Pierre Marza
OCTOPUS: Enhancing the Spatial-Awareness of Vision SSMs with Multi-Dimensional Scans and Traversal Selection
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:State space models (SSMs) have recently emerged as an alternative to transformers due to their unique ability of modeling global relationships in text with linear complexity. However, their success in vision tasks has been limited due to their causal formulation, which is suitable for sequential text but detrimental in the spatial domain where causality breaks the inherent spatial relationships among pixels or patches. As a result, standard SSMs fail to capture local spatial coherence, often linking non-adjacent patches while ignoring neighboring ones that are visually correlated. To address these limitations, we introduce OCTOPUS , a novel architecture that preserves both global context and local spatial structure within images, while maintaining the linear complexity of SSMs. OCTOPUS performs discrete reoccurrence along eight principal orientations, going forward or backward in the horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions, allowing effective information exchange across all spatially connected regions while maintaining independence among unrelated patches. This design enables multi-directional recurrence, capturing both global context and local spatial structure with SSM-level efficiency. In our classification and segmentation benchmarks, OCTOPUS demonstrates notable improvements in boundary preservation and region consistency, as evident from the segmentation results, while maintaining relatively better classification accuracy compared to existing V-SSM based models. These results suggest that OCTOPUS appears as a foundation method for multi-directional recurrence as a scalable and effective mechanism for building spatially aware and computationally efficient vision architectures.
TICON: A Slide-Level Tile Contextualizer for Histopathology Representation Learning
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:The interpretation of small tiles in large whole slide images (WSI) often needs a larger image context. We introduce TICON, a transformer-based tile representation contextualizer that produces rich, contextualized embeddings for ''any'' application in computational pathology. Standard tile encoder-based pipelines, which extract embeddings of tiles stripped from their context, fail to model the rich slide-level information essential for both local and global tasks. Furthermore, different tile-encoders excel at different downstream tasks. Therefore, a unified model is needed to contextualize embeddings derived from ''any'' tile-level foundation model. TICON addresses this need with a single, shared encoder, pretrained using a masked modeling objective to simultaneously unify and contextualize representations from diverse tile-level pathology foundation models. Our experiments demonstrate that TICON-contextualized embeddings significantly improve performance across many different tasks, establishing new state-of-the-art results on tile-level benchmarks (i.e., HEST-Bench, THUNDER, CATCH) and slide-level benchmarks (i.e., Patho-Bench). Finally, we pretrain an aggregator on TICON to form a slide-level foundation model, using only 11K WSIs, outperforming SoTA slide-level foundation models pretrained with up to 350K WSIs.
Controllable Latent Space Augmentation for Digital Pathology
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Whole slide image (WSI) analysis in digital pathology presents unique challenges due to the gigapixel resolution of WSIs and the scarcity of dense supervision signals. While Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) is a natural fit for slide-level tasks, training robust models requires large and diverse datasets. Even though image augmentation techniques could be utilized to increase data variability and reduce overfitting, implementing them effectively is not a trivial task. Traditional patch-level augmentation is prohibitively expensive due to the large number of patches extracted from each WSI, and existing feature-level augmentation methods lack control over transformation semantics. We introduce HistAug, a fast and efficient generative model for controllable augmentations in the latent space for digital pathology. By conditioning on explicit patch-level transformations (e.g., hue, erosion), HistAug generates realistic augmented embeddings while preserving initial semantic information. Our method allows the processing of a large number of patches in a single forward pass efficiently, while at the same time consistently improving MIL model performance. Experiments across multiple slide-level tasks and diverse organs show that HistAug outperforms existing methods, particularly in low-data regimes. Ablation studies confirm the benefits of learned transformations over noise-based perturbations and highlight the importance of uniform WSI-wise augmentation. Code is available at https://github.com/MICS-Lab/HistAug.
THUNDER: Tile-level Histopathology image UNDERstanding benchmark
Jul 10, 2025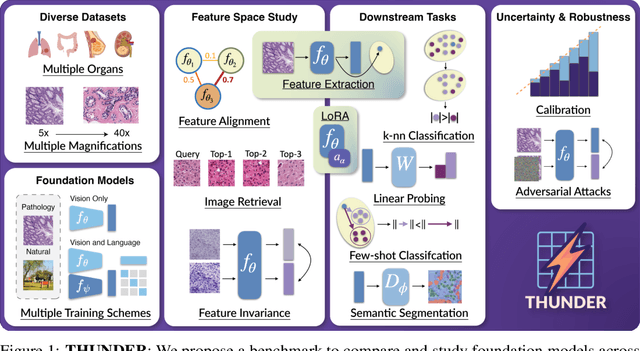
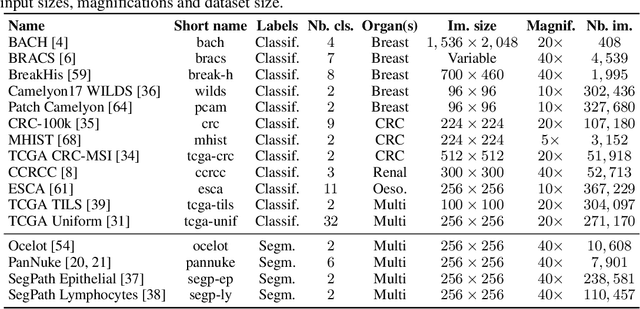

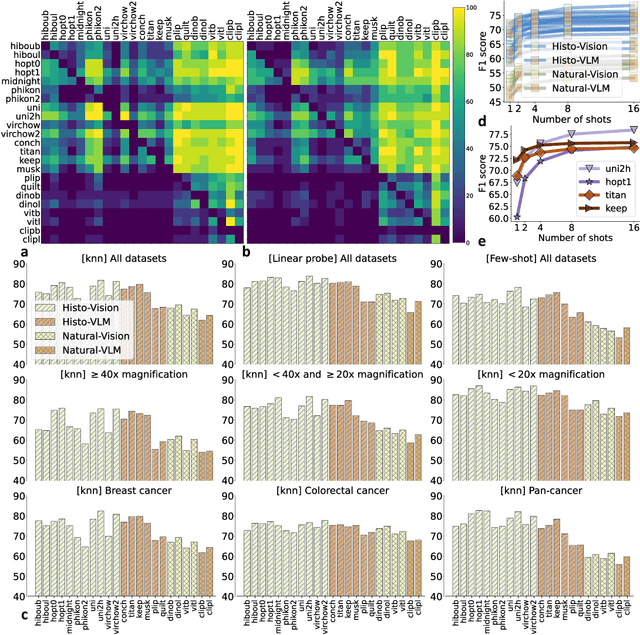
Abstract:Progress in a research field can be hard to assess, in particular when many concurrent methods are proposed in a short period of time. This is the case in digital pathology, where many foundation models have been released recently to serve as feature extractors for tile-level images, being used in a variety of downstream tasks, both for tile- and slide-level problems. Benchmarking available methods then becomes paramount to get a clearer view of the research landscape. In particular, in critical domains such as healthcare, a benchmark should not only focus on evaluating downstream performance, but also provide insights about the main differences between methods, and importantly, further consider uncertainty and robustness to ensure a reliable usage of proposed models. For these reasons, we introduce THUNDER, a tile-level benchmark for digital pathology foundation models, allowing for efficient comparison of many models on diverse datasets with a series of downstream tasks, studying their feature spaces and assessing the robustness and uncertainty of predictions informed by their embeddings. THUNDER is a fast, easy-to-use, dynamic benchmark that can already support a large variety of state-of-the-art foundation, as well as local user-defined models for direct tile-based comparison. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive comparison of 23 foundation models on 16 different datasets covering diverse tasks, feature analysis, and robustness. The code for THUNDER is publicly available at https://github.com/MICS-Lab/thunder.
Task-conditioned adaptation of visual features in multi-task policy learning
Feb 12, 2024Abstract:Successfully addressing a wide variety of tasks is a core ability of autonomous agents, which requires flexibly adapting the underlying decision-making strategies and, as we argue in this work, also adapting the underlying perception modules. An analogical argument would be the human visual system, which uses top-down signals to focus attention determined by the current task. Similarly, in this work, we adapt pre-trained large vision models conditioned on specific downstream tasks in the context of multi-task policy learning. We introduce task-conditioned adapters that do not require finetuning any pre-trained weights, combined with a single policy trained with behavior cloning and capable of addressing multiple tasks. We condition the policy and visual adapters on task embeddings, which can be selected at inference if the task is known, or alternatively inferred from a set of example demonstrations. To this end, we propose a new optimization-based estimator. We evaluate the method on a wide variety of tasks of the CortexBench benchmark and show that, compared to existing work, it can be addressed with a single policy. In particular, we demonstrate that adapting visual features is a key design choice and that the method generalizes to unseen tasks given visual demonstrations.
AutoNeRF: Training Implicit Scene Representations with Autonomous Agents
Apr 21, 2023Abstract:Implicit representations such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have been shown to be very effective at novel view synthesis. However, these models typically require manual and careful human data collection for training. In this paper, we present AutoNeRF, a method to collect data required to train NeRFs using autonomous embodied agents. Our method allows an agent to explore an unseen environment efficiently and use the experience to build an implicit map representation autonomously. We compare the impact of different exploration strategies including handcrafted frontier-based exploration and modular approaches composed of trained high-level planners and classical low-level path followers. We train these models with different reward functions tailored to this problem and evaluate the quality of the learned representations on four different downstream tasks: classical viewpoint rendering, map reconstruction, planning, and pose refinement. Empirical results show that NeRFs can be trained on actively collected data using just a single episode of experience in an unseen environment, and can be used for several downstream robotic tasks, and that modular trained exploration models significantly outperform the classical baselines.
Multi-Object Navigation with dynamically learned neural implicit representations
Oct 11, 2022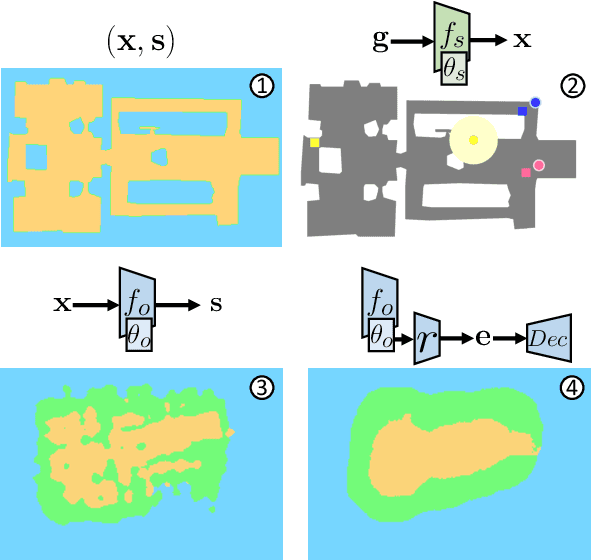
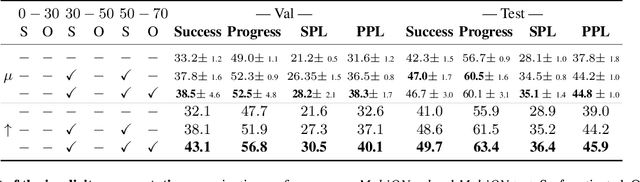
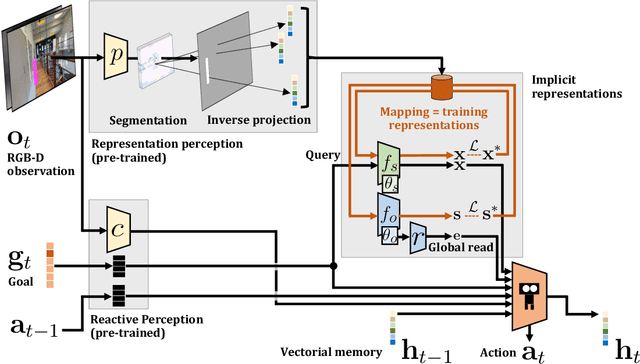
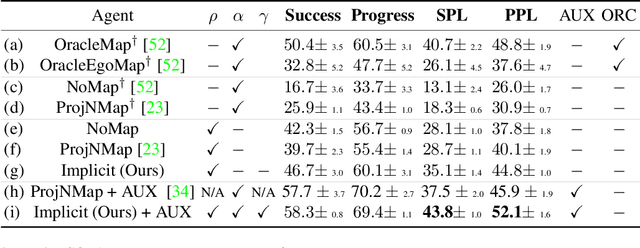
Abstract:Understanding and mapping a new environment are core abilities of any autonomously navigating agent. While classical robotics usually estimates maps in a stand-alone manner with SLAM variants, which maintain a topological or metric representation, end-to-end learning of navigation keeps some form of memory in a neural network. Networks are typically imbued with inductive biases, which can range from vectorial representations to birds-eye metric tensors or topological structures. In this work, we propose to structure neural networks with two neural implicit representations, which are learned dynamically during each episode and map the content of the scene: (i) the Semantic Finder predicts the position of a previously seen queried object; (ii) the Occupancy and Exploration Implicit Representation encapsulates information about explored area and obstacles, and is queried with a novel global read mechanism which directly maps from function space to a usable embedding space. Both representations are leveraged by an agent trained with Reinforcement Learning (RL) and learned online during each episode. We evaluate the agent on Multi-Object Navigation and show the high impact of using neural implicit representations as a memory source.
An experimental study of the vision-bottleneck in VQA
Feb 14, 2022Abstract:As in many tasks combining vision and language, both modalities play a crucial role in Visual Question Answering (VQA). To properly solve the task, a given model should both understand the content of the proposed image and the nature of the question. While the fusion between modalities, which is another obviously important part of the problem, has been highly studied, the vision part has received less attention in recent work. Current state-of-the-art methods for VQA mainly rely on off-the-shelf object detectors delivering a set of object bounding boxes and embeddings, which are then combined with question word embeddings through a reasoning module. In this paper, we propose an in-depth study of the vision-bottleneck in VQA, experimenting with both the quantity and quality of visual objects extracted from images. We also study the impact of two methods to incorporate the information about objects necessary for answering a question, in the reasoning module directly, and earlier in the object selection stage. This work highlights the importance of vision in the context of VQA, and the interest of tailoring vision methods used in VQA to the task at hand.
Teaching Agents how to Map: Spatial Reasoning for Multi-Object Navigation
Jul 13, 2021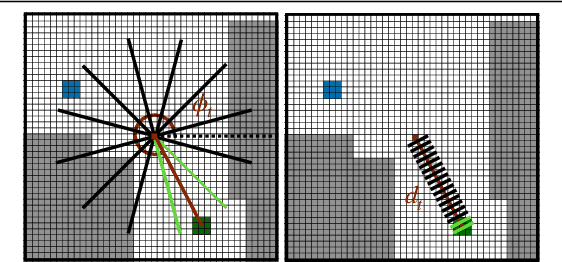
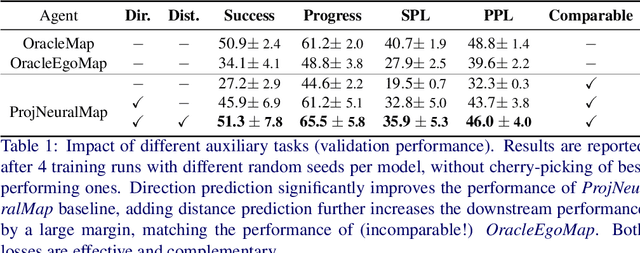
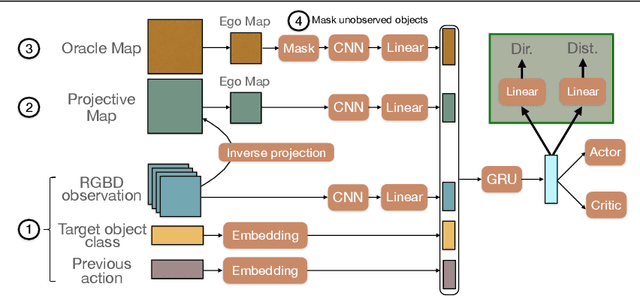

Abstract:In the context of visual navigation, the capacity to map a novel environment is necessary for an agent to exploit its observation history in the considered place and efficiently reach known goals. This ability can be associated with spatial reasoning, where an agent is able to perceive spatial relationships and regularities, and discover object affordances. In classical Reinforcement Learning (RL) setups, this capacity is learned from reward alone. We introduce supplementary supervision in the form of auxiliary tasks designed to favor the emergence of spatial perception capabilities in agents trained for a goal-reaching downstream objective. We show that learning to estimate metrics quantifying the spatial relationships between an agent at a given location and a goal to reach has a high positive impact in Multi-Object Navigation settings. Our method significantly improves the performance of different baseline agents, that either build an explicit or implicit representation of the environment, even matching the performance of incomparable oracle agents taking ground-truth maps as input.
DeepLPF: Deep Local Parametric Filters for Image Enhancement
Mar 31, 2020



Abstract:Digital artists often improve the aesthetic quality of digital photographs through manual retouching. Beyond global adjustments, professional image editing programs provide local adjustment tools operating on specific parts of an image. Options include parametric (graduated, radial filters) and unconstrained brush tools. These highly expressive tools enable a diverse set of local image enhancements. However, their use can be time consuming, and requires artistic capability. State-of-the-art automated image enhancement approaches typically focus on learning pixel-level or global enhancements. The former can be noisy and lack interpretability, while the latter can fail to capture fine-grained adjustments. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to automatically enhance images using learned spatially local filters of three different types (Elliptical Filter, Graduated Filter, Polynomial Filter). We introduce a deep neural network, dubbed Deep Local Parametric Filters (DeepLPF), which regresses the parameters of these spatially localized filters that are then automatically applied to enhance the image. DeepLPF provides a natural form of model regularization and enables interpretable, intuitive adjustments that lead to visually pleasing results. We report on multiple benchmarks and show that DeepLPF produces state-of-the-art performance on two variants of the MIT-Adobe-5K dataset, often using a fraction of the parameters required for competing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge