Rajvi Kapadia
Minimal Evidence Group Identification for Claim Verification
Apr 24, 2024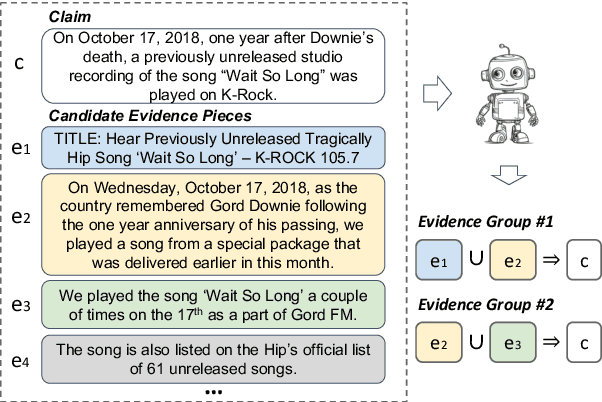
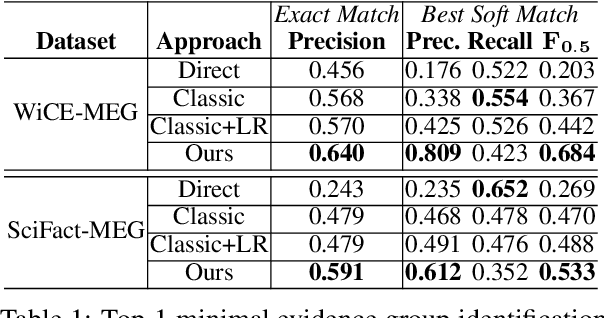
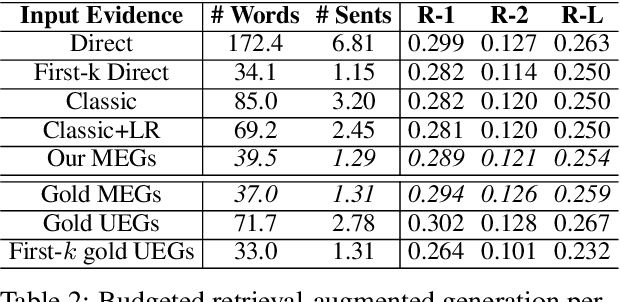
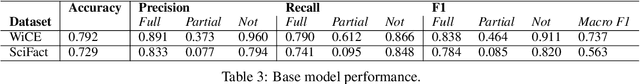
Abstract:Claim verification in real-world settings (e.g. against a large collection of candidate evidences retrieved from the web) typically requires identifying and aggregating a complete set of evidence pieces that collectively provide full support to the claim. The problem becomes particularly challenging when there exists distinct sets of evidence that could be used to verify the claim from different perspectives. In this paper, we formally define and study the problem of identifying such minimal evidence groups (MEGs) for claim verification. We show that MEG identification can be reduced from Set Cover problem, based on entailment inference of whether a given evidence group provides full/partial support to a claim. Our proposed approach achieves 18.4% and 34.8% absolute improvements on the WiCE and SciFact datasets over LLM prompting. Finally, we demonstrate the benefits of MEGs in downstream applications such as claim generation.
Gecko: Versatile Text Embeddings Distilled from Large Language Models
Mar 29, 2024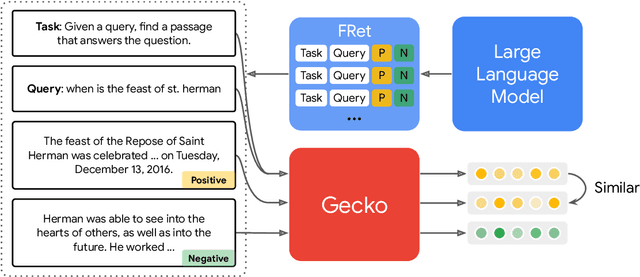
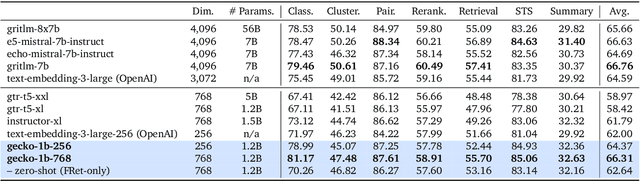

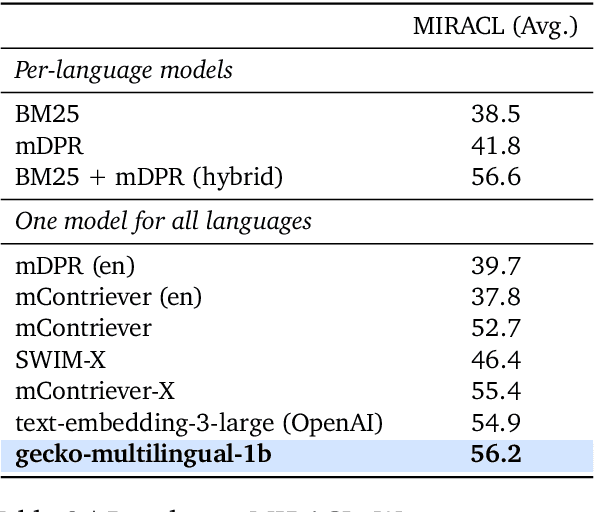
Abstract:We present Gecko, a compact and versatile text embedding model. Gecko achieves strong retrieval performance by leveraging a key idea: distilling knowledge from large language models (LLMs) into a retriever. Our two-step distillation process begins with generating diverse, synthetic paired data using an LLM. Next, we further refine the data quality by retrieving a set of candidate passages for each query, and relabeling the positive and hard negative passages using the same LLM. The effectiveness of our approach is demonstrated by the compactness of the Gecko. On the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB), Gecko with 256 embedding dimensions outperforms all existing entries with 768 embedding size. Gecko with 768 embedding dimensions achieves an average score of 66.31, competing with 7x larger models and 5x higher dimensional embeddings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge