Rim Rekik
Quality assessment of 3D human animation: Subjective and objective evaluation
May 29, 2025Abstract:Virtual human animations have a wide range of applications in virtual and augmented reality. While automatic generation methods of animated virtual humans have been developed, assessing their quality remains challenging. Recently, approaches introducing task-oriented evaluation metrics have been proposed, leveraging neural network training. However, quality assessment measures for animated virtual humans that are not generated with parametric body models have yet to be developed. In this context, we introduce a first such quality assessment measure leveraging a novel data-driven framework. First, we generate a dataset of virtual human animations together with their corresponding subjective realism evaluation scores collected with a user study. Second, we use the resulting dataset to learn predicting perceptual evaluation scores. Results indicate that training a linear regressor on our dataset results in a correlation of 90%, which outperforms a state of the art deep learning baseline.
Patch-based learning of adaptive Total Variation parameter maps for blind image denoising
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:We consider a patch-based learning approach defined in terms of neural networks to estimate spatially adaptive regularisation parameter maps for image denoising with weighted Total Variation and test it to situations when the noise distribution is unknown. As an example, we consider situations where noise could be either Gaussian or Poisson and perform preliminary model selection by a standard binary classification network. Then, we define a patch-based approach where at each image pixel an optimal weighting between TV regularisation and the corresponding data fidelity is learned in a supervised way using reference natural image patches upon optimisation of SSIM and in a sliding window fashion. Extensive numerical results are reported for both noise models, showing significant improvement w.r.t. results obtained by means of optimal scalar regularisation.
4DHumanOutfit: a multi-subject 4D dataset of human motion sequences in varying outfits exhibiting large displacements
Jun 12, 2023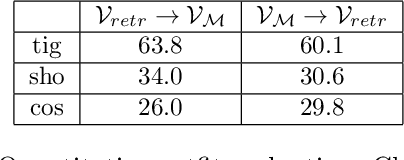
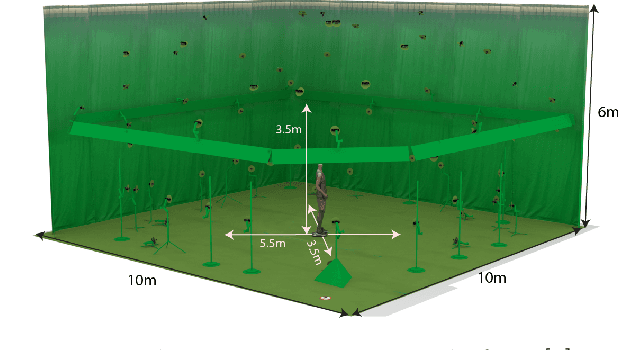

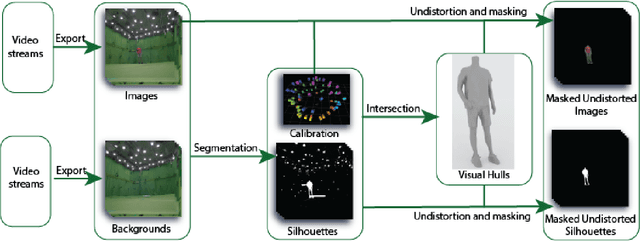
Abstract:This work presents 4DHumanOutfit, a new dataset of densely sampled spatio-temporal 4D human motion data of different actors, outfits and motions. The dataset is designed to contain different actors wearing different outfits while performing different motions in each outfit. In this way, the dataset can be seen as a cube of data containing 4D motion sequences along 3 axes with identity, outfit and motion. This rich dataset has numerous potential applications for the processing and creation of digital humans, e.g. augmented reality, avatar creation and virtual try on. 4DHumanOutfit is released for research purposes at https://kinovis.inria.fr/4dhumanoutfit/. In addition to image data and 4D reconstructions, the dataset includes reference solutions for each axis. We present independent baselines along each axis that demonstrate the value of these reference solutions for evaluation tasks.
Correspondence-free online human motion retargeting
Feb 01, 2023



Abstract:We present a novel data-driven framework for unsupervised human motion retargeting which animates a target body shape with a source motion. This allows to retarget motions between different characters by animating a target subject with a motion of a source subject. Our method is correspondence-free,~\ie neither spatial correspondences between the source and target shapes nor temporal correspondences between different frames of the source motion are required. Our proposed method directly animates a target shape with arbitrary sequences of humans in motion, possibly captured using 4D acquisition platforms or consumer devices. Our framework takes into account long-term temporal context of $1$ second during retargeting while accounting for surface details. To achieve this, we take inspiration from two lines of existing work: skeletal motion retargeting, which leverages long-term temporal context at the cost of surface detail, and surface-based retargeting, which preserves surface details without considering long-term temporal context. We unify the advantages of these works by combining a learnt skinning field with a skeletal retargeting approach. During inference, our method runs online,~\ie the input can be processed in a serial way, and retargeting is performed in a single forward pass per frame. Experiments show that including long-term temporal context during training improves the method's accuracy both in terms of the retargeted skeletal motion and the detail preservation. Furthermore, our method generalizes well on unobserved motions and body shapes. We demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art results on two test datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge