Robert Wilson
The TESS Ten Thousand Catalog: 10,001 uniformly-vetted and -validated Eclipsing Binary Stars detected in Full-Frame Image data by machine learning and analyzed by citizen scientists
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) has surveyed nearly the entire sky in Full-Frame Image mode with a time resolution of 200 seconds to 30 minutes and a temporal baseline of at least 27 days. In addition to the primary goal of discovering new exoplanets, TESS is exceptionally capable at detecting variable stars, and in particular short-period eclipsing binaries which are relatively common, making up a few percent of all stars, and represent powerful astrophysical laboratories for deep investigations of stellar formation and evolution. We combed Sectors 1-82 of TESS Full-Frame Image data searching for eclipsing binary stars using a neural network that identified ~1.2 million stars with eclipse-like features. Of these, we have performed an in-depth analysis on ~60,000 targets using automated methods and manual inspection by citizen scientists. Here we present a catalog of 10001 uniformly-vetted and -validated eclipsing binary stars that passed all our ephemeris and photocenter tests, as well as complementary visual inspection. Of these, 7936 are new eclipsing binaries while the remaining 2065 are known systems for which we update the published ephemerides. We outline the detection and analysis of the targets, discuss the properties of the sample, and highlight potentially interesting systems. Finally, we also provide a list of ~900,000 unvetted and unvalidated targets for which the neural network found eclipse-like features with a score higher than 0.9, and for which there are no known eclipsing binaries within a sky-projected separation of a TESS pixel (~21 arcsec).
Centaur: a foundation model of human cognition
Oct 26, 2024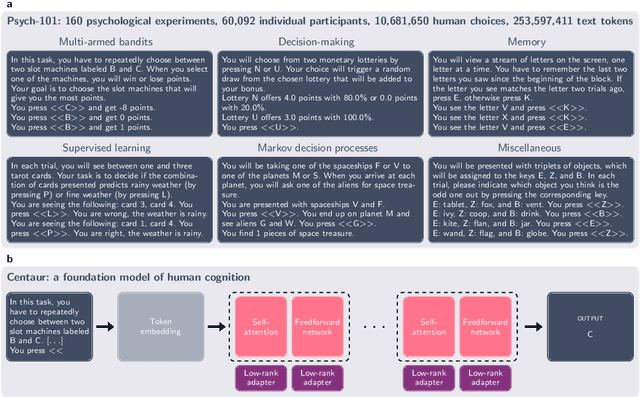

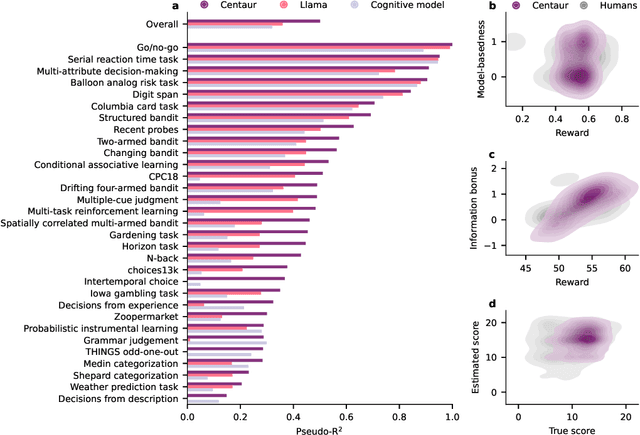
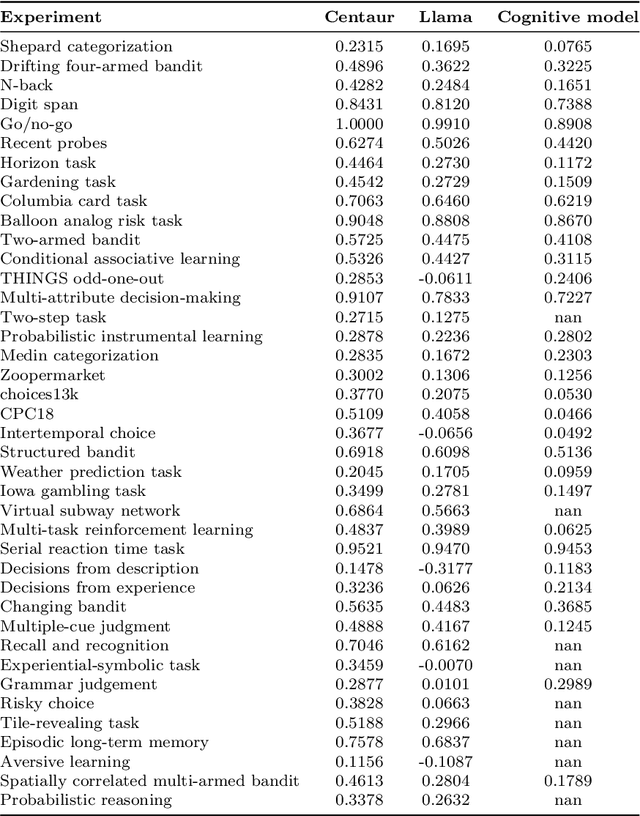
Abstract:Establishing a unified theory of cognition has been a major goal of psychology. While there have been previous attempts to instantiate such theories by building computational models, we currently do not have one model that captures the human mind in its entirety. Here we introduce Centaur, a computational model that can predict and simulate human behavior in any experiment expressible in natural language. We derived Centaur by finetuning a state-of-the-art language model on a novel, large-scale data set called Psych-101. Psych-101 reaches an unprecedented scale, covering trial-by-trial data from over 60,000 participants performing over 10,000,000 choices in 160 experiments. Centaur not only captures the behavior of held-out participants better than existing cognitive models, but also generalizes to new cover stories, structural task modifications, and entirely new domains. Furthermore, we find that the model's internal representations become more aligned with human neural activity after finetuning. Taken together, Centaur is the first real candidate for a unified model of human cognition. We anticipate that it will have a disruptive impact on the cognitive sciences, challenging the existing paradigm for developing computational models.
Toward a Wearable Biosensor Ecosystem on ROS 2 for Real-time Human-Robot Interaction Systems
Oct 08, 2021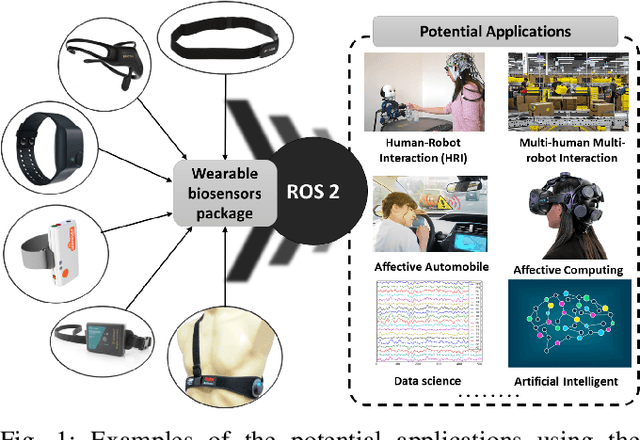
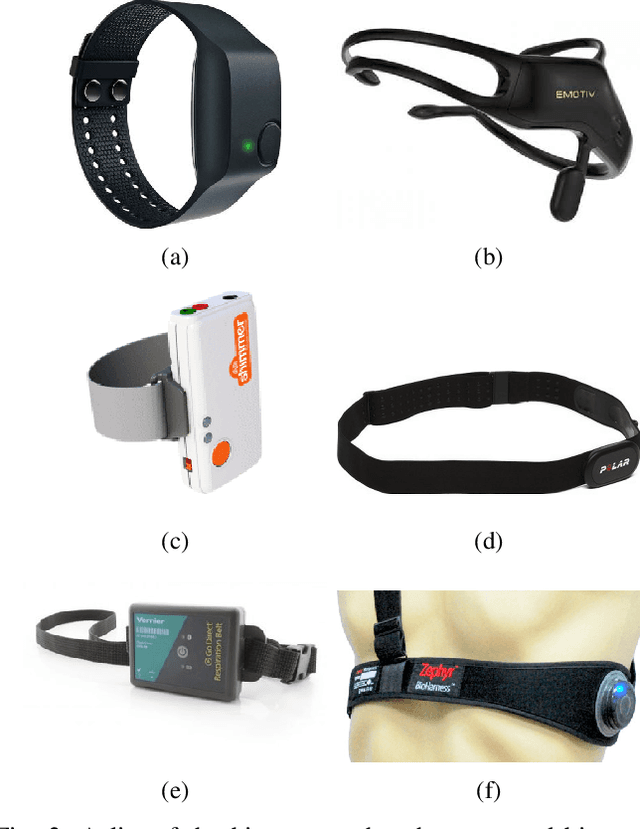
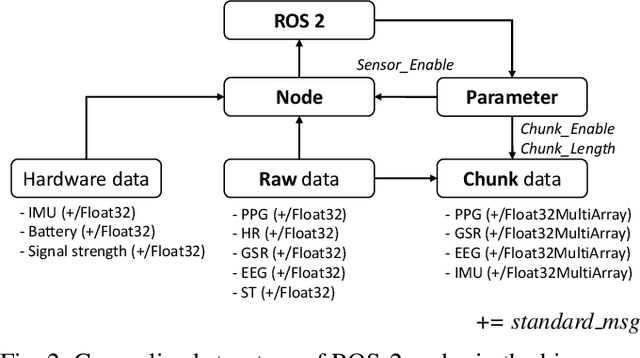

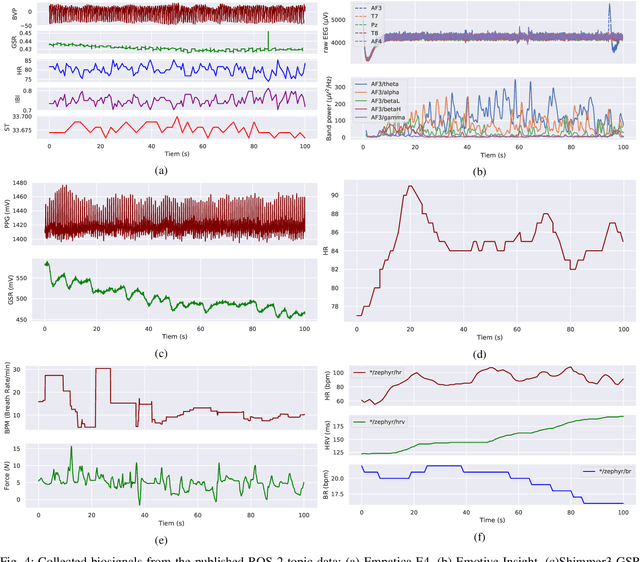
Abstract:Wearable biosensors can enable continuous human data capture, facilitating development of real-world Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) systems. However, a lack of standardized libraries and implementations adds extraneous complexity to HRI system designs, and precludes collaboration across disciplines and institutions. Here, we introduce a novel wearable biosensor package for the Robot Operating System 2 (ROS 2) system. The ROS2 officially supports real-time computing and multi-robot systems, and thus provides easy-to-use and reliable streaming data from multiple nodes. The package standardizes biosensor HRI integration, lowers the technical barrier of entry, and expands the biosensor ecosystem into the robotics field. Each biosensor package node follows a generalized node and topic structure concentrated on ease of use. Current package capabilities, listed by biosensor, highlight package standardization. Collected example data demonstrate a full integration of each biosensor into ROS2. We expect that standardization of this biosensors package for ROS2 will greatly simplify use and cross-collaboration across many disciplines. The wearable biosensor package is made publicly available on GitHub at \https://github.com/SMARTlab-Purdue/ros2-foxy-wearable-biosensors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge