Salar Mohtaj
Order in the Evaluation Court: A Critical Analysis of NLG Evaluation Trends
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Despite advances in Natural Language Generation (NLG), evaluation remains challenging. Although various new metrics and LLM-as-a-judge (LaaJ) methods are proposed, human judgment persists as the gold standard. To systematically review how NLG evaluation has evolved, we employ an automatic information extraction scheme to gather key information from NLG papers, focusing on different evaluation methods (metrics, LaaJ and human evaluation). With extracted metadata from 14,171 papers across four major conferences (ACL, EMNLP, NAACL, and INLG) over the past six years, we reveal several critical findings: (1) Task Divergence: While Dialogue Generation demonstrates a rapid shift toward LaaJ (>40% in 2025), Machine Translation remains locked into n-gram metrics, and Question Answering exhibits a substantial decline in the proportion of studies conducting human evaluation. (2) Metric Inertia: Despite the development of semantic metrics, general-purpose metrics (e.g., BLEU, ROUGE) continue to be widely used across tasks without empirical justification, often lacking the discriminative power to distinguish between specific quality criteria. (3) Human-LaaJ Divergence: Our association analysis challenges the assumption that LLMs act as mere proxies for humans; LaaJ and human evaluations prioritize very different signals, and explicit validation is scarce (<8% of papers comparing the two), with only moderate to low correlation. Based on these observations, we derive practical recommendations to improve the rigor of future NLG evaluation.
A Transfer Learning Based Model for Text Readability Assessment in German
Jul 13, 2022



Abstract:Text readability assessment has a wide range of applications for different target people, from language learners to people with disabilities. The fast pace of textual content production on the web makes it impossible to measure text complexity without the benefit of machine learning and natural language processing techniques. Although various research addressed the readability assessment of English text in recent years, there is still room for improvement of the models for other languages. In this paper, we proposed a new model for text complexity assessment for German text based on transfer learning. Our results show that the model outperforms more classical solutions based on linguistic features extraction from input text. The best model is based on the BERT pre-trained language model achieved the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 0.483.
PerPaDa: A Persian Paraphrase Dataset based on Implicit Crowdsourcing Data Collection
Jan 17, 2022



Abstract:In this paper we introduce PerPaDa, a Persian paraphrase dataset that is collected from users' input in a plagiarism detection system. As an implicit crowdsourcing experience, we have gathered a large collection of original and paraphrased sentences from Hamtajoo; a Persian plagiarism detection system, in which users try to conceal cases of text re-use in their documents by paraphrasing and re-submitting manuscripts for analysis. The compiled dataset contains 2446 instances of paraphrasing. In order to improve the overall quality of the collected data, some heuristics have been used to exclude sentences that don't meet the proposed criteria. The introduced corpus is much larger than the available datasets for the task of paraphrase identification in Persian. Moreover, there is less bias in the data compared to the similar datasets, since the users did not try some fixed predefined rules in order to generate similar texts to their original inputs.
MuLVE, A Multi-Language Vocabulary Evaluation Data Set
Jan 17, 2022



Abstract:Vocabulary learning is vital to foreign language learning. Correct and adequate feedback is essential to successful and satisfying vocabulary training. However, many vocabulary and language evaluation systems perform on simple rules and do not account for real-life user learning data. This work introduces Multi-Language Vocabulary Evaluation Data Set (MuLVE), a data set consisting of vocabulary cards and real-life user answers, labeled indicating whether the user answer is correct or incorrect. The data source is user learning data from the Phase6 vocabulary trainer. The data set contains vocabulary questions in German and English, Spanish, and French as target language and is available in four different variations regarding pre-processing and deduplication. We experiment to fine-tune pre-trained BERT language models on the downstream task of vocabulary evaluation with the proposed MuLVE data set. The results provide outstanding results of > 95.5 accuracy and F2-score. The data set is available on the European Language Grid.
A Feature Extraction based Model for Hate Speech Identification
Jan 11, 2022

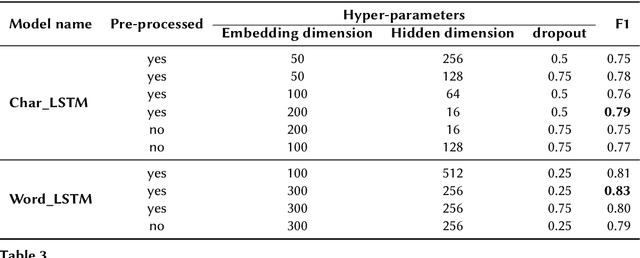
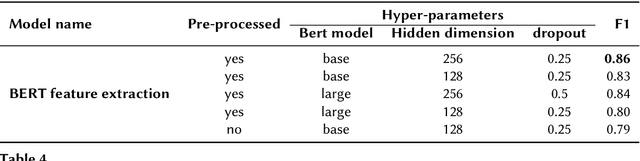
Abstract:The detection of hate speech online has become an important task, as offensive language such as hurtful, obscene and insulting content can harm marginalized people or groups. This paper presents TU Berlin team experiments and results on the task 1A and 1B of the shared task on hate speech and offensive content identification in Indo-European languages 2021. The success of different Natural Language Processing models is evaluated for the respective subtasks throughout the competition. We tested different models based on recurrent neural networks in word and character levels and transfer learning approaches based on Bert on the provided dataset by the competition. Among the tested models that have been used for the experiments, the transfer learning-based models achieved the best results in both subtasks.
Hamtajoo: A Persian Plagiarism Checker for Academic Manuscripts
Dec 27, 2021



Abstract:In recent years, due to the high availability of electronic documents through the Web, the plagiarism has become a serious challenge, especially among scholars. Various plagiarism detection systems have been developed to prevent text re-use and to confront plagiarism. Although it is almost easy to detect duplicate text in academic manuscripts, finding patterns of text re-use that has been semantically changed is of great importance. Another important issue is to deal with less resourced languages, which there are low volume of text for training purposes and also low performance in tools for NLP applications. In this paper, we introduce Hamtajoo, a Persian plagiarism detection system for academic manuscripts. Moreover, we describe the overall structure of the system along with the algorithms used in each stage. In order to evaluate the performance of the proposed system, we used a plagiarism detection corpus comply with the PAN standards.
Untrue.News: A New Search Engine For Fake Stories
Feb 16, 2020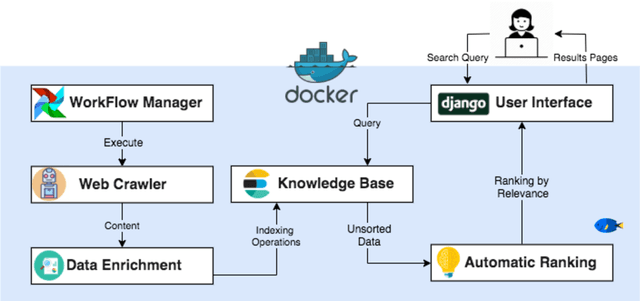

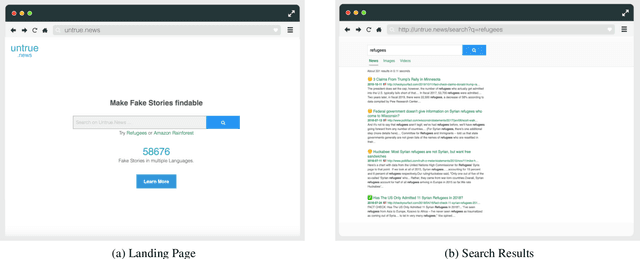
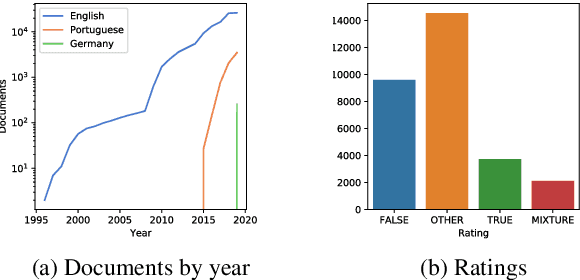
Abstract:In this paper, we demonstrate Untrue News, a new search engine for fake stories. Untrue News is easy to use and offers useful features such as: a) a multi-language option combining fake stories from different countries and languages around the same subject or person; b) an user privacy protector, avoiding the filter bubble by employing a bias-free ranking scheme; and c) a collaborative platform that fosters the development of new tools for fighting disinformation. Untrue News relies on Elasticsearch, a new scalable analytic search engine based on the Lucene library that provides near real-time results. We demonstrate two key scenarios: the first related to a politician - looking how the categories are shown for different types of fake stories - and a second related to a refugee - showing the multilingual tool. A prototype of Untrue News is accessible via http://untrue.news
Subjective Assessment of Text Complexity: A Dataset for German Language
Apr 16, 2019

Abstract:This paper presents TextComplexityDE, a dataset consisting of 1000 sentences in German language taken from 23 Wikipedia articles in 3 different article-genres to be used for developing text-complexity predictor models and automatic text simplification in German language. The dataset includes subjective assessment of different text-complexity aspects provided by German learners in level A and B. In addition, it contains manual simplification of 250 of those sentences provided by native speakers and subjective assessment of the simplified sentences by participants from the target group. The subjective ratings were collected using both laboratory studies and crowdsourcing approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge