Ratheesh Kalarot
Plug-and-Play Diffusion Distillation
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have shown tremendous results in image generation. However, due to the iterative nature of the diffusion process and its reliance on classifier-free guidance, inference times are slow. In this paper, we propose a new distillation approach for guided diffusion models in which an external lightweight guide model is trained while the original text-to-image model remains frozen. We show that our method reduces the inference computation of classifier-free guided latent-space diffusion models by almost half, and only requires 1\% trainable parameters of the base model. Furthermore, once trained, our guide model can be applied to various fine-tuned, domain-specific versions of the base diffusion model without the need for additional training: this "plug-and-play" functionality drastically improves inference computation while maintaining the visual fidelity of generated images. Empirically, we show that our approach is able to produce visually appealing results and achieve a comparable FID score to the teacher with as few as 8 to 16 steps.
A Data Perspective on Enhanced Identity Preservation for Diffusion Personalization
Nov 07, 2023
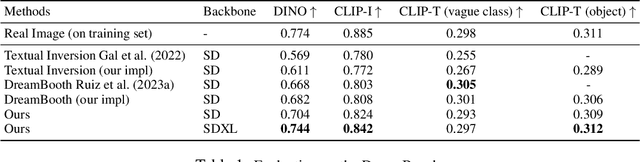

Abstract:Large text-to-image models have revolutionized the ability to generate imagery using natural language. However, particularly unique or personal visual concepts, such as your pet, an object in your house, etc., will not be captured by the original model. This has led to interest in how to inject new visual concepts, bound to a new text token, using as few as 4-6 examples. Despite significant progress, this task remains a formidable challenge, particularly in preserving the subject's identity. While most researchers attempt to to address this issue by modifying model architectures, our approach takes a data-centric perspective, advocating the modification of data rather than the model itself. We introduce a novel regularization dataset generation strategy on both the text and image level; demonstrating the importance of a rich and structured regularization dataset (automatically generated) to prevent losing text coherence and better identity preservation. The better quality is enabled by allowing up to 5x more fine-tuning iterations without overfitting and degeneration. The generated renditions of the desired subject preserve even fine details such as text and logos; all while maintaining the ability to generate diverse samples that follow the input text prompt. Since our method focuses on data augmentation, rather than adjusting the model architecture, it is complementary and can be combined with prior work. We show on established benchmarks that our data-centric approach forms the new state of the art in terms of image quality, with the best trade-off between identity preservation, diversity, and text alignment.
Component Attention Guided Face Super-Resolution Network: CAGFace
Oct 19, 2019



Abstract:To make the best use of the underlying structure of faces, the collective information through face datasets and the intermediate estimates during the upsampling process, here we introduce a fully convolutional multi-stage neural network for 4$\times$ super-resolution for face images. We implicitly impose facial component-wise attention maps using a segmentation network to allow our network to focus on face-inherent patterns. Each stage of our network is composed of a stem layer, a residual backbone, and spatial upsampling layers. We recurrently apply stages to reconstruct an intermediate image, and then reuse its space-to-depth converted versions to bootstrap and enhance image quality progressively. Our experiments show that our face super-resolution method achieves quantitatively superior and perceptually pleasing results in comparison to state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge