Sai Meher Karthik Duddu
Gemini Embedding: Generalizable Embeddings from Gemini
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:In this report, we introduce Gemini Embedding, a state-of-the-art embedding model leveraging the power of Gemini, Google's most capable large language model. Capitalizing on Gemini's inherent multilingual and code understanding capabilities, Gemini Embedding produces highly generalizable embeddings for text spanning numerous languages and textual modalities. The representations generated by Gemini Embedding can be precomputed and applied to a variety of downstream tasks including classification, similarity, clustering, ranking, and retrieval. Evaluated on the Massive Multilingual Text Embedding Benchmark (MMTEB), which includes over one hundred tasks across 250+ languages, Gemini Embedding substantially outperforms prior state-of-the-art models, demonstrating considerable improvements in embedding quality. Achieving state-of-the-art performance across MMTEB's multilingual, English, and code benchmarks, our unified model demonstrates strong capabilities across a broad selection of tasks and surpasses specialized domain-specific models.
Gecko: Versatile Text Embeddings Distilled from Large Language Models
Mar 29, 2024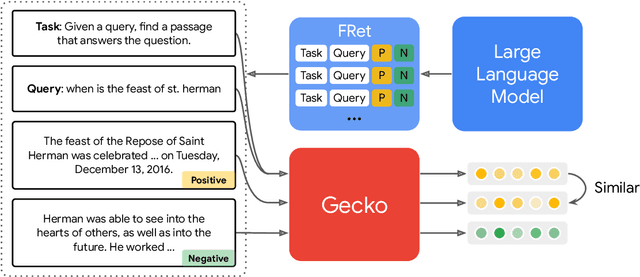
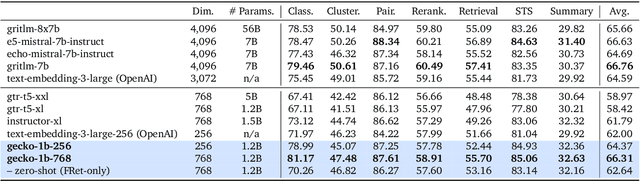

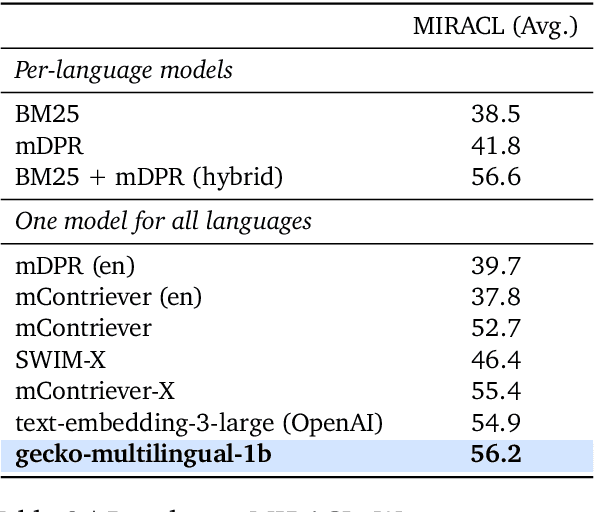
Abstract:We present Gecko, a compact and versatile text embedding model. Gecko achieves strong retrieval performance by leveraging a key idea: distilling knowledge from large language models (LLMs) into a retriever. Our two-step distillation process begins with generating diverse, synthetic paired data using an LLM. Next, we further refine the data quality by retrieving a set of candidate passages for each query, and relabeling the positive and hard negative passages using the same LLM. The effectiveness of our approach is demonstrated by the compactness of the Gecko. On the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB), Gecko with 256 embedding dimensions outperforms all existing entries with 768 embedding size. Gecko with 768 embedding dimensions achieves an average score of 66.31, competing with 7x larger models and 5x higher dimensional embeddings.
Rethinking the Role of Token Retrieval in Multi-Vector Retrieval
Apr 04, 2023Abstract:Multi-vector retrieval models such as ColBERT [Khattab and Zaharia, 2020] allow token-level interactions between queries and documents, and hence achieve state of the art on many information retrieval benchmarks. However, their non-linear scoring function cannot be scaled to millions of documents, necessitating a three-stage process for inference: retrieving initial candidates via token retrieval, accessing all token vectors, and scoring the initial candidate documents. The non-linear scoring function is applied over all token vectors of each candidate document, making the inference process complicated and slow. In this paper, we aim to simplify the multi-vector retrieval by rethinking the role of token retrieval. We present XTR, ConteXtualized Token Retriever, which introduces a simple, yet novel, objective function that encourages the model to retrieve the most important document tokens first. The improvement to token retrieval allows XTR to rank candidates only using the retrieved tokens rather than all tokens in the document, and enables a newly designed scoring stage that is two-to-three orders of magnitude cheaper than that of ColBERT. On the popular BEIR benchmark, XTR advances the state-of-the-art by 2.8 nDCG@10 without any distillation. Detailed analysis confirms our decision to revisit the token retrieval stage, as XTR demonstrates much better recall of the token retrieval stage compared to ColBERT.
Multi-Vector Retrieval as Sparse Alignment
Nov 02, 2022



Abstract:Multi-vector retrieval models improve over single-vector dual encoders on many information retrieval tasks. In this paper, we cast the multi-vector retrieval problem as sparse alignment between query and document tokens. We propose AligneR, a novel multi-vector retrieval model that learns sparsified pairwise alignments between query and document tokens (e.g. `dog' vs. `puppy') and per-token unary saliences reflecting their relative importance for retrieval. We show that controlling the sparsity of pairwise token alignments often brings significant performance gains. While most factoid questions focusing on a specific part of a document require a smaller number of alignments, others requiring a broader understanding of a document favor a larger number of alignments. Unary saliences, on the other hand, decide whether a token ever needs to be aligned with others for retrieval (e.g. `kind' from `kind of currency is used in new zealand}'). With sparsified unary saliences, we are able to prune a large number of query and document token vectors and improve the efficiency of multi-vector retrieval. We learn the sparse unary saliences with entropy-regularized linear programming, which outperforms other methods to achieve sparsity. In a zero-shot setting, AligneR scores 51.1 points nDCG@10, achieving a new retriever-only state-of-the-art on 13 tasks in the BEIR benchmark. In addition, adapting pairwise alignments with a few examples (<= 8) further improves the performance up to 15.7 points nDCG@10 for argument retrieval tasks. The unary saliences of AligneR helps us to keep only 20% of the document token representations with minimal performance loss. We further show that our model often produces interpretable alignments and significantly improves its performance when initialized from larger language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge