Peter Soyer
Prompt-driven Latent Domain Generalization for Medical Image Classification
Jan 05, 2024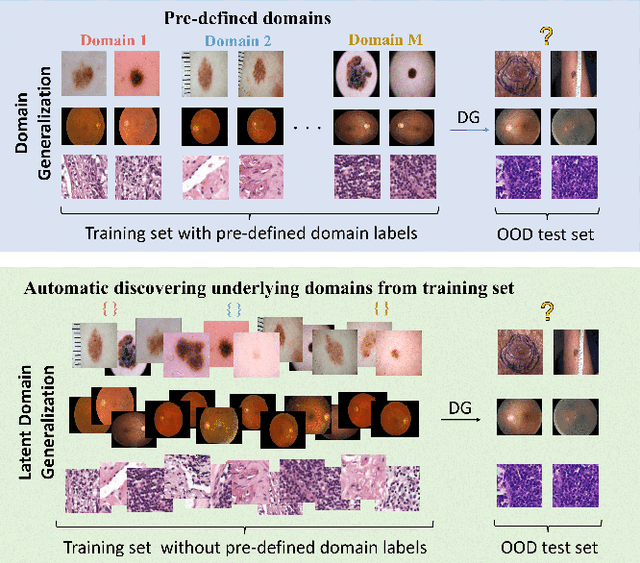
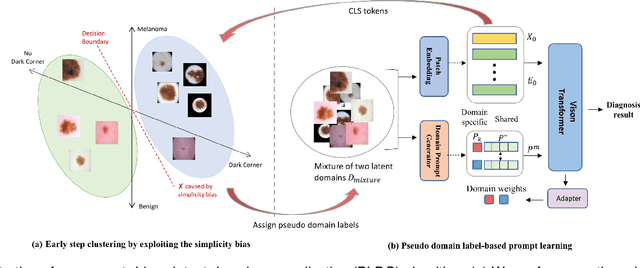
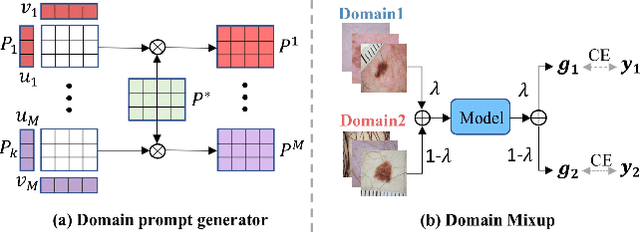
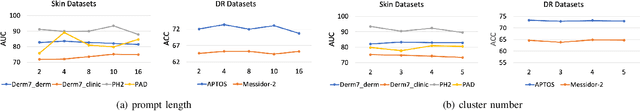
Abstract:Deep learning models for medical image analysis easily suffer from distribution shifts caused by dataset artifacts bias, camera variations, differences in the imaging station, etc., leading to unreliable diagnoses in real-world clinical settings. Domain generalization (DG) methods, which aim to train models on multiple domains to perform well on unseen domains, offer a promising direction to solve the problem. However, existing DG methods assume domain labels of each image are available and accurate, which is typically feasible for only a limited number of medical datasets. To address these challenges, we propose a novel DG framework for medical image classification without relying on domain labels, called Prompt-driven Latent Domain Generalization (PLDG). PLDG consists of unsupervised domain discovery and prompt learning. This framework first discovers pseudo domain labels by clustering the bias-associated style features, then leverages collaborative domain prompts to guide a Vision Transformer to learn knowledge from discovered diverse domains. To facilitate cross-domain knowledge learning between different prompts, we introduce a domain prompt generator that enables knowledge sharing between domain prompts and a shared prompt. A domain mixup strategy is additionally employed for more flexible decision margins and mitigates the risk of incorrect domain assignments. Extensive experiments on three medical image classification tasks and one debiasing task demonstrate that our method can achieve comparable or even superior performance than conventional DG algorithms without relying on domain labels. Our code will be publicly available upon the paper is accepted.
EPVT: Environment-aware Prompt Vision Transformer for Domain Generalization in Skin Lesion Recognition
Apr 09, 2023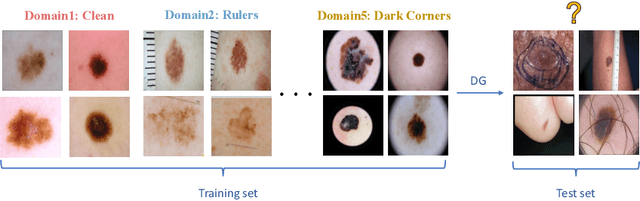
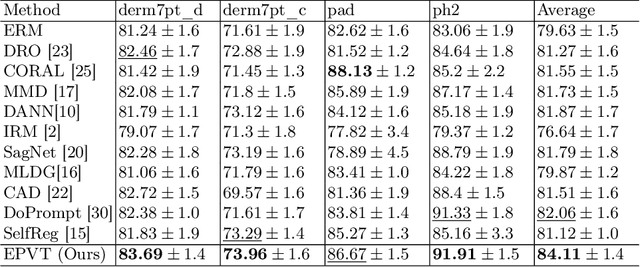
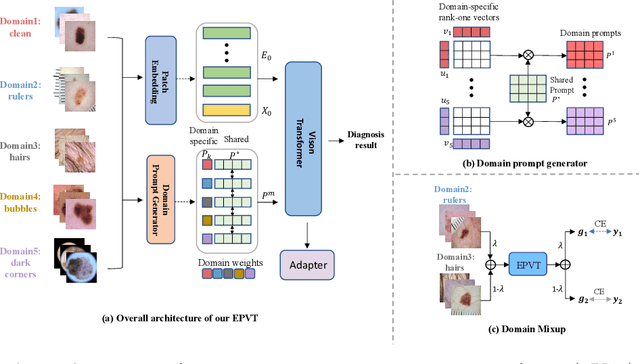
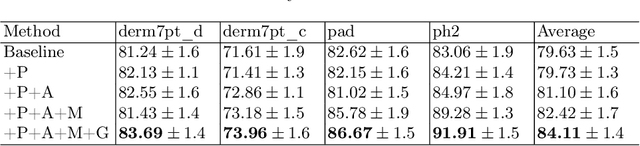
Abstract:Skin lesion recognition using deep learning has made remarkable progress, and there is an increasing need for deploying these systems in real-world scenarios. However, recent research has revealed that deep neural networks for skin lesion recognition may overly depend on disease-irrelevant image artifacts (i.e. dark corners, dense hairs), leading to poor generalization in unseen environments. To address this issue, we propose a novel domain generalization method called EPVT, which involves embedding prompts into the vision transformer to collaboratively learn knowledge from diverse domains. Concretely, EPVT leverages a set of domain prompts, each of which plays as a domain expert, to capture domain-specific knowledge; and a shared prompt for general knowledge over the entire dataset. To facilitate knowledge sharing and the interaction of different prompts, we introduce a domain prompt generator that enables low-rank multiplicative updates between domain prompts and the shared prompt. A domain mixup strategy is additionally devised to reduce the co-occurring artifacts in each domain, which allows for more flexible decision margins and mitigates the issue of incorrectly assigned domain labels. Experiments on four out-of-distribution datasets and six different biased ISIC datasets demonstrate the superior generalization ability of EPVT in skin lesion recognition across various environments. Our code and dataset will be released at https://github.com/SiyuanYan1/EPVT.
Towards Trustable Skin Cancer Diagnosis via Rewriting Model's Decision
Mar 02, 2023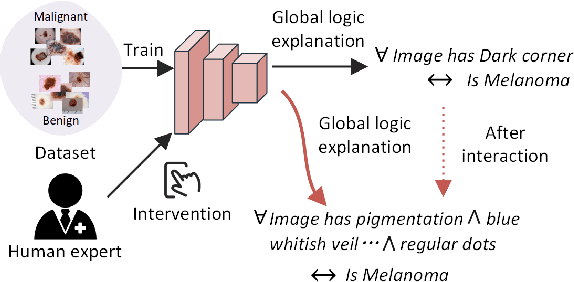
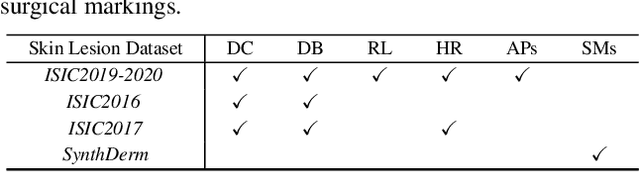
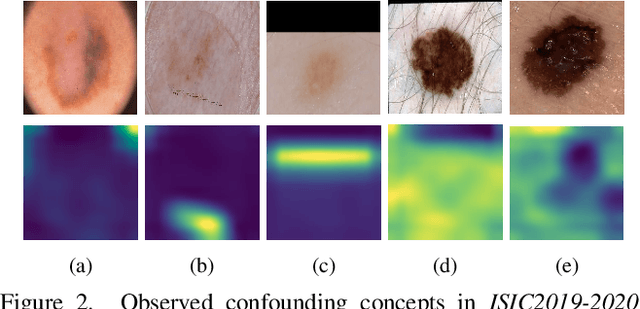
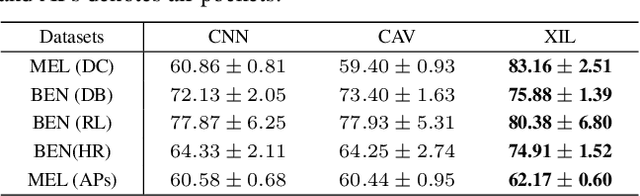
Abstract:Deep neural networks have demonstrated promising performance on image recognition tasks. However, they may heavily rely on confounding factors, using irrelevant artifacts or bias within the dataset as the cue to improve performance. When a model performs decision-making based on these spurious correlations, it can become untrustable and lead to catastrophic outcomes when deployed in the real-world scene. In this paper, we explore and try to solve this problem in the context of skin cancer diagnosis. We introduce a human-in-the-loop framework in the model training process such that users can observe and correct the model's decision logic when confounding behaviors happen. Specifically, our method can automatically discover confounding factors by analyzing the co-occurrence behavior of the samples. It is capable of learning confounding concepts using easily obtained concept exemplars. By mapping the black-box model's feature representation onto an explainable concept space, human users can interpret the concept and intervene via first order-logic instruction. We systematically evaluate our method on our newly crafted, well-controlled skin lesion dataset and several public skin lesion datasets. Experiments show that our method can effectively detect and remove confounding factors from datasets without any prior knowledge about the category distribution and does not require fully annotated concept labels. We also show that our method enables the model to focus on clinical-related concepts, improving the model's performance and trustworthiness during model inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge