Rongzhen Li
MCAM: Multimodal Causal Analysis Model for Ego-Vehicle-Level Driving Video Understanding
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:Accurate driving behavior recognition and reasoning are critical for autonomous driving video understanding. However, existing methods often tend to dig out the shallow causal, fail to address spurious correlations across modalities, and ignore the ego-vehicle level causality modeling. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel Multimodal Causal Analysis Model (MCAM) that constructs latent causal structures between visual and language modalities. Firstly, we design a multi-level feature extractor to capture long-range dependencies. Secondly, we design a causal analysis module that dynamically models driving scenarios using a directed acyclic graph (DAG) of driving states. Thirdly, we utilize a vision-language transformer to align critical visual features with their corresponding linguistic expressions. Extensive experiments on the BDD-X, and CoVLA datasets demonstrate that MCAM achieves SOTA performance in visual-language causal relationship learning. Furthermore, the model exhibits superior capability in capturing causal characteristics within video sequences, showcasing its effectiveness for autonomous driving applications. The code is available at https://github.com/SixCorePeach/MCAM.
Can LLMs like GPT-4 outperform traditional AI tools in dementia diagnosis? Maybe, but not today
Jun 02, 2023



Abstract:Recent investigations show that large language models (LLMs), specifically GPT-4, not only have remarkable capabilities in common Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks but also exhibit human-level performance on various professional and academic benchmarks. However, whether GPT-4 can be directly used in practical applications and replace traditional artificial intelligence (AI) tools in specialized domains requires further experimental validation. In this paper, we explore the potential of LLMs such as GPT-4 to outperform traditional AI tools in dementia diagnosis. Comprehensive comparisons between GPT-4 and traditional AI tools are conducted to examine their diagnostic accuracy in a clinical setting. Experimental results on two real clinical datasets show that, although LLMs like GPT-4 demonstrate potential for future advancements in dementia diagnosis, they currently do not surpass the performance of traditional AI tools. The interpretability and faithfulness of GPT-4 are also evaluated by comparison with real doctors. We discuss the limitations of GPT-4 in its current state and propose future research directions to enhance GPT-4 in dementia diagnosis.
Sufficient Reasons for A Zero-Day Intrusion Detection Artificial Immune System
Apr 05, 2022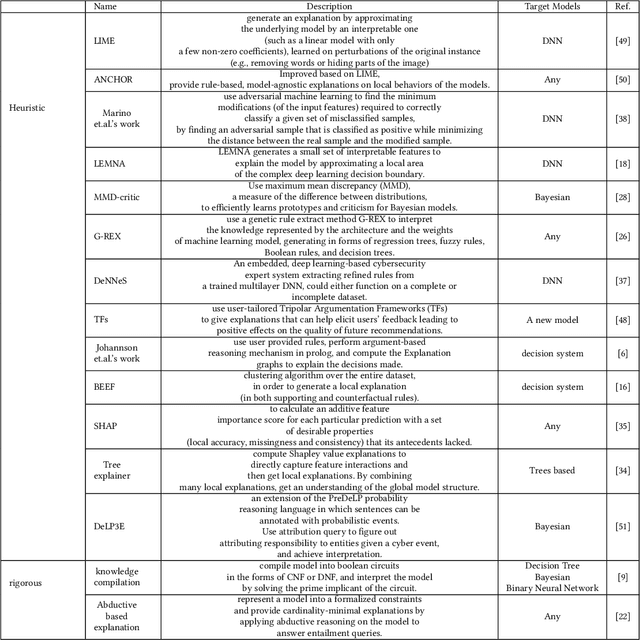
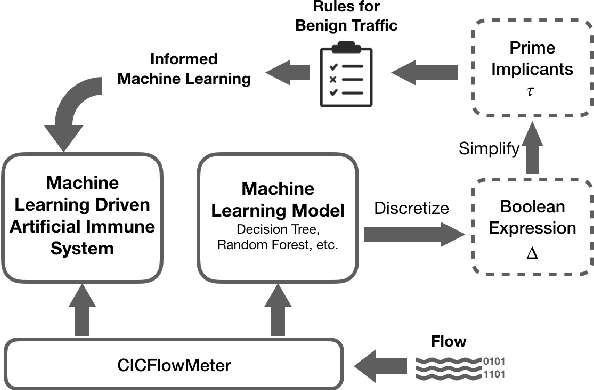
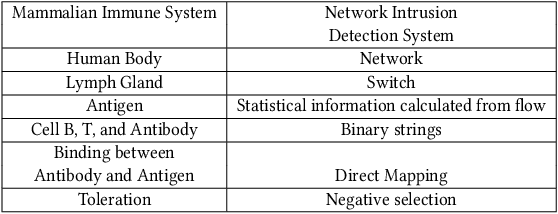

Abstract:The Internet is the most complex machine humankind has ever built, and how to defense it from intrusions is even more complex. With the ever increasing of new intrusions, intrusion detection task rely on Artificial Intelligence more and more. Interpretability and transparency of the machine learning model is the foundation of trust in AI-driven intrusion detection results. Current interpretation Artificial Intelligence technologies in intrusion detection are heuristic, which is neither accurate nor sufficient. This paper proposed a rigorous interpretable Artificial Intelligence driven intrusion detection approach, based on artificial immune system. Details of rigorous interpretation calculation process for a decision tree model is presented. Prime implicant explanation for benign traffic flow are given in detail as rule for negative selection of the cyber immune system. Experiments are carried out in real-life traffic.
CorefDRE: Document-level Relation Extraction with coreference resolution
Feb 22, 2022

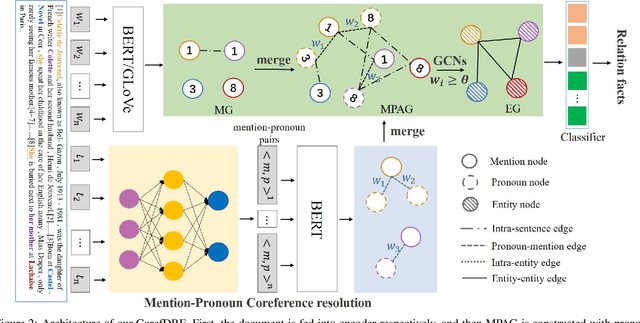
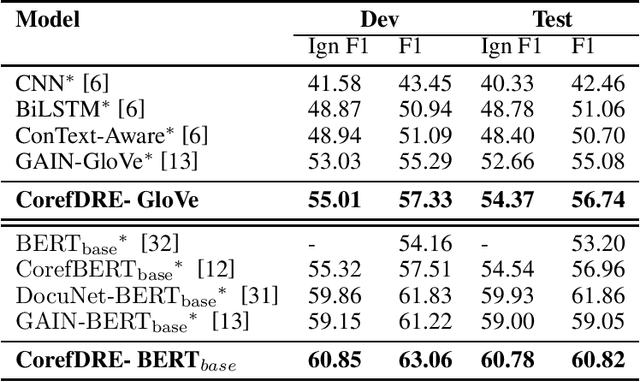
Abstract:Document-level relation extraction is to extract relation facts from a document consisting of multiple sentences, in which pronoun crossed sentences are a ubiquitous phenomenon against a single sentence. However, most of the previous works focus more on mentions coreference resolution except for pronouns, and rarely pay attention to mention-pronoun coreference and capturing the relations. To represent multi-sentence features by pronouns, we imitate the reading process of humans by leveraging coreference information when dynamically constructing a heterogeneous graph to enhance semantic information. Since the pronoun is notoriously ambiguous in the graph, a mention-pronoun coreference resolution is introduced to calculate the affinity between pronouns and corresponding mentions, and the noise suppression mechanism is proposed to reduce the noise caused by pronouns. Experiments on the public dataset, DocRED, DialogRE and MPDD, show that Coref-aware Doc-level Relation Extraction based on Graph Inference Network outperforms the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge