Qiudan Zhang
DBGroup: Dual-Branch Point Grouping for Weakly Supervised 3D Instance Segmentation
Nov 13, 2025
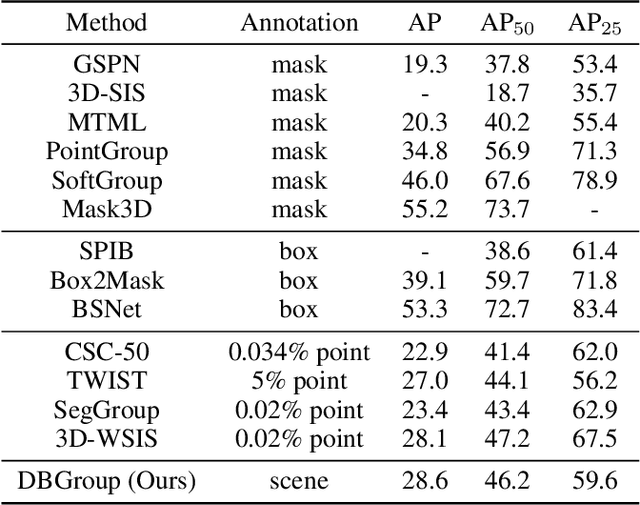

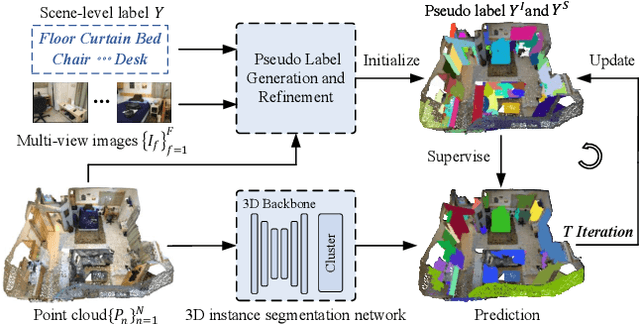
Abstract:Weakly supervised 3D instance segmentation is essential for 3D scene understanding, especially as the growing scale of data and high annotation costs associated with fully supervised approaches. Existing methods primarily rely on two forms of weak supervision: one-thing-one-click annotations and bounding box annotations, both of which aim to reduce labeling efforts. However, these approaches still encounter limitations, including labor-intensive annotation processes, high complexity, and reliance on expert annotators. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{DBGroup}, a two-stage weakly supervised 3D instance segmentation framework that leverages scene-level annotations as a more efficient and scalable alternative. In the first stage, we introduce a Dual-Branch Point Grouping module to generate pseudo labels guided by semantic and mask cues extracted from multi-view images. To further improve label quality, we develop two refinement strategies: Granularity-Aware Instance Merging and Semantic Selection and Propagation. The second stage involves multi-round self-training on an end-to-end instance segmentation network using the refined pseudo-labels. Additionally, we introduce an Instance Mask Filter strategy to address inconsistencies within the pseudo labels. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DBGroup achieves competitive performance compared to sparse-point-level supervised 3D instance segmentation methods, while surpassing state-of-the-art scene-level supervised 3D semantic segmentation approaches. Code is available at https://github.com/liuxuexun/DBGroup.
LESS: Label-Efficient and Single-Stage Referring 3D Segmentation
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:Referring 3D Segmentation is a visual-language task that segments all points of the specified object from a 3D point cloud described by a sentence of query. Previous works perform a two-stage paradigm, first conducting language-agnostic instance segmentation then matching with given text query. However, the semantic concepts from text query and visual cues are separately interacted during the training, and both instance and semantic labels for each object are required, which is time consuming and human-labor intensive. To mitigate these issues, we propose a novel Referring 3D Segmentation pipeline, Label-Efficient and Single-Stage, dubbed LESS, which is only under the supervision of efficient binary mask. Specifically, we design a Point-Word Cross-Modal Alignment module for aligning the fine-grained features of points and textual embedding. Query Mask Predictor module and Query-Sentence Alignment module are introduced for coarse-grained alignment between masks and query. Furthermore, we propose an area regularization loss, which coarsely reduces irrelevant background predictions on a large scale. Besides, a point-to-point contrastive loss is proposed concentrating on distinguishing points with subtly similar features. Through extensive experiments, we achieve state-of-the-art performance on ScanRefer dataset by surpassing the previous methods about 3.7% mIoU using only binary labels.
3D Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation with 2D Vision-Language Guidance
Jul 13, 2024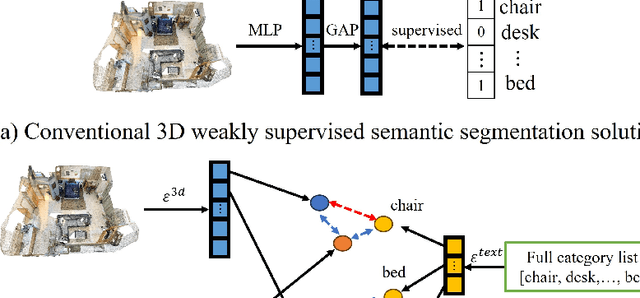
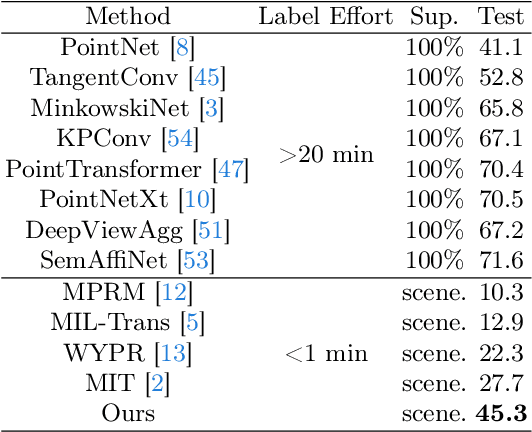
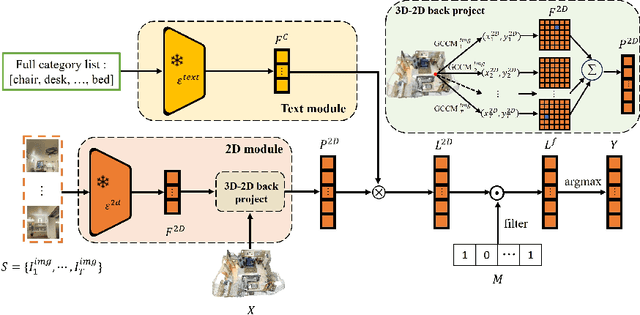
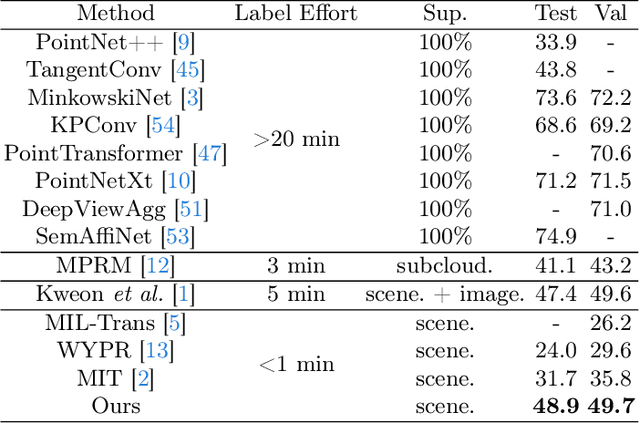
Abstract:In this paper, we propose 3DSS-VLG, a weakly supervised approach for 3D Semantic Segmentation with 2D Vision-Language Guidance, an alternative approach that a 3D model predicts dense-embedding for each point which is co-embedded with both the aligned image and text spaces from the 2D vision-language model. Specifically, our method exploits the superior generalization ability of the 2D vision-language models and proposes the Embeddings Soft-Guidance Stage to utilize it to implicitly align 3D embeddings and text embeddings. Moreover, we introduce the Embeddings Specialization Stage to purify the feature representation with the help of a given scene-level label, specifying a better feature supervised by the corresponding text embedding. Thus, the 3D model is able to gain informative supervisions both from the image embedding and text embedding, leading to competitive segmentation performances. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to investigate 3D weakly supervised semantic segmentation by using the textual semantic information of text category labels. Moreover, with extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments, we present that our 3DSS-VLG is able not only to achieve the state-of-the-art performance on both S3DIS and ScanNet datasets, but also to maintain strong generalization capability.
Weakly-Supervised 3D Scene Graph Generation via Visual-Linguistic Assisted Pseudo-labeling
Apr 03, 2024



Abstract:Learning to build 3D scene graphs is essential for real-world perception in a structured and rich fashion. However, previous 3D scene graph generation methods utilize a fully supervised learning manner and require a large amount of entity-level annotation data of objects and relations, which is extremely resource-consuming and tedious to obtain. To tackle this problem, we propose 3D-VLAP, a weakly-supervised 3D scene graph generation method via Visual-Linguistic Assisted Pseudo-labeling. Specifically, our 3D-VLAP exploits the superior ability of current large-scale visual-linguistic models to align the semantics between texts and 2D images, as well as the naturally existing correspondences between 2D images and 3D point clouds, and thus implicitly constructs correspondences between texts and 3D point clouds. First, we establish the positional correspondence from 3D point clouds to 2D images via camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters, thereby achieving alignment of 3D point clouds and 2D images. Subsequently, a large-scale cross-modal visual-linguistic model is employed to indirectly align 3D instances with the textual category labels of objects by matching 2D images with object category labels. The pseudo labels for objects and relations are then produced for 3D-VLAP model training by calculating the similarity between visual embeddings and textual category embeddings of objects and relations encoded by the visual-linguistic model, respectively. Ultimately, we design an edge self-attention based graph neural network to generate scene graphs of 3D point cloud scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our 3D-VLAP achieves comparable results with current advanced fully supervised methods, meanwhile significantly alleviating the pressure of data annotation.
Weakly-Supervised 3D Visual Grounding based on Visual Linguistic Alignment
Dec 15, 2023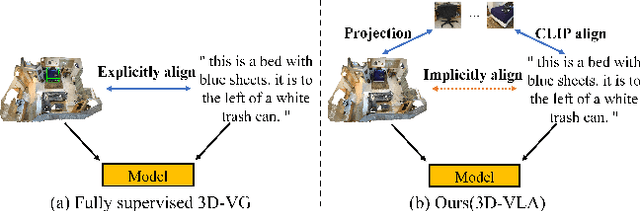
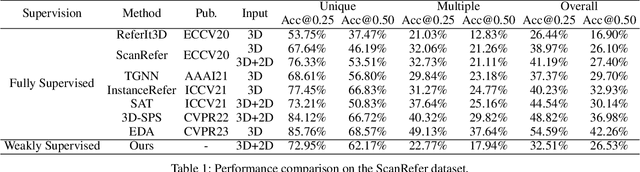
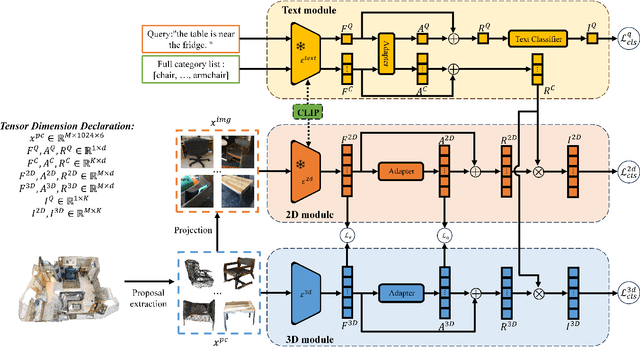
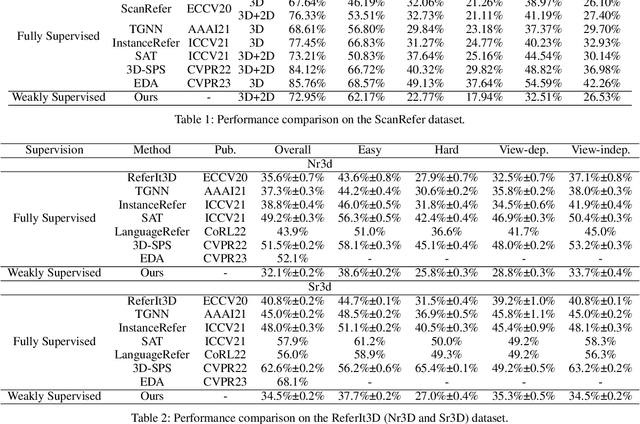
Abstract:Learning to ground natural language queries to target objects or regions in 3D point clouds is quite essential for 3D scene understanding. Nevertheless, existing 3D visual grounding approaches require a substantial number of bounding box annotations for text queries, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive to obtain. In this paper, we propose \textbf{3D-VLA}, a weakly supervised approach for \textbf{3D} visual grounding based on \textbf{V}isual \textbf{L}inguistic \textbf{A}lignment. Our 3D-VLA exploits the superior ability of current large-scale vision-language models (VLMs) on aligning the semantics between texts and 2D images, as well as the naturally existing correspondences between 2D images and 3D point clouds, and thus implicitly constructs correspondences between texts and 3D point clouds with no need for fine-grained box annotations in the training procedure. During the inference stage, the learned text-3D correspondence will help us ground the text queries to the 3D target objects even without 2D images. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to investigate 3D visual grounding in a weakly supervised manner by involving large scale vision-language models, and extensive experiments on ReferIt3D and ScanRefer datasets demonstrate that our 3D-VLA achieves comparable and even superior results over the fully supervised methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge