Saheb Chhabra
Class Equilibrium using Coulomb's Law
Apr 25, 2021
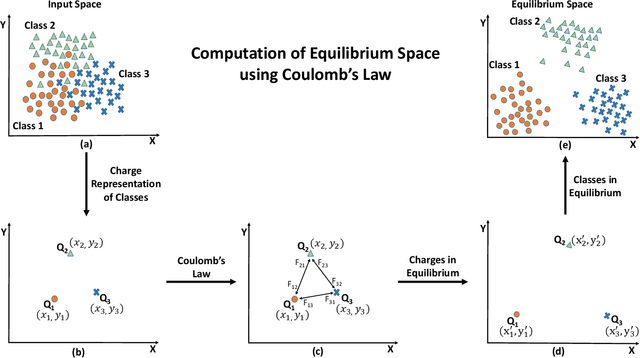

Abstract:Projection algorithms learn a transformation function to project the data from input space to the feature space, with the objective of increasing the inter-class distance. However, increasing the inter-class distance can affect the intra-class distance. Maintaining an optimal inter-class separation among the classes without affecting the intra-class distance of the data distribution is a challenging task. In this paper, inspired by the Coulomb's law of Electrostatics, we propose a new algorithm to compute the equilibrium space of any data distribution where the separation among the classes is optimal. The algorithm further learns the transformation between the input space and equilibrium space to perform classification in the equilibrium space. The performance of the proposed algorithm is evaluated on four publicly available datasets at three different resolutions. It is observed that the proposed algorithm performs well for low-resolution images.
Attack Agnostic Adversarial Defense via Visual Imperceptible Bound
Oct 25, 2020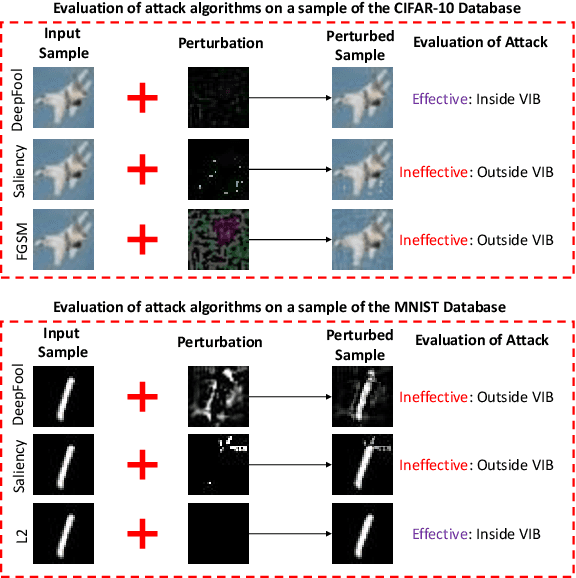
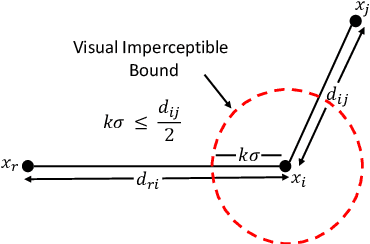
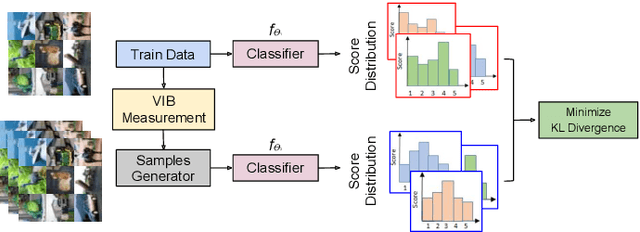
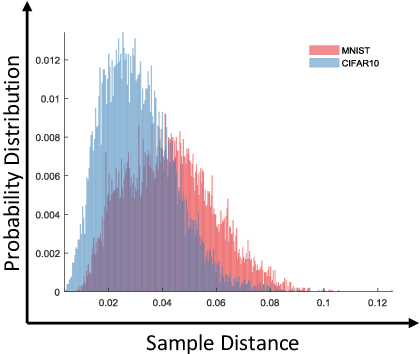
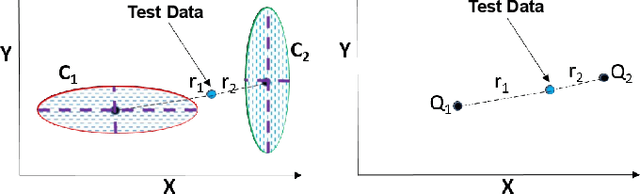
Abstract:The high susceptibility of deep learning algorithms against structured and unstructured perturbations has motivated the development of efficient adversarial defense algorithms. However, the lack of generalizability of existing defense algorithms and the high variability in the performance of the attack algorithms for different databases raises several questions on the effectiveness of the defense algorithms. In this research, we aim to design a defense model that is robust within a certain bound against both seen and unseen adversarial attacks. This bound is related to the visual appearance of an image, and we termed it as \textit{Visual Imperceptible Bound (VIB)}. To compute this bound, we propose a novel method that uses the database characteristics. The VIB is further used to measure the effectiveness of attack algorithms. The performance of the proposed defense model is evaluated on the MNIST, CIFAR-10, and Tiny ImageNet databases on multiple attacks that include C\&W ($l_2$) and DeepFool. The proposed defense model is not only able to increase the robustness against several attacks but also retain or improve the classification accuracy on an original clean test set. The proposed algorithm is attack agnostic, i.e. it does not require any knowledge of the attack algorithm.
Unravelling Small Sample Size Problems in the Deep Learning World
Aug 08, 2020
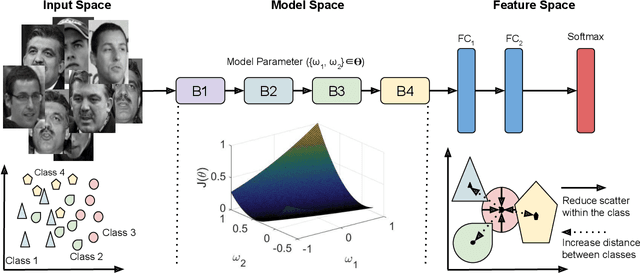
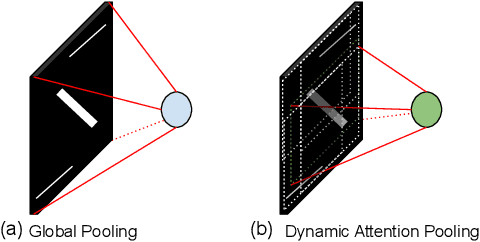
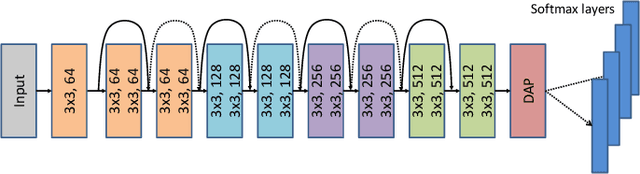
Abstract:The growth and success of deep learning approaches can be attributed to two major factors: availability of hardware resources and availability of large number of training samples. For problems with large training databases, deep learning models have achieved superlative performances. However, there are a lot of \textit{small sample size or $S^3$} problems for which it is not feasible to collect large training databases. It has been observed that deep learning models do not generalize well on $S^3$ problems and specialized solutions are required. In this paper, we first present a review of deep learning algorithms for small sample size problems in which the algorithms are segregated according to the space in which they operate, i.e. input space, model space, and feature space. Secondly, we present Dynamic Attention Pooling approach which focuses on extracting global information from the most discriminative sub-part of the feature map. The performance of the proposed dynamic attention pooling is analyzed with state-of-the-art ResNet model on relatively small publicly available datasets such as SVHN, C10, C100, and TinyImageNet.
Subclass Contrastive Loss for Injured Face Recognition
Aug 05, 2020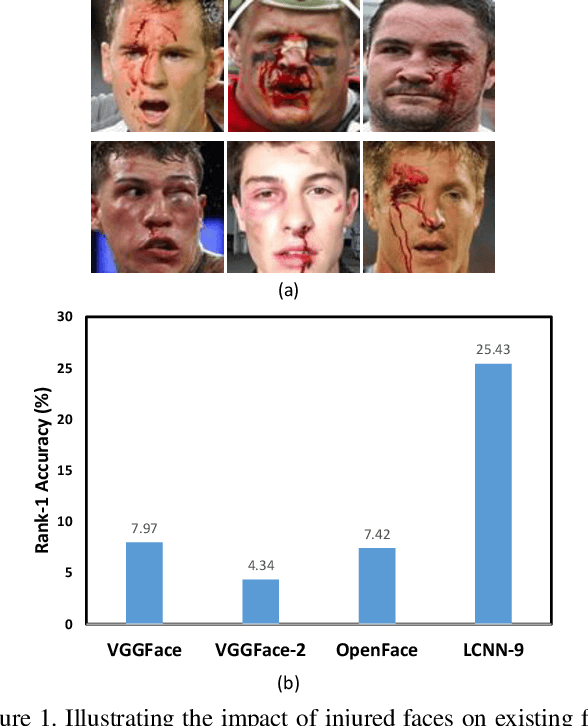
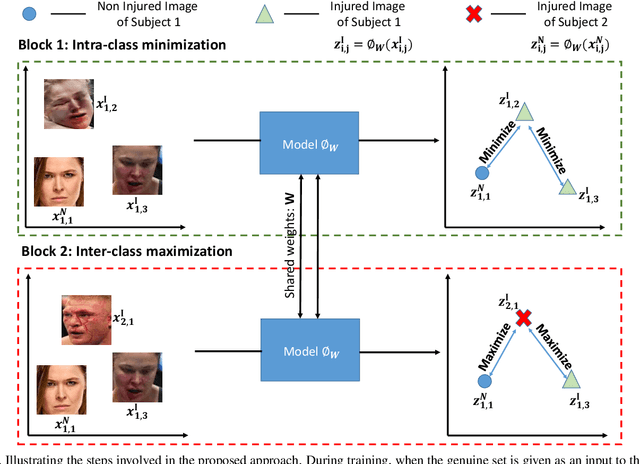
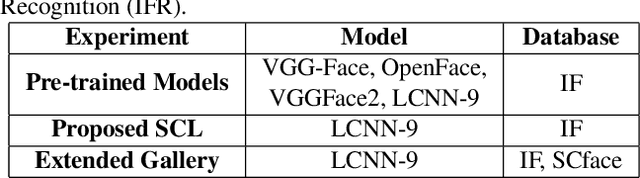
Abstract:Deaths and injuries are common in road accidents, violence, and natural disaster. In such cases, one of the main tasks of responders is to retrieve the identity of the victims to reunite families and ensure proper identification of deceased/ injured individuals. Apart from this, identification of unidentified dead bodies due to violence and accidents is crucial for the police investigation. In the absence of identification cards, current practices for this task include DNA profiling and dental profiling. Face is one of the most commonly used and widely accepted biometric modalities for recognition. However, face recognition is challenging in the presence of facial injuries such as swelling, bruises, blood clots, laceration, and avulsion which affect the features used in recognition. In this paper, for the first time, we address the problem of injured face recognition and propose a novel Subclass Contrastive Loss (SCL) for this task. A novel database, termed as Injured Face (IF) database, is also created to instigate research in this direction. Experimental analysis shows that the proposed loss function surpasses existing algorithm for injured face recognition.
Multi-Task Driven Explainable Diagnosis of COVID-19 using Chest X-ray Images
Aug 03, 2020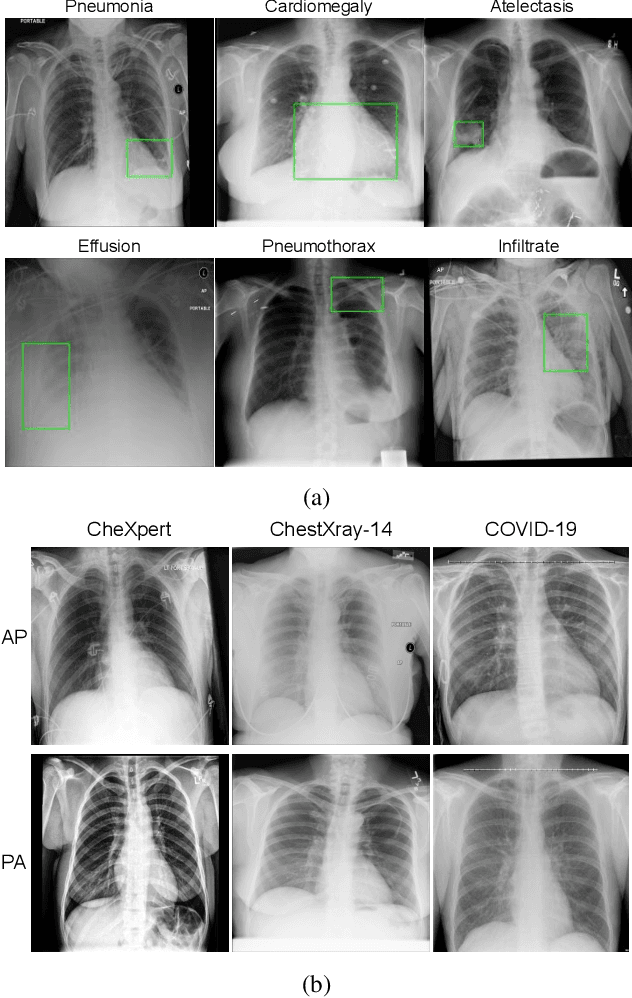
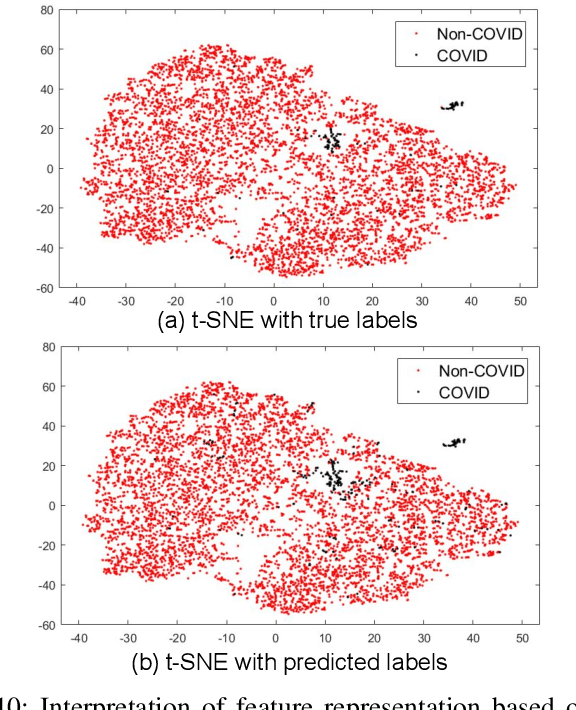
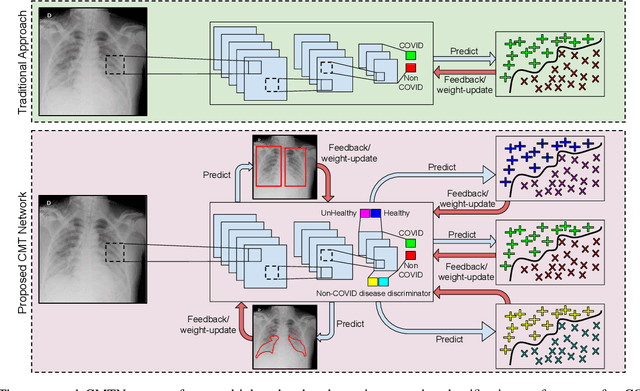
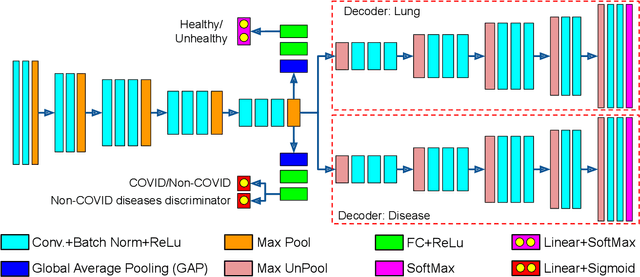
Abstract:With increasing number of COVID-19 cases globally, all the countries are ramping up the testing numbers. While the RT-PCR kits are available in sufficient quantity in several countries, others are facing challenges with limited availability of testing kits and processing centers in remote areas. This has motivated researchers to find alternate methods of testing which are reliable, easily accessible and faster. Chest X-Ray is one of the modalities that is gaining acceptance as a screening modality. Towards this direction, the paper has two primary contributions. Firstly, we present the COVID-19 Multi-Task Network which is an automated end-to-end network for COVID-19 screening. The proposed network not only predicts whether the CXR has COVID-19 features present or not, it also performs semantic segmentation of the regions of interest to make the model explainable. Secondly, with the help of medical professionals, we manually annotate the lung regions of 9000 frontal chest radiographs taken from ChestXray-14, CheXpert and a consolidated COVID-19 dataset. Further, 200 chest radiographs pertaining to COVID-19 patients are also annotated for semantic segmentation. This database will be released to the research community.
Data Fine-tuning
Dec 10, 2018
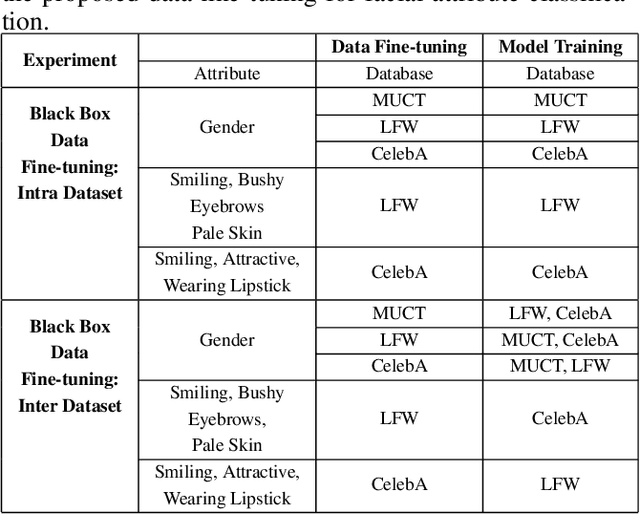
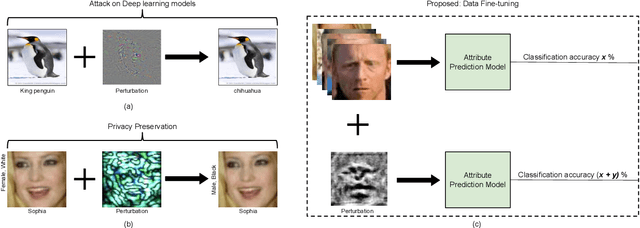

Abstract:In real-world applications, commercial off-the-shelf systems are utilized for performing automated facial analysis including face recognition, emotion recognition, and attribute prediction. However, a majority of these commercial systems act as black boxes due to the inaccessibility of the model parameters which makes it challenging to fine-tune the models for specific applications. Stimulated by the advances in adversarial perturbations, this research proposes the concept of Data Fine-tuning to improve the classification accuracy of a given model without changing the parameters of the model. This is accomplished by modeling it as data (image) perturbation problem. A small amount of "noise" is added to the input with the objective of minimizing the classification loss without affecting the (visual) appearance. Experiments performed on three publicly available datasets LFW, CelebA, and MUCT, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed concept.
Anonymizing k-Facial Attributes via Adversarial Perturbations
Sep 28, 2018



Abstract:A face image not only provides details about the identity of a subject but also reveals several attributes such as gender, race, sexual orientation, and age. Advancements in machine learning algorithms and popularity of sharing images on the World Wide Web, including social media websites, have increased the scope of data analytics and information profiling from photo collections. This poses a serious privacy threat for individuals who do not want to be profiled. This research presents a novel algorithm for anonymizing selective attributes which an individual does not want to share without affecting the visual quality of images. Using the proposed algorithm, a user can select single or multiple attributes to be surpassed while preserving identity information and visual content. The proposed adversarial perturbation based algorithm embeds imperceptible noise in an image such that attribute prediction algorithm for the selected attribute yields incorrect classification result, thereby preserving the information according to user's choice. Experiments on three popular databases i.e. MUCT, LFWcrop, and CelebA show that the proposed algorithm not only anonymizes k-attributes, but also preserves image quality and identity information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge