art by about 20% to 50% on different detection tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge