Qichao Ma
CopyLens: Dynamically Flagging Copyrighted Sub-Dataset Contributions to LLM Outputs
Oct 06, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have become pervasive due to their knowledge absorption and text-generation capabilities. Concurrently, the copyright issue for pretraining datasets has been a pressing concern, particularly when generation includes specific styles. Previous methods either focus on the defense of identical copyrighted outputs or find interpretability by individual tokens with computational burdens. However, the gap between them exists, where direct assessments of how dataset contributions impact LLM outputs are missing. Once the model providers ensure copyright protection for data holders, a more mature LLM community can be established. To address these limitations, we introduce CopyLens, a new framework to analyze how copyrighted datasets may influence LLM responses. Specifically, a two-stage approach is employed: First, based on the uniqueness of pretraining data in the embedding space, token representations are initially fused for potential copyrighted texts, followed by a lightweight LSTM-based network to analyze dataset contributions. With such a prior, a contrastive-learning-based non-copyright OOD detector is designed. Our framework can dynamically face different situations and bridge the gap between current copyright detection methods. Experiments show that CopyLens improves efficiency and accuracy by 15.2% over our proposed baseline, 58.7% over prompt engineering methods, and 0.21 AUC over OOD detection baselines.
PE-Planner: A Performance-Enhanced Quadrotor Motion Planner for Autonomous Flight in Complex and Dynamic Environments
Mar 19, 2024
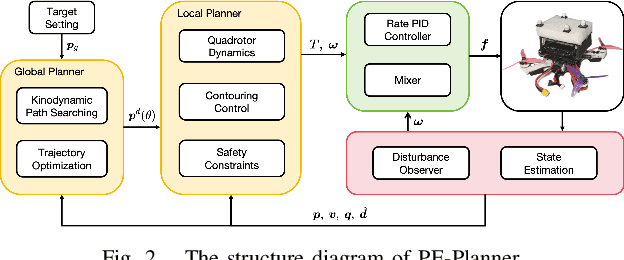

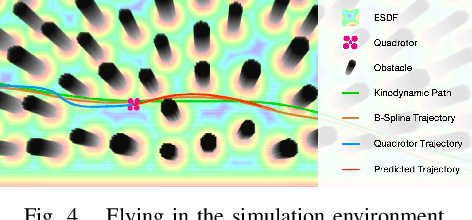
Abstract:The role of a motion planner is pivotal in quadrotor applications, yet existing methods often struggle to adapt to complex environments, limiting their ability to achieve fast, safe, and robust flight. In this letter, we introduce a performance-enhanced quadrotor motion planner designed for autonomous flight in complex environments including dense obstacles, dynamic obstacles, and unknown disturbances. The global planner generates an initial trajectory through kinodynamic path searching and refines it using B-spline trajectory optimization. Subsequently, the local planner takes into account the quadrotor dynamics, estimated disturbance, global reference trajectory, control cost, time cost, and safety constraints to generate real-time control inputs, utilizing the framework of model predictive contouring control. Both simulations and real-world experiments corroborate the heightened robustness, safety, and speed of the proposed motion planner. Additionally, our motion planner achieves flights at more than 6.8 m/s in a challenging and complex racing scenario.
SRL-ORCA: A Socially Aware Multi-Agent Mapless Navigation Algorithm In Complex Dynamic Scenes
Jun 18, 2023
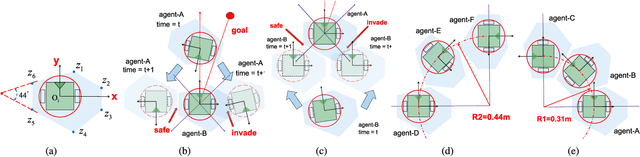
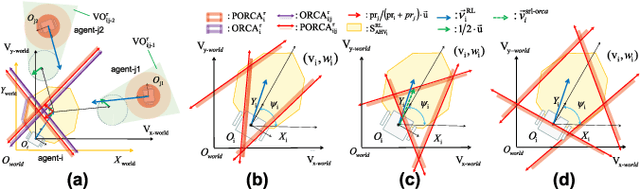
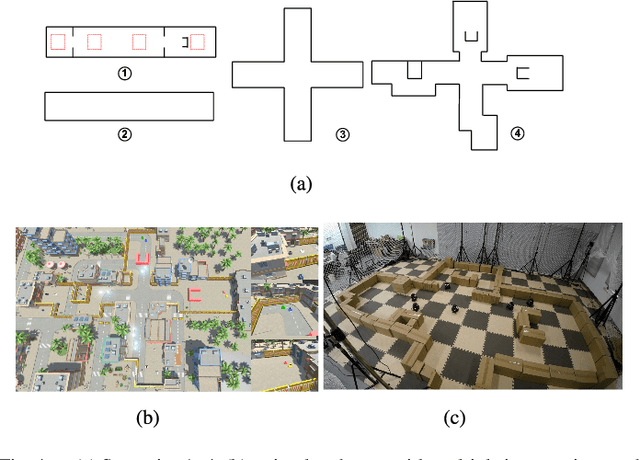
Abstract:For real-world navigation, it is important to endow robots with the capabilities to navigate safely and efficiently in a complex environment with both dynamic and non-convex static obstacles. However, achieving path-finding in non-convex complex environments without maps as well as enabling multiple robots to follow social rules for obstacle avoidance remains challenging problems. In this letter, we propose a socially aware robot mapless navigation algorithm, namely Safe Reinforcement Learning-Optimal Reciprocal Collision Avoidance (SRL-ORCA). This is a multi-agent safe reinforcement learning algorithm by using ORCA as an external knowledge to provide a safety guarantee. This algorithm further introduces traffic norms of human society to improve social comfort and achieve cooperative avoidance by following human social customs. The result of experiments shows that SRL-ORCA learns strategies to obey specific traffic rules. Compared to DRL, SRL-ORCA shows a significant improvement in navigation success rate in different complex scenarios mixed with the application of the same training network. SRL-ORCA is able to cope with non-convex obstacle environments without falling into local minimal regions and has a 14.1\% improvement in path quality (i.e., the average time to target) compared to ORCA. Videos are available at https://youtu.be/huhXfCDkGws.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge