Pranoot Hatwar
Investment Ranking Challenge: Identifying the best performing stocks based on their semi-annual returns
Jun 20, 2019
Abstract:In the IEEE Investment ranking challenge 2018, participants were asked to build a model which would identify the best performing stocks based on their returns over a forward six months window. Anonymized financial predictors and semi-annual returns were provided for a group of anonymized stocks from 1996 to 2017, which were divided into 42 non-overlapping six months period. The second half of 2017 was used as an out-of-sample test of the model's performance. Metrics used were Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient and Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG) of the top 20% of a model's predicted rankings. The top six participants were invited to describe their approach. The solutions used were varied and were based on selecting a subset of data to train, combination of deep and shallow neural networks, different boosting algorithms, different models with different sets of features, linear support vector machine, combination of convoltional neural network (CNN) and Long short term memory (LSTM).
BASS Net: Band-Adaptive Spectral-Spatial Feature Learning Neural Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Dec 02, 2016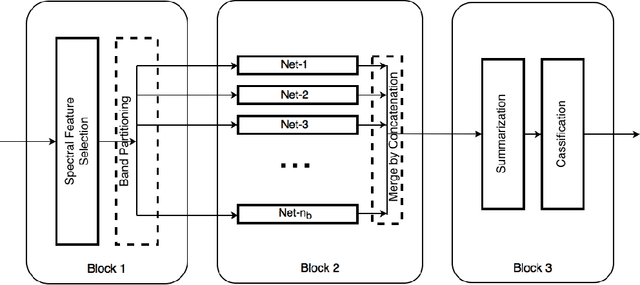
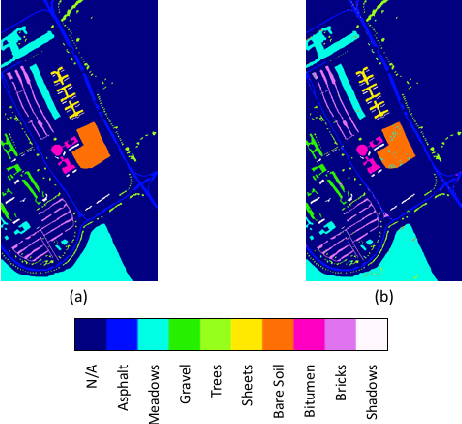
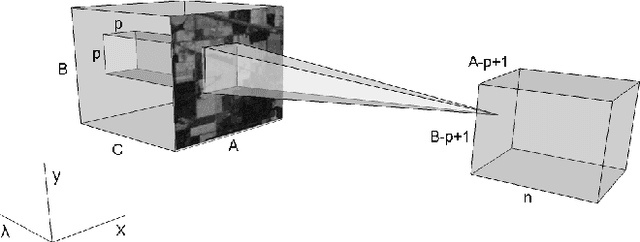
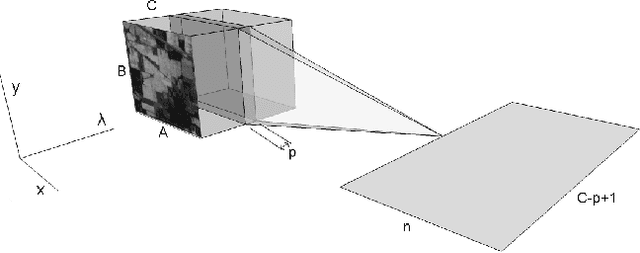
Abstract:Deep learning based landcover classification algorithms have recently been proposed in literature. In hyperspectral images (HSI) they face the challenges of large dimensionality, spatial variability of spectral signatures and scarcity of labeled data. In this article we propose an end-to-end deep learning architecture that extracts band specific spectral-spatial features and performs landcover classification. The architecture has fewer independent connection weights and thus requires lesser number of training data. The method is found to outperform the highest reported accuracies on popular hyperspectral image data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge