Petr Motlicek
Idiap Research Institute
Text-only adaptation in LLM-based ASR through text denoising
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Adapting automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems based on large language models (LLMs) to new domains using text-only data is a significant yet underexplored challenge. Standard fine-tuning of the LLM on target-domain text often disrupts the critical alignment between speech and text modalities learned by the projector, degrading performance. We introduce a novel text-only adaptation method that emulates the audio projection task by treating it as a text denoising task. Our approach thus trains the LLM to recover clean transcripts from noisy inputs. This process effectively adapts the model to a target domain while preserving cross-modal alignment. Our solution is lightweight, requiring no architectural changes or additional parameters. Extensive evaluation on two datasets demonstrates up to 22.1% relative improvement, outperforming recent state-of-the-art text-only adaptation methods.
Reducing Prompt Sensitivity in LLM-based Speech Recognition Through Learnable Projection
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:LLM-based automatic speech recognition (ASR), a well-established approach, connects speech foundation models to large language models (LLMs) through a speech-to-LLM projector, yielding promising results. A common design choice in these architectures is the use of a fixed, manually defined prompt during both training and inference. This setup not only enables applicability across a range of practical scenarios, but also helps maximize model performance. However, the impact of prompt design remains underexplored. This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of commonly used prompts across diverse datasets, showing that prompt choice significantly affects ASR performance and introduces instability, with no single prompt performing best across all cases. Inspired by the speech-to-LLM projector, we propose a prompt projector module, a simple, model-agnostic extension that learns to project prompt embeddings to more effective regions of the LLM input space, without modifying the underlying LLM-based ASR model. Experiments on four datasets show that the addition of a prompt projector consistently improves performance, reduces variability, and outperforms the best manually selected prompts.
Adaptive Multimodal Person Recognition: A Robust Framework for Handling Missing Modalities
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Person recognition systems often rely on audio, visual, or behavioral cues, but real-world conditions frequently result in missing or degraded modalities. To address this challenge, we propose a Trimodal person identification framework that integrates voice, face, and gesture modalities, while remaining robust to modality loss. Our approach leverages multi-task learning to process each modality independently, followed by a cross-attention and gated fusion mechanisms to facilitate interaction across modalities. Moreover, a confidence-weighted fusion strategy dynamically adapts to missing and low-quality data, ensuring optimal classification even in Unimodal or Bimodal scenarios. We evaluate our method on CANDOR, a newly introduced interview-based multimodal dataset, which we benchmark for the first time. Our results demonstrate that the proposed Trimodal system achieves 99.18% Top-1 accuracy on person identification tasks, outperforming conventional Unimodal and late-fusion approaches. In addition, we evaluate our model on the VoxCeleb1 dataset as a benchmark and reach 99.92% accuracy in Bimodal mode. Moreover, we show that our system maintains high accuracy even when one or two modalities are unavailable, making it a robust solution for real-world person recognition applications. The code and data for this work are publicly available.
SDialog: A Python Toolkit for End-to-End Agent Building, User Simulation, Dialog Generation, and Evaluation
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:We present SDialog, an MIT-licensed open-source Python toolkit that unifies dialog generation, evaluation and mechanistic interpretability into a single end-to-end framework for building and analyzing LLM-based conversational agents. Built around a standardized \texttt{Dialog} representation, SDialog provides: (1) persona-driven multi-agent simulation with composable orchestration for controlled, synthetic dialog generation, (2) comprehensive evaluation combining linguistic metrics, LLM-as-a-judge and functional correctness validators, (3) mechanistic interpretability tools for activation inspection and steering via feature ablation and induction, and (4) audio generation with full acoustic simulation including 3D room modeling and microphone effects. The toolkit integrates with all major LLM backends, enabling mixed-backend experiments under a unified API. By coupling generation, evaluation, and interpretability in a dialog-centric architecture, SDialog enables researchers to build, benchmark and understand conversational systems more systematically.
TokenVerse++: Towards Flexible Multitask Learning with Dynamic Task Activation
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Token-based multitasking frameworks like TokenVerse require all training utterances to have labels for all tasks, hindering their ability to leverage partially annotated datasets and scale effectively. We propose TokenVerse++, which introduces learnable vectors in the acoustic embedding space of the XLSR-Transducer ASR model for dynamic task activation. This core mechanism enables training with utterances labeled for only a subset of tasks, a key advantage over TokenVerse. We demonstrate this by successfully integrating a dataset with partial labels, specifically for ASR and an additional task, language identification, improving overall performance. TokenVerse++ achieves results on par with or exceeding TokenVerse across multiple tasks, establishing it as a more practical multitask alternative without sacrificing ASR performance.
SDialog: A Python Toolkit for Synthetic Dialogue Generation and Analysis
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:The advancement of conversational AI systems relies on the availability of high-quality, flexible, and reproducible synthetic dialogues for training, evaluation, and benchmarking. SDialog is a modular, extensible Python toolkit designed to address the challenges of synthetic dialogue generation and analysis. By leveraging instruction-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs), SDialog provides abstractions for personas, orchestration, and scenario management, enabling the creation of realistic, diverse, and controllable conversational data for research and development. SDialog supports workflows such as multi-agent simulation and scenario-driven generation, and represents a step forward in the standardization of tools and frameworks for synthetic data generation, a crucial advancement for ensuring reproducibility in today's fast-evolving research landscape.
Better Semi-supervised Learning for Multi-domain ASR Through Incremental Retraining and Data Filtering
Jun 05, 2025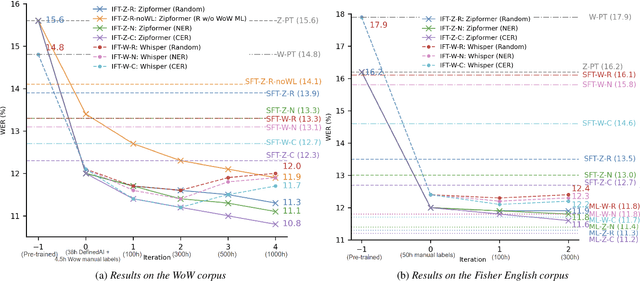
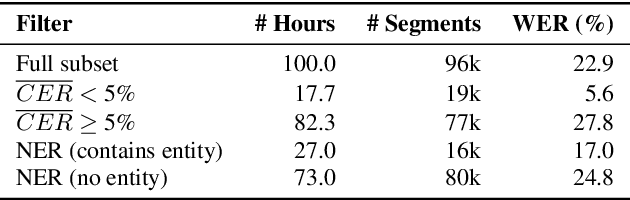
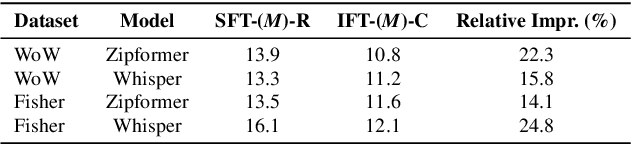
Abstract:Fine-tuning pretrained ASR models for specific domains is challenging when labeled data is scarce. But unlabeled audio and labeled data from related domains are often available. We propose an incremental semi-supervised learning pipeline that first integrates a small in-domain labeled set and an auxiliary dataset from a closely related domain, achieving a relative improvement of 4% over no auxiliary data. Filtering based on multi-model consensus or named entity recognition (NER) is then applied to select and iteratively refine pseudo-labels, showing slower performance saturation compared to random selection. Evaluated on the multi-domain Wow call center and Fisher English corpora, it outperforms single-step fine-tuning. Consensus-based filtering outperforms other methods, providing up to 22.3% relative improvement on Wow and 24.8% on Fisher over single-step fine-tuning with random selection. NER is the second-best filter, providing competitive performance at a lower computational cost.
A Differentiable Alignment Framework for Sequence-to-Sequence Modeling via Optimal Transport
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Accurate sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) alignment is critical for applications like medical speech analysis and language learning tools relying on automatic speech recognition (ASR). State-of-the-art end-to-end (E2E) ASR systems, such as the Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) and transducer-based models, suffer from peaky behavior and alignment inaccuracies. In this paper, we propose a novel differentiable alignment framework based on one-dimensional optimal transport, enabling the model to learn a single alignment and perform ASR in an E2E manner. We introduce a pseudo-metric, called Sequence Optimal Transport Distance (SOTD), over the sequence space and discuss its theoretical properties. Based on the SOTD, we propose Optimal Temporal Transport Classification (OTTC) loss for ASR and contrast its behavior with CTC. Experimental results on the TIMIT, AMI, and LibriSpeech datasets show that our method considerably improves alignment performance, though with a trade-off in ASR performance when compared to CTC. We believe this work opens new avenues for seq2seq alignment research, providing a solid foundation for further exploration and development within the community.
Performance evaluation of SLAM-ASR: The Good, the Bad, the Ugly, and the Way Forward
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:Recent research has demonstrated that training a linear connector between speech foundation encoders and large language models (LLMs) enables this architecture to achieve strong ASR capabilities. Despite the impressive results, it remains unclear whether these simple approaches are robust enough across different scenarios and speech conditions, such as domain shifts and different speech perturbations. In this paper, we address these questions by conducting various ablation experiments using a recent and widely adopted approach called SLAM-ASR. We present novel empirical findings that offer insights on how to effectively utilize the SLAM-ASR architecture across a wide range of settings. Our main findings indicate that the SLAM-ASR exhibits poor performance in cross-domain evaluation settings. Additionally, speech perturbations within in-domain data, such as changes in speed or the presence of additive noise, can significantly impact performance. Our findings offer critical insights for fine-tuning and configuring robust LLM-based ASR models, tailored to different data characteristics and computational resources.
Dialog2Flow: Pre-training Soft-Contrastive Action-Driven Sentence Embeddings for Automatic Dialog Flow Extraction
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:Efficiently deriving structured workflows from unannotated dialogs remains an underexplored and formidable challenge in computational linguistics. Automating this process could significantly accelerate the manual design of workflows in new domains and enable the grounding of large language models in domain-specific flowcharts, enhancing transparency and controllability. In this paper, we introduce Dialog2Flow (D2F) embeddings, which differ from conventional sentence embeddings by mapping utterances to a latent space where they are grouped according to their communicative and informative functions (i.e., the actions they represent). D2F allows for modeling dialogs as continuous trajectories in a latent space with distinct action-related regions. By clustering D2F embeddings, the latent space is quantized, and dialogs can be converted into sequences of region/action IDs, facilitating the extraction of the underlying workflow. To pre-train D2F, we build a comprehensive dataset by unifying twenty task-oriented dialog datasets with normalized per-turn action annotations. We also introduce a novel soft contrastive loss that leverages the semantic information of these actions to guide the representation learning process, showing superior performance compared to standard supervised contrastive loss. Evaluation against various sentence embeddings, including dialog-specific ones, demonstrates that D2F yields superior qualitative and quantitative results across diverse domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge