Rama Kumar Pasumarthi
Self-Attentive Document Interaction Networks for Permutation Equivariant Ranking
Oct 23, 2019



Abstract:How to leverage cross-document interactions to improve ranking performance is an important topic in information retrieval (IR) research. However, this topic has not been well-studied in the learning-to-rank setting and most of the existing work still treats each document independently while scoring. The recent development of deep learning shows strength in modeling complex relationships across sequences and sets. It thus motivates us to study how to leverage cross-document interactions for learning-to-rank in the deep learning framework. In this paper, we formally define the permutation-equivariance requirement for a scoring function that captures cross-document interactions. We then propose a self-attention based document interaction network and show that it satisfies the permutation-equivariant requirement, and can generate scores for document sets of varying sizes. Our proposed methods can automatically learn to capture document interactions without any auxiliary information, and can scale across large document sets. We conduct experiments on three ranking datasets: the benchmark Web30k, a Gmail search, and a Google Drive Quick Access dataset. Experimental results show that our proposed methods are both more effective and efficient than baselines.
Domain Adaptation for Enterprise Email Search
Jun 19, 2019


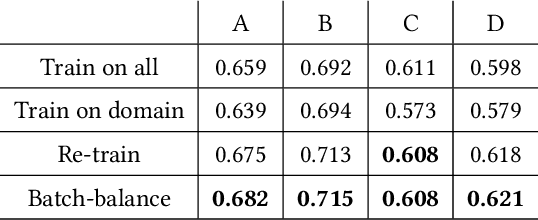
Abstract:In the enterprise email search setting, the same search engine often powers multiple enterprises from various industries: technology, education, manufacturing, etc. However, using the same global ranking model across different enterprises may result in suboptimal search quality, due to the corpora differences and distinct information needs. On the other hand, training an individual ranking model for each enterprise may be infeasible, especially for smaller institutions with limited data. To address this data challenge, in this paper we propose a domain adaptation approach that fine-tunes the global model to each individual enterprise. In particular, we propose a novel application of the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) approach to information retrieval, which attempts to bridge the gap between the global data distribution and the data distribution for a given individual enterprise. We conduct a comprehensive set of experiments on a large-scale email search engine, and demonstrate that the MMD approach consistently improves the search quality for multiple individual domains, both in comparison to the global ranking model, as well as several competitive domain adaptation baselines including adversarial learning methods.
* Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval
Gated-Attention Architectures for Task-Oriented Language Grounding
Jan 09, 2018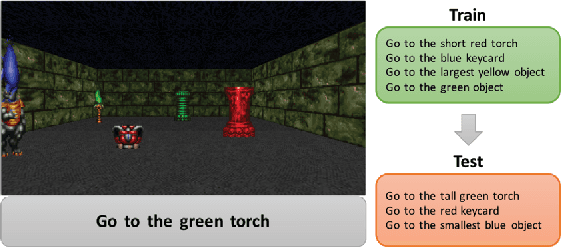
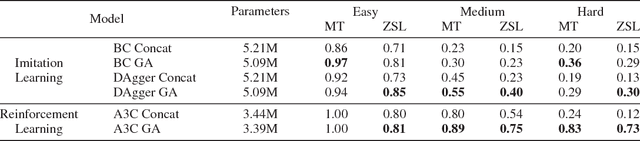
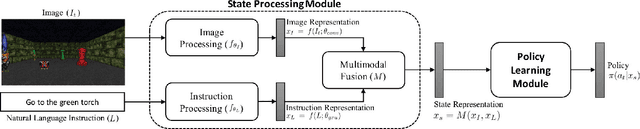
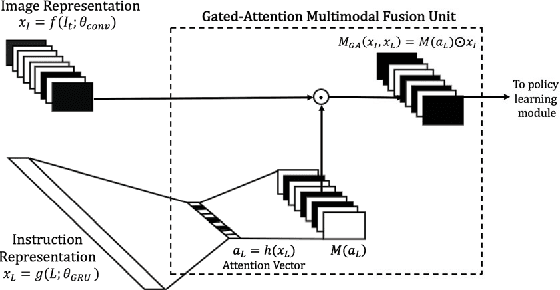
Abstract:To perform tasks specified by natural language instructions, autonomous agents need to extract semantically meaningful representations of language and map it to visual elements and actions in the environment. This problem is called task-oriented language grounding. We propose an end-to-end trainable neural architecture for task-oriented language grounding in 3D environments which assumes no prior linguistic or perceptual knowledge and requires only raw pixels from the environment and the natural language instruction as input. The proposed model combines the image and text representations using a Gated-Attention mechanism and learns a policy to execute the natural language instruction using standard reinforcement and imitation learning methods. We show the effectiveness of the proposed model on unseen instructions as well as unseen maps, both quantitatively and qualitatively. We also introduce a novel environment based on a 3D game engine to simulate the challenges of task-oriented language grounding over a rich set of instructions and environment states.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge