Ryan Stonebraker
An Addendum to NeBula: Towards Extending TEAM CoSTAR's Solution to Larger Scale Environments
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an appendix to the original NeBula autonomy solution developed by the TEAM CoSTAR (Collaborative SubTerranean Autonomous Robots), participating in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge. Specifically, this paper presents extensions to NeBula's hardware, software, and algorithmic components that focus on increasing the range and scale of the exploration environment. From the algorithmic perspective, we discuss the following extensions to the original NeBula framework: (i) large-scale geometric and semantic environment mapping; (ii) an adaptive positioning system; (iii) probabilistic traversability analysis and local planning; (iv) large-scale POMDP-based global motion planning and exploration behavior; (v) large-scale networking and decentralized reasoning; (vi) communication-aware mission planning; and (vii) multi-modal ground-aerial exploration solutions. We demonstrate the application and deployment of the presented systems and solutions in various large-scale underground environments, including limestone mine exploration scenarios as well as deployment in the DARPA Subterranean challenge.
Copiloting Autonomous Multi-Robot Missions: A Game-inspired Supervisory Control Interface
Apr 13, 2022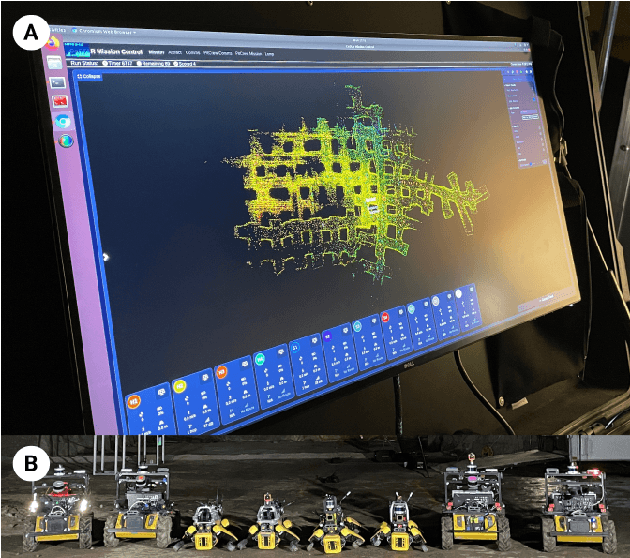
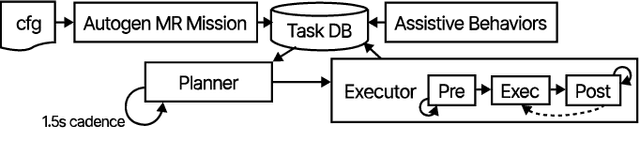
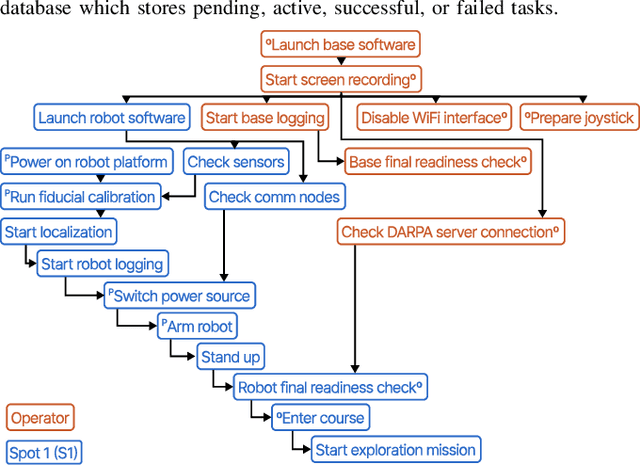
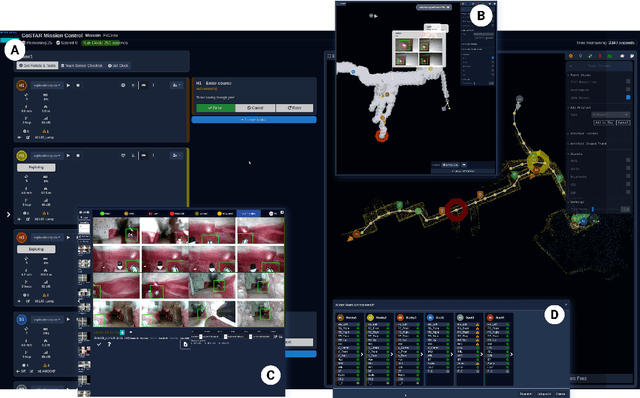
Abstract:Real-world deployment of new technology and capabilities can be daunting. The recent DARPA Subterranean (SubT) Challenge, for instance, aimed at the advancement of robotic platforms and autonomy capabilities in three one-year development pushes. While multi-agent systems are traditionally deployed in controlled and structured environments that allow for controlled testing (e.g., warehouses), the SubT challenge targeted various types of unknown underground environments that imposed the risk of robot loss in the case of failure. In this work, we introduce a video game-inspired interface, an autonomous mission assistant, and test and deploy these using a heterogeneous multi-agent system in challenging environments. This work leads to improved human-supervisory control for a multi-agent system reducing overhead from application switching, task planning, execution, and verification while increasing available exploration time with this human-autonomy teaming platform.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge