Vinicius Woloszyn
How Vulnerable Are Automatic Fake News Detection Methods to Adversarial Attacks?
Jul 16, 2021
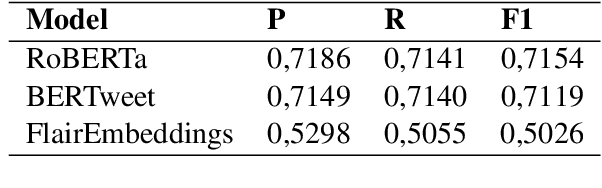
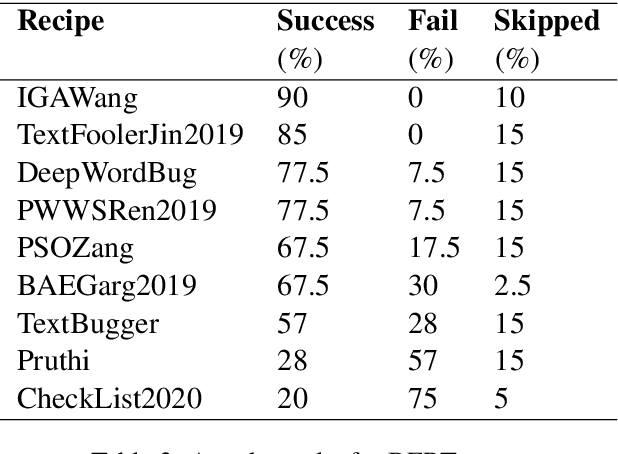
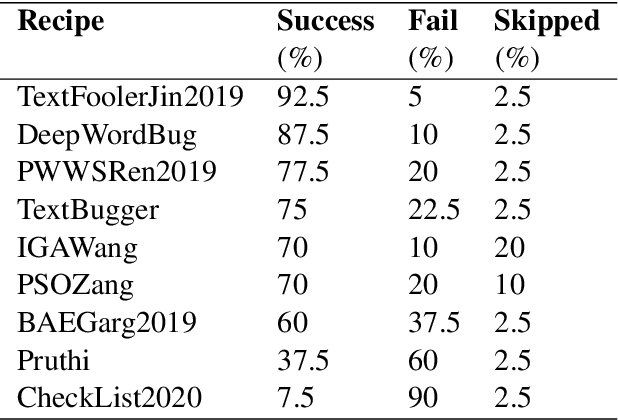
Abstract:As the spread of false information on the internet has increased dramatically in recent years, more and more attention is being paid to automated fake news detection. Some fake news detection methods are already quite successful. Nevertheless, there are still many vulnerabilities in the detection algorithms. The reason for this is that fake news publishers can structure and formulate their texts in such a way that a detection algorithm does not expose this text as fake news. This paper shows that it is possible to automatically attack state-of-the-art models that have been trained to detect Fake News, making these vulnerable. For this purpose, corresponding models were first trained based on a dataset. Then, using Text-Attack, an attempt was made to manipulate the trained models in such a way that previously correctly identified fake news was classified as true news. The results show that it is possible to automatically bypass Fake News detection mechanisms, leading to implications concerning existing policy initiatives.
BOPI: A Programming Interface For Reuse Of Research Data Available On DSpace Repositories
Mar 17, 2021
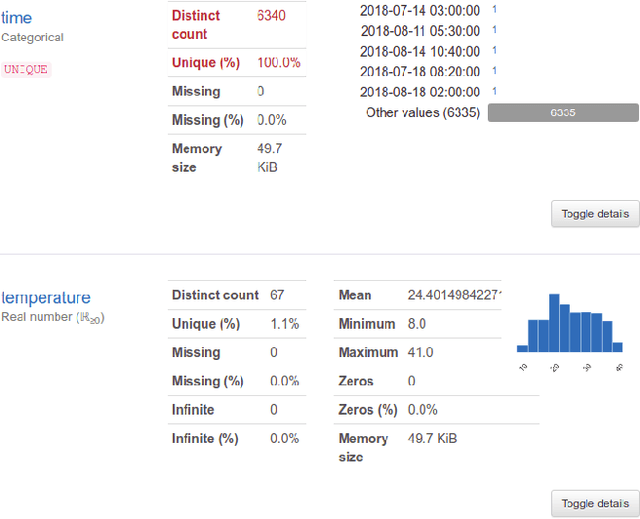
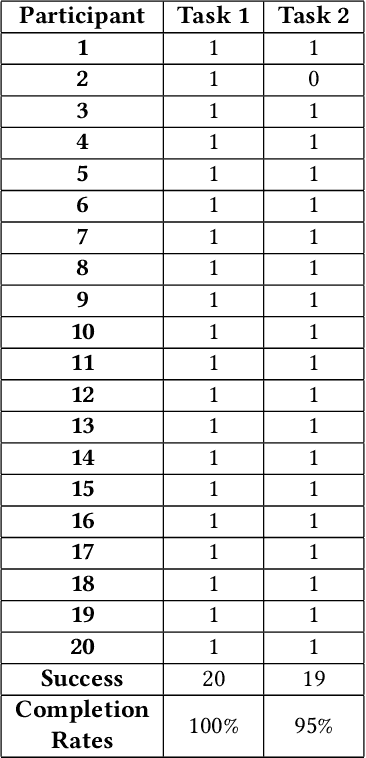
Abstract:A recent study showed that more than 70% of researchers fail to reproduce their peers's experiments and more than half fail to reproduce their own experiments. Obviously, from a perspective of scientific quality this is a more than unsatisfying numbers. One approach to mitigate this flaw lies in the transparent provision of relevant research data to increase the base of available material to evaluate and possibly reconduct experiments. However, such data needs to be presented and accessed in a findable and purposefully usable way. In this work, we report the development of a programming interface to enhance findability and accessibility of research data (available in DSpace systems) and hence reproducibility of scientific experiments with data. This interface allows researchers to (i) find research data in multiples languages trough automatic translation of metadata; (ii) display a preview of data without download it beforehand; (iii) provide a detailed statistics of the data with interactive graphs for quality assessment; (iv) automatic download of data directly from Python-based experiments. Usability tests revealed that this interface improves the effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction during the reuse of research data.
Untrue.News: A New Search Engine For Fake Stories
Feb 16, 2020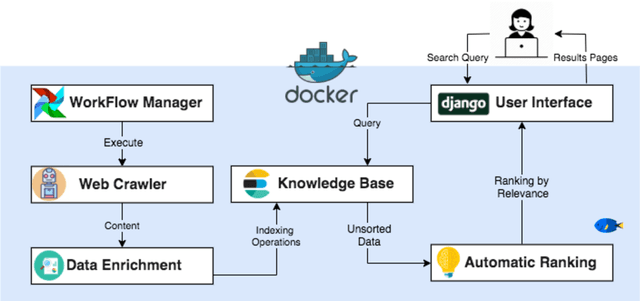

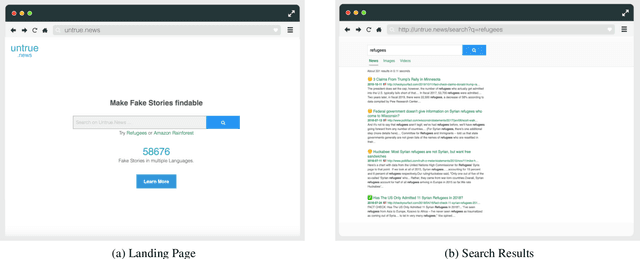
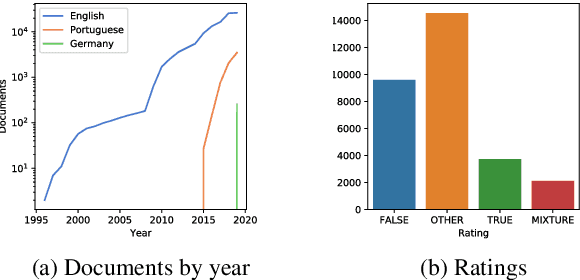
Abstract:In this paper, we demonstrate Untrue News, a new search engine for fake stories. Untrue News is easy to use and offers useful features such as: a) a multi-language option combining fake stories from different countries and languages around the same subject or person; b) an user privacy protector, avoiding the filter bubble by employing a bias-free ranking scheme; and c) a collaborative platform that fosters the development of new tools for fighting disinformation. Untrue News relies on Elasticsearch, a new scalable analytic search engine based on the Lucene library that provides near real-time results. We demonstrate two key scenarios: the first related to a politician - looking how the categories are shown for different types of fake stories - and a second related to a refugee - showing the multilingual tool. A prototype of Untrue News is accessible via http://untrue.news
Is there Gender bias and stereotype in Portuguese Word Embeddings?
Oct 10, 2018

Abstract:In this work, we propose an analysis of the presence of gender bias associated with professions in Portuguese word embeddings. The objective of this work is to study gender implications related to stereotyped professions for women and men in the context of the Portuguese language.
Modeling, comprehending and summarizing textual content by graphs
Jul 01, 2018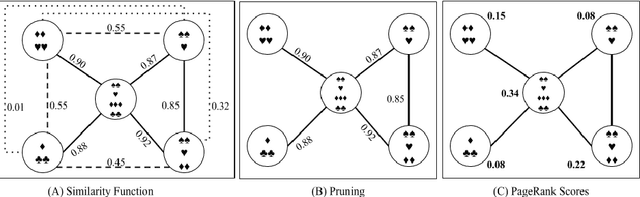

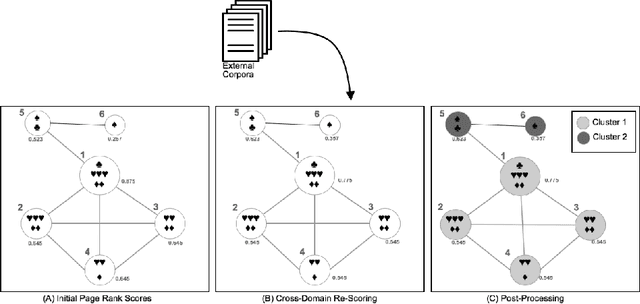
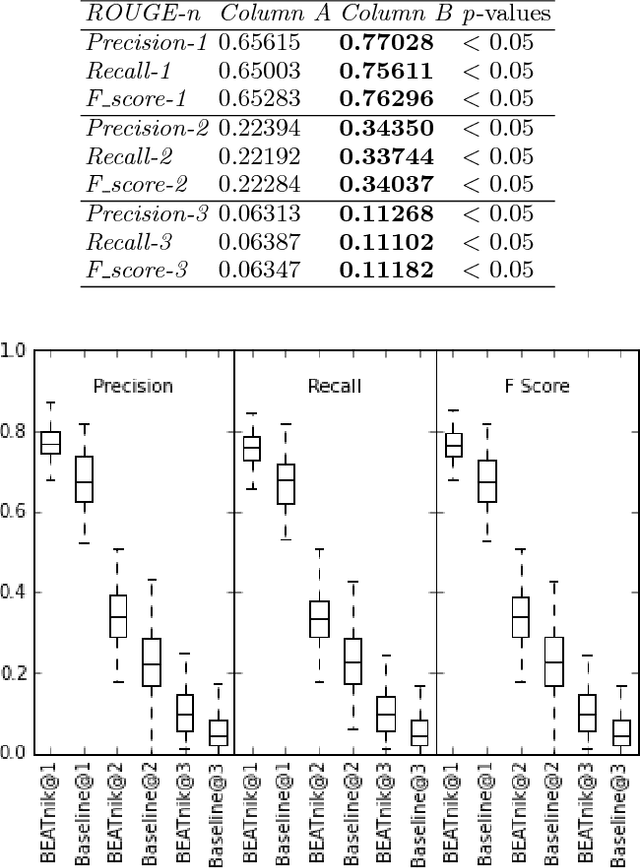
Abstract:Automatic Text Summarization strategies have been successfully employed to digest text collections and extract its essential content. Usually, summaries are generated using textual corpora that belongs to the same domain area where the summary will be used. Nonetheless, there are special cases where it is not found enough textual sources, and one possible alternative is to generate a summary from a different domain. One manner to summarize texts consists of using a graph model. This model allows giving more importance to words corresponding to the main concepts from the target domain found in the summarized text. This gives the reader an overview of the main text concepts as well as their relationships. However, this kind of summarization presents a significant number of repeated terms when compared to human-generated summaries. In this paper, we present an approach to produce graph-model extractive summaries of texts, meeting the target domain exigences and treating the terms repetition problem. To evaluate the proposition, we performed a series of experiments showing that the proposed approach statistically improves the performance of a model based on Graph Centrality, achieving better coverage, accuracy, and recall.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge