Qingtian Bian
BrainOOD: Out-of-distribution Generalizable Brain Network Analysis
Feb 02, 2025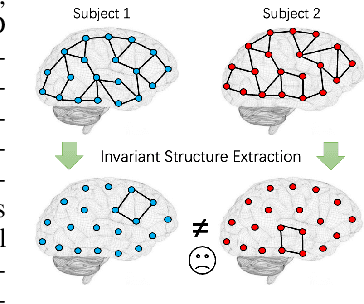
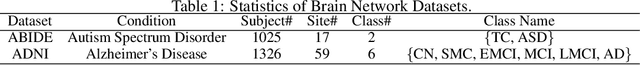
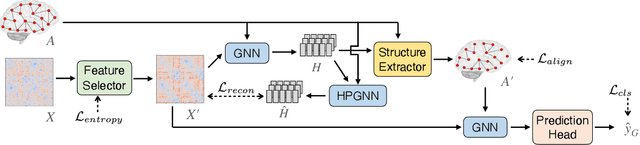
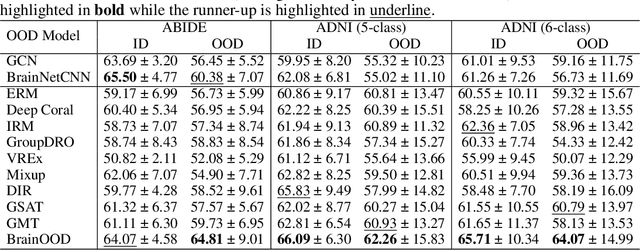
Abstract:In neuroscience, identifying distinct patterns linked to neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer's and Autism, is critical for early diagnosis and effective intervention. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown promising in analyzing brain networks, but there are two major challenges in using GNNs: (1) distribution shifts in multi-site brain network data, leading to poor Out-of-Distribution (OOD) generalization, and (2) limited interpretability in identifying key brain regions critical to neurological disorders. Existing graph OOD methods, while effective in other domains, struggle with the unique characteristics of brain networks. To bridge these gaps, we introduce BrainOOD, a novel framework tailored for brain networks that enhances GNNs' OOD generalization and interpretability. BrainOOD framework consists of a feature selector and a structure extractor, which incorporates various auxiliary losses including an improved Graph Information Bottleneck (GIB) objective to recover causal subgraphs. By aligning structure selection across brain networks and filtering noisy features, BrainOOD offers reliable interpretations of critical brain regions. Our approach outperforms 16 existing methods and improves generalization to OOD subjects by up to 8.5%. Case studies highlight the scientific validity of the patterns extracted, which aligns with the findings in known neuroscience literature. We also propose the first OOD brain network benchmark, which provides a foundation for future research in this field. Our code is available at https://github.com/AngusMonroe/BrainOOD.
ABXI: Invariant Interest Adaptation for Task-Guided Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation (CDSR) has recently gained attention for countering data sparsity by transferring knowledge across domains. A common approach merges domain-specific sequences into cross-domain sequences, serving as bridges to connect domains. One key challenge is to correctly extract the shared knowledge among these sequences and appropriately transfer it. Most existing works directly transfer unfiltered cross-domain knowledge rather than extracting domain-invariant components and adaptively integrating them into domain-specific modelings. Another challenge lies in aligning the domain-specific and cross-domain sequences. Existing methods align these sequences based on timestamps, but this approach can cause prediction mismatches when the current tokens and their targets belong to different domains. In such cases, the domain-specific knowledge carried by the current tokens may degrade performance. To address these challenges, we propose the A-B-Cross-to-Invariant Learning Recommender (ABXI). Specifically, leveraging LoRA's effectiveness for efficient adaptation, ABXI incorporates two types of LoRAs to facilitate knowledge adaptation. First, all sequences are processed through a shared encoder that employs a domain LoRA for each sequence, thereby preserving unique domain characteristics. Next, we introduce an invariant projector that extracts domain-invariant interests from cross-domain representations, utilizing an invariant LoRA to adapt these interests into modeling each specific domain. Besides, to avoid prediction mismatches, all domain-specific sequences are aligned to match the domains of the cross-domain ground truths. Experimental results on three datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms other CDSR counterparts by a large margin. The codes are available in \url{https://github.com/DiMarzioBian/ABXI}.
Contrasformer: A Brain Network Contrastive Transformer for Neurodegenerative Condition Identification
Sep 17, 2024Abstract:Understanding neurological disorder is a fundamental problem in neuroscience, which often requires the analysis of brain networks derived from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data. Despite the prevalence of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and Graph Transformers in various domains, applying them to brain networks faces challenges. Specifically, the datasets are severely impacted by the noises caused by distribution shifts across sub-populations and the neglect of node identities, both obstruct the identification of disease-specific patterns. To tackle these challenges, we propose Contrasformer, a novel contrastive brain network Transformer. It generates a prior-knowledge-enhanced contrast graph to address the distribution shifts across sub-populations by a two-stream attention mechanism. A cross attention with identity embedding highlights the identity of nodes, and three auxiliary losses ensure group consistency. Evaluated on 4 functional brain network datasets over 4 different diseases, Contrasformer outperforms the state-of-the-art methods for brain networks by achieving up to 10.8\% improvement in accuracy, which demonstrates its efficacy in neurological disorder identification. Case studies illustrate its interpretability, especially in the context of neuroscience. This paper provides a solution for analyzing brain networks, offering valuable insights into neurological disorders. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/AngusMonroe/Contrasformer}.
CPMR: Context-Aware Incremental Sequential Recommendation with Pseudo-Multi-Task Learning
Sep 16, 2023Abstract:The motivations of users to make interactions can be divided into static preference and dynamic interest. To accurately model user representations over time, recent studies in sequential recommendation utilize information propagation and evolution to mine from batches of arriving interactions. However, they ignore the fact that people are easily influenced by the recent actions of other users in the contextual scenario, and applying evolution across all historical interactions dilutes the importance of recent ones, thus failing to model the evolution of dynamic interest accurately. To address this issue, we propose a Context-Aware Pseudo-Multi-Task Recommender System (CPMR) to model the evolution in both historical and contextual scenarios by creating three representations for each user and item under different dynamics: static embedding, historical temporal states, and contextual temporal states. To dually improve the performance of temporal states evolution and incremental recommendation, we design a Pseudo-Multi-Task Learning (PMTL) paradigm by stacking the incremental single-target recommendations into one multi-target task for joint optimization. Within the PMTL paradigm, CPMR employs a shared-bottom network to conduct the evolution of temporal states across historical and contextual scenarios, as well as the fusion of them at the user-item level. In addition, CPMR incorporates one real tower for incremental predictions, and two pseudo towers dedicated to updating the respective temporal states based on new batches of interactions. Experimental results on four benchmark recommendation datasets show that CPMR consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines and achieves significant gains on three of them. The code is available at: https://github.com/DiMarzioBian/CPMR.
* Accepted by CIKM 2023. Alias: "Modeling Context-Aware Temporal Dynamics via Pseudo-Multi-Task Learning"
Contrastive Graph Pooling for Explainable Classification of Brain Networks
Jul 07, 2023



Abstract:Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is a commonly used technique to measure neural activation. Its application has been particularly important in identifying underlying neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Autism. Recent analysis of fMRI data models the brain as a graph and extracts features by graph neural networks (GNNs). However, the unique characteristics of fMRI data require a special design of GNN. Tailoring GNN to generate effective and domain-explainable features remains challenging. In this paper, we propose a contrastive dual-attention block and a differentiable graph pooling method called ContrastPool to better utilize GNN for brain networks, meeting fMRI-specific requirements. We apply our method to 5 resting-state fMRI brain network datasets of 3 diseases and demonstrate its superiority over state-of-the-art baselines. Our case study confirms that the patterns extracted by our method match the domain knowledge in neuroscience literature, and disclose direct and interesting insights. Our contributions underscore the potential of ContrastPool for advancing the understanding of brain networks and neurodegenerative conditions.
Union Subgraph Neural Networks
May 25, 2023Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are widely used for graph representation learning in many application domains. The expressiveness of vanilla GNNs is upper-bounded by 1-dimensional Weisfeiler-Leman (1-WL) test as they operate on rooted subtrees through iterative message passing. In this paper, we empower GNNs by injecting neighbor-connectivity information extracted from a new type of substructure. We first investigate different kinds of connectivities existing in a local neighborhood and identify a substructure called union subgraph, which is able to capture the complete picture of the 1-hop neighborhood of an edge. We then design a shortest-path-based substructure descriptor that possesses three nice properties and can effectively encode the high-order connectivities in union subgraphs. By infusing the encoded neighbor connectivities, we propose a novel model, namely Union Subgraph Neural Network (UnionSNN), which is proven to be strictly more powerful than 1-WL in distinguishing non-isomorphic graphs. Additionally, the local encoding from union subgraphs can also be injected into arbitrary message-passing neural networks (MPNNs) and Transformer-based models as a plugin. Extensive experiments on 17 benchmarks of both graph-level and node-level tasks demonstrate that UnionSNN outperforms state-of-the-art baseline models, with competitive computational efficiency. The injection of our local encoding to existing models is able to boost the performance by up to 11.09%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge