Roberto-Rafael Maura-Rivero
Jackpot! Alignment as a Maximal Lottery
Jan 31, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), the standard for aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human values, is known to fail to satisfy properties that are intuitively desirable, such as respecting the preferences of the majority \cite{ge2024axioms}. To overcome these issues, we propose the use of a probabilistic Social Choice rule called \emph{maximal lotteries} as a replacement for RLHF. We show that a family of alignment techniques, namely Nash Learning from Human Feedback (NLHF) \cite{munos2023nash} and variants, approximate maximal lottery outcomes and thus inherit its beneficial properties. We confirm experimentally that our proposed methodology handles situations that arise when working with preferences more robustly than standard RLHF, including supporting the preferences of the majority, providing principled ways of handling non-transitivities in the preference data, and robustness to irrelevant alternatives. This results in systems that better incorporate human values and respect human intentions.
Utility-inspired Reward Transformations Improve Reinforcement Learning Training of Language Models
Jan 08, 2025Abstract:Current methods that train large language models (LLMs) with reinforcement learning feedback, often resort to averaging outputs of multiple rewards functions during training. This overlooks crucial aspects of individual reward dimensions and inter-reward dependencies that can lead to sub-optimal outcomes in generations. In this work, we show how linear aggregation of rewards exhibits some vulnerabilities that can lead to undesired properties of generated text. We then propose a transformation of reward functions inspired by economic theory of utility functions (specifically Inada conditions), that enhances sensitivity to low reward values while diminishing sensitivity to already high values. We compare our approach to the existing baseline methods that linearly aggregate rewards and show how the Inada-inspired reward feedback is superior to traditional weighted averaging. We quantitatively and qualitatively analyse the difference in the methods, and see that models trained with Inada-transformations score as more helpful while being less harmful.
Soft Condorcet Optimization for Ranking of General Agents
Nov 04, 2024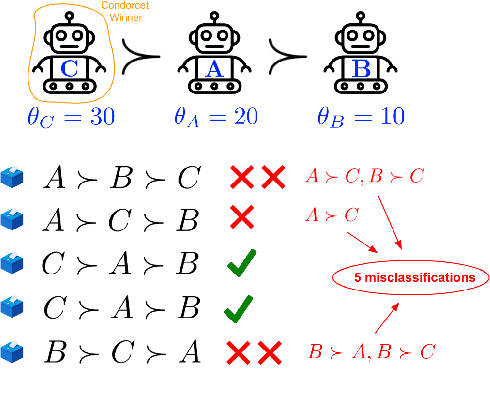
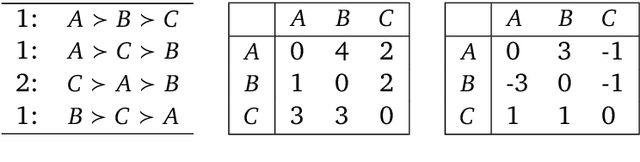
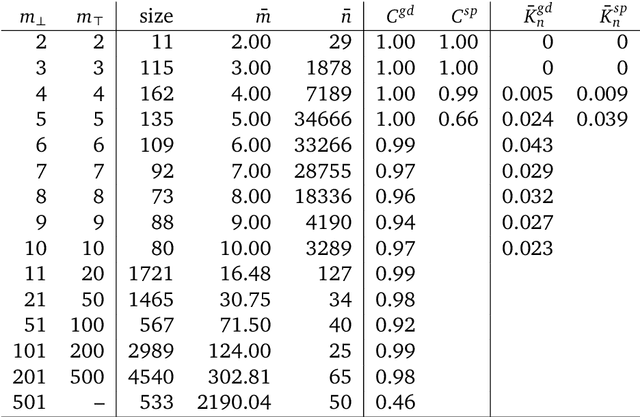
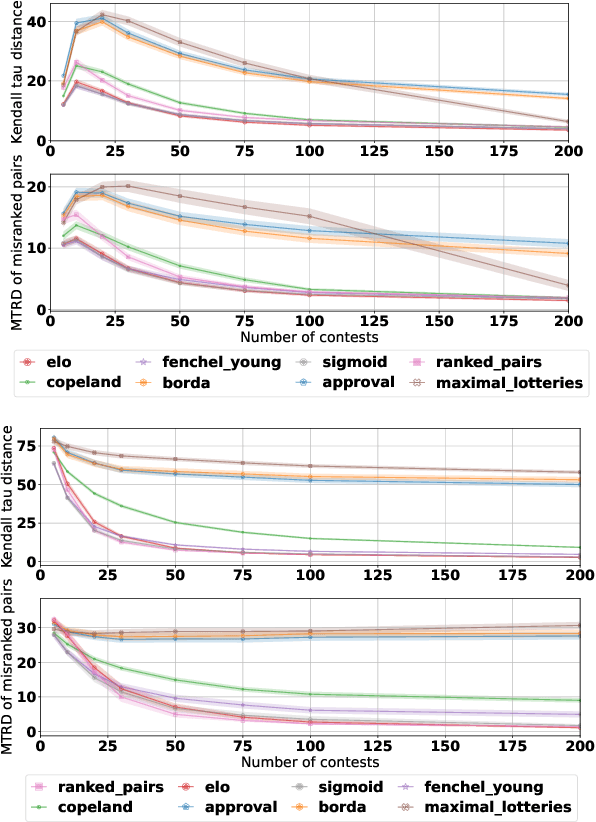
Abstract:A common way to drive progress of AI models and agents is to compare their performance on standardized benchmarks. Comparing the performance of general agents requires aggregating their individual performances across a potentially wide variety of different tasks. In this paper, we describe a novel ranking scheme inspired by social choice frameworks, called Soft Condorcet Optimization (SCO), to compute the optimal ranking of agents: the one that makes the fewest mistakes in predicting the agent comparisons in the evaluation data. This optimal ranking is the maximum likelihood estimate when evaluation data (which we view as votes) are interpreted as noisy samples from a ground truth ranking, a solution to Condorcet's original voting system criteria. SCO ratings are maximal for Condorcet winners when they exist, which we show is not necessarily true for the classical rating system Elo. We propose three optimization algorithms to compute SCO ratings and evaluate their empirical performance. When serving as an approximation to the Kemeny-Young voting method, SCO rankings are on average 0 to 0.043 away from the optimal ranking in normalized Kendall-tau distance across 865 preference profiles from the PrefLib open ranking archive. In a simulated noisy tournament setting, SCO achieves accurate approximations to the ground truth ranking and the best among several baselines when 59\% or more of the preference data is missing. Finally, SCO ranking provides the best approximation to the optimal ranking, measured on held-out test sets, in a problem containing 52,958 human players across 31,049 games of the classic seven-player game of Diplomacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge