Peter H. N. De With
Symmetrical Flow Matching: Unified Image Generation, Segmentation, and Classification with Score-Based Generative Models
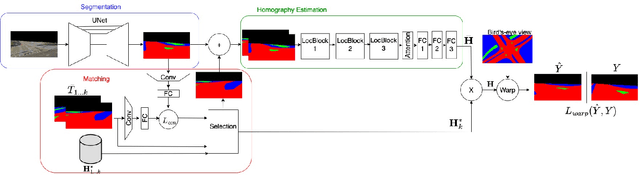
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Flow Matching has emerged as a powerful framework for learning continuous transformations between distributions, enabling high-fidelity generative modeling. This work introduces Symmetrical Flow Matching (SymmFlow), a new formulation that unifies semantic segmentation, classification, and image generation within a single model. Using a symmetric learning objective, SymmFlow models forward and reverse transformations jointly, ensuring bi-directional consistency, while preserving sufficient entropy for generative diversity. A new training objective is introduced to explicitly retain semantic information across flows, featuring efficient sampling while preserving semantic structure, allowing for one-step segmentation and classification without iterative refinement. Unlike previous approaches that impose strict one-to-one mapping between masks and images, SymmFlow generalizes to flexible conditioning, supporting both pixel-level and image-level class labels. Experimental results on various benchmarks demonstrate that SymmFlow achieves state-of-the-art performance on semantic image synthesis, obtaining FID scores of 11.9 on CelebAMask-HQ and 7.0 on COCO-Stuff with only 25 inference steps. Additionally, it delivers competitive results on semantic segmentation and shows promising capabilities in classification tasks. The code will be publicly available.
TeG: Temporal-Granularity Method for Anomaly Detection with Attention in Smart City Surveillance
Nov 17, 2024Abstract:Anomaly detection in video surveillance has recently gained interest from the research community. Temporal duration of anomalies vary within video streams, leading to complications in learning the temporal dynamics of specific events. This paper presents a temporal-granularity method for an anomaly detection model (TeG) in real-world surveillance, combining spatio-temporal features at different time-scales. The TeG model employs multi-head cross-attention blocks and multi-head self-attention blocks for this purpose. Additionally, we extend the UCF-Crime dataset with new anomaly types relevant to Smart City research project. The TeG model is deployed and validated in a city surveillance system, achieving successful real-time results in industrial settings.
MTFL: Multi-Timescale Feature Learning for Weakly-Supervised Anomaly Detection in Surveillance Videos
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Detection of anomaly events is relevant for public safety and requires a combination of fine-grained motion information and contextual events at variable time-scales. To this end, we propose a Multi-Timescale Feature Learning (MTFL) method to enhance the representation of anomaly features. Short, medium, and long temporal tubelets are employed to extract spatio-temporal video features using a Video Swin Transformer. Experimental results demonstrate that MTFL outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the UCF-Crime dataset, achieving an anomaly detection performance 89.78% AUC. Moreover, it performs complementary to SotA with 95.32% AUC on the ShanghaiTech and 84.57% AP on the XD-Violence dataset. Furthermore, we generate an extended dataset of the UCF-Crime for development and evaluation on a wider range of anomalies, namely Video Anomaly Detection Dataset (VADD), involving 2,591 videos in 18 classes with extensive coverage of realistic anomalies.
Exploring the Effect of Dataset Diversity in Self-Supervised Learning for Surgical Computer Vision
Jul 26, 2024Abstract:Over the past decade, computer vision applications in minimally invasive surgery have rapidly increased. Despite this growth, the impact of surgical computer vision remains limited compared to other medical fields like pathology and radiology, primarily due to the scarcity of representative annotated data. Whereas transfer learning from large annotated datasets such as ImageNet has been conventionally the norm to achieve high-performing models, recent advancements in self-supervised learning (SSL) have demonstrated superior performance. In medical image analysis, in-domain SSL pretraining has already been shown to outperform ImageNet-based initialization. Although unlabeled data in the field of surgical computer vision is abundant, the diversity within this data is limited. This study investigates the role of dataset diversity in SSL for surgical computer vision, comparing procedure-specific datasets against a more heterogeneous general surgical dataset across three different downstream surgical applications. The obtained results show that using solely procedure-specific data can lead to substantial improvements of 13.8%, 9.5%, and 36.8% compared to ImageNet pretraining. However, extending this data with more heterogeneous surgical data further increases performance by an additional 5.0%, 5.2%, and 2.5%, suggesting that increasing diversity within SSL data is beneficial for model performance. The code and pretrained model weights are made publicly available at https://github.com/TimJaspers0801/SurgeNet.
Transformer-based Fusion of 2D-pose and Spatio-temporal Embeddings for Distracted Driver Action Recognition
Mar 11, 2024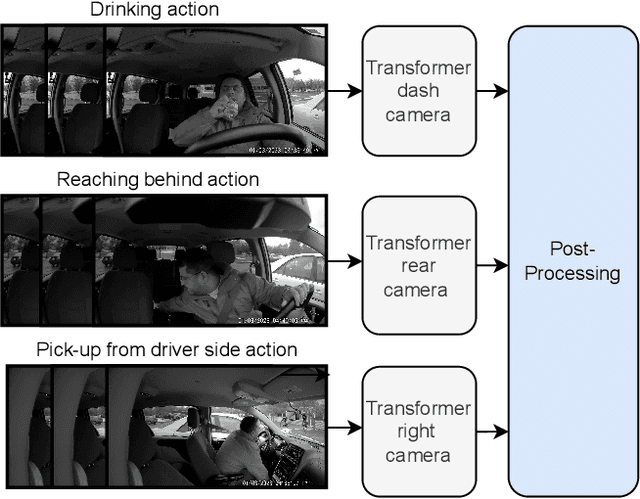
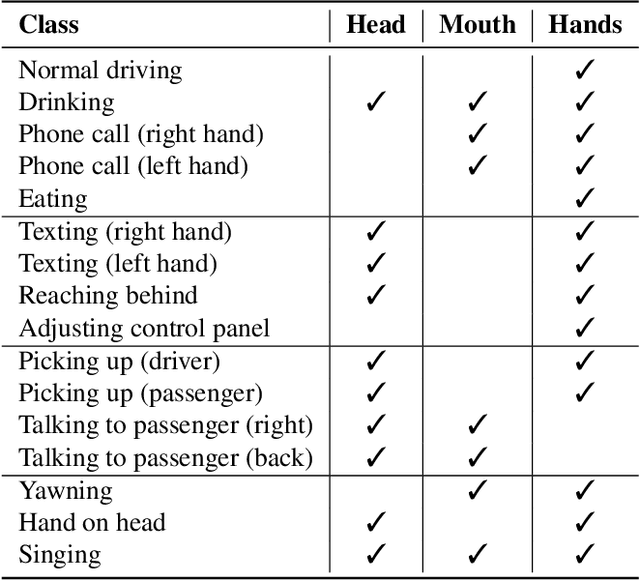
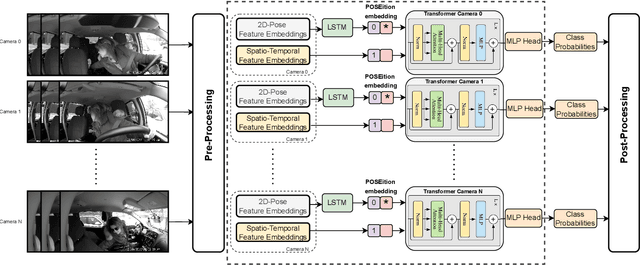
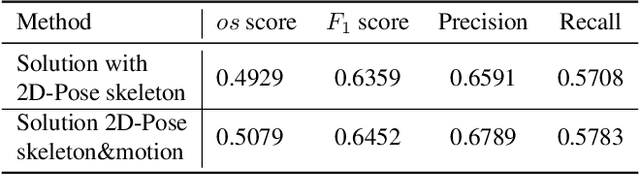
Abstract:Classification and localization of driving actions over time is important for advanced driver-assistance systems and naturalistic driving studies. Temporal localization is challenging because it requires robustness, reliability, and accuracy. In this study, we aim to improve the temporal localization and classification accuracy performance by adapting video action recognition and 2D human-pose estimation networks to one model. Therefore, we design a transformer-based fusion architecture to effectively combine 2D-pose features and spatio-temporal features. The model uses 2D-pose features as the positional embedding of the transformer architecture and spatio-temporal features as the main input to the encoder of the transformer. The proposed solution is generic and independent of the camera numbers and positions, giving frame-based class probabilities as output. Finally, the post-processing step combines information from different camera views to obtain final predictions and eliminate false positives. The model performs well on the A2 test set of the 2023 NVIDIA AI City Challenge for naturalistic driving action recognition, achieving the overlap score of the organizer-defined distracted driver behaviour metric of 0.5079.
Density-Guided Label Smoothing for Temporal Localization of Driving Actions
Mar 11, 2024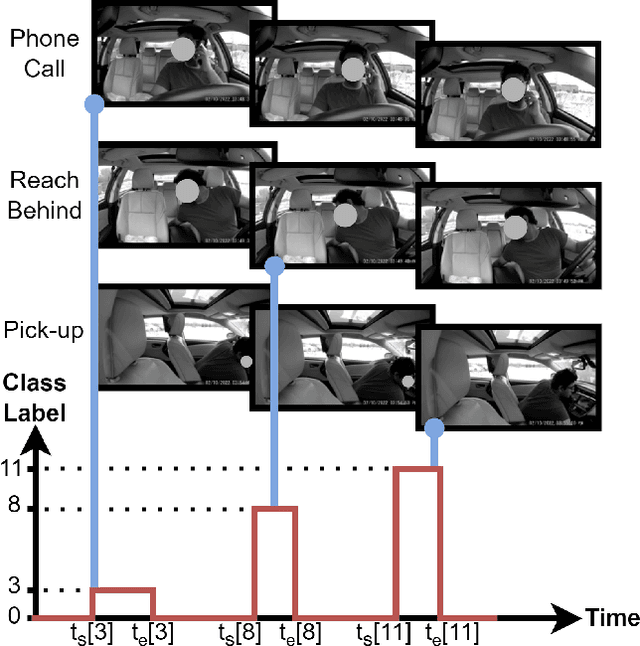
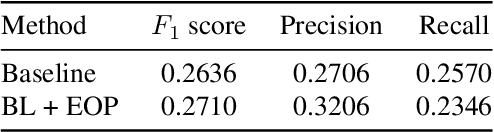
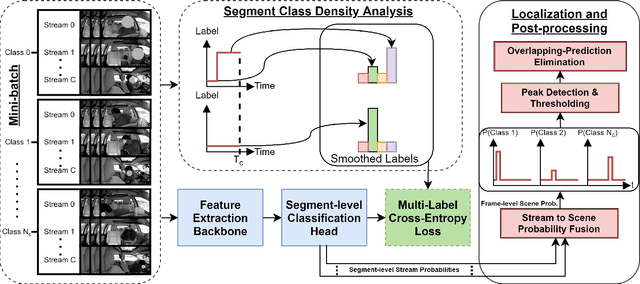
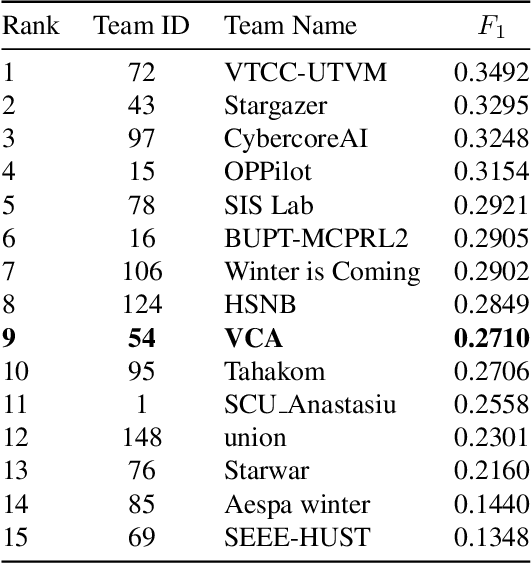
Abstract:Temporal localization of driving actions plays a crucial role in advanced driver-assistance systems and naturalistic driving studies. However, this is a challenging task due to strict requirements for robustness, reliability and accurate localization. In this work, we focus on improving the overall performance by efficiently utilizing video action recognition networks and adapting these to the problem of action localization. To this end, we first develop a density-guided label smoothing technique based on label probability distributions to facilitate better learning from boundary video-segments that typically include multiple labels. Second, we design a post-processing step to efficiently fuse information from video-segments and multiple camera views into scene-level predictions, which facilitates elimination of false positives. Our methodology yields a competitive performance on the A2 test set of the naturalistic driving action recognition track of the 2022 NVIDIA AI City Challenge with an F1 score of 0.271.
Detection of Object Throwing Behavior in Surveillance Videos
Mar 11, 2024



Abstract:Anomalous behavior detection is a challenging research area within computer vision. Progress in this area enables automated detection of dangerous behavior using surveillance camera feeds. A dangerous behavior that is often overlooked in other research is the throwing action in traffic flow, which is one of the unique requirements of our Smart City project to enhance public safety. This paper proposes a solution for throwing action detection in surveillance videos using deep learning. At present, datasets for throwing actions are not publicly available. To address the use-case of our Smart City project, we first generate the novel public 'Throwing Action' dataset, consisting of 271 videos of throwing actions performed by traffic participants, such as pedestrians, bicyclists, and car drivers, and 130 normal videos without throwing actions. Second, we compare the performance of different feature extractors for our anomaly detection method on the UCF-Crime and Throwing-Action datasets. The explored feature extractors are the Convolutional 3D (C3D) network, the Inflated 3D ConvNet (I3D) network, and the Multi-Fiber Network (MFNet). Finally, the performance of the anomaly detection algorithm is improved by applying the Adam optimizer instead of Adadelta, and proposing a mean normal loss function that covers the multitude of normal situations in traffic. Both aspects yield better anomaly detection performance. Besides this, the proposed mean normal loss function lowers the false alarm rate on the combined dataset. The experimental results reach an area under the ROC curve of 86.10 for the Throwing-Action dataset, and 80.13 on the combined dataset, respectively.
Automated Camera Calibration via Homography Estimation with GNNs
Nov 05, 2023

Abstract:Over the past few decades, a significant rise of camera-based applications for traffic monitoring has occurred. Governments and local administrations are increasingly relying on the data collected from these cameras to enhance road safety and optimize traffic conditions. However, for effective data utilization, it is imperative to ensure accurate and automated calibration of the involved cameras. This paper proposes a novel approach to address this challenge by leveraging the topological structure of intersections. We propose a framework involving the generation of a set of synthetic intersection viewpoint images from a bird's-eye-view image, framed as a graph of virtual cameras to model these images. Using the capabilities of Graph Neural Networks, we effectively learn the relationships within this graph, thereby facilitating the estimation of a homography matrix. This estimation leverages the neighbourhood representation for any real-world camera and is enhanced by exploiting multiple images instead of a single match. In turn, the homography matrix allows the retrieval of extrinsic calibration parameters. As a result, the proposed framework demonstrates superior performance on both synthetic datasets and real-world cameras, setting a new state-of-the-art benchmark.
Homography Estimation in Complex Topological Scenes
Aug 02, 2023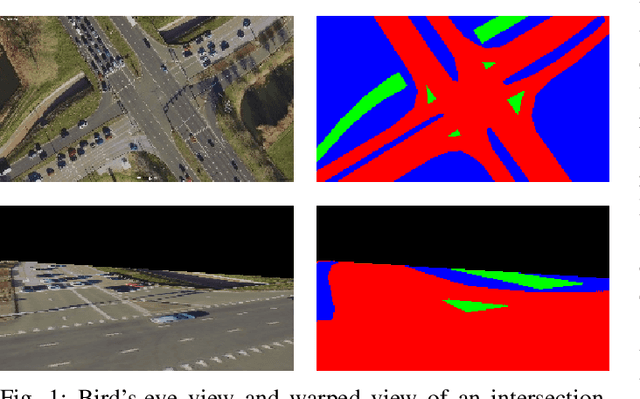
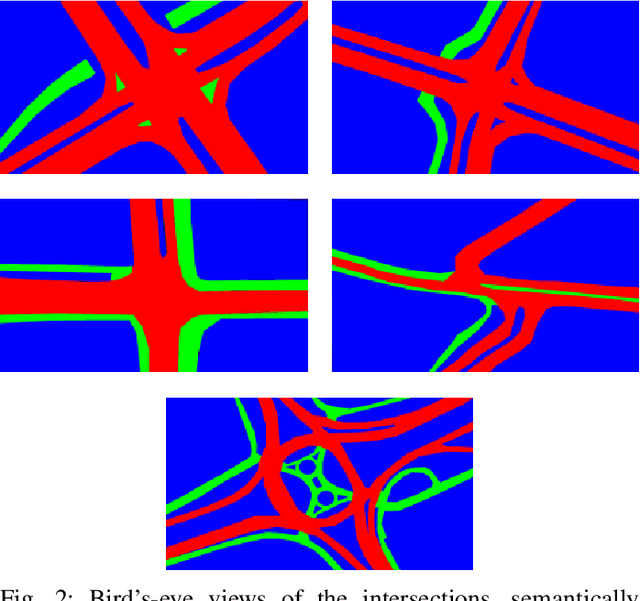
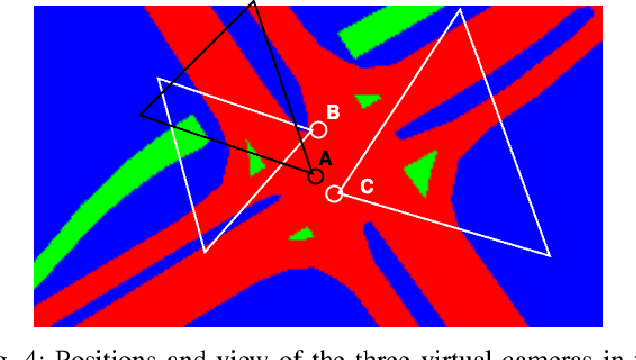
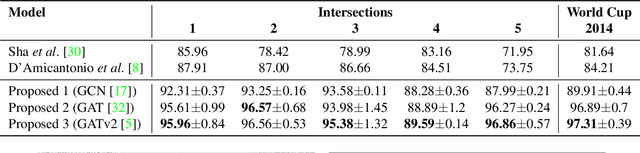
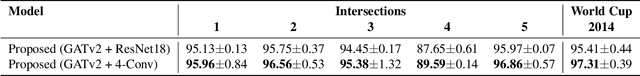
Abstract:Surveillance videos and images are used for a broad set of applications, ranging from traffic analysis to crime detection. Extrinsic camera calibration data is important for most analysis applications. However, security cameras are susceptible to environmental conditions and small camera movements, resulting in a need for an automated re-calibration method that can account for these varying conditions. In this paper, we present an automated camera-calibration process leveraging a dictionary-based approach that does not require prior knowledge on any camera settings. The method consists of a custom implementation of a Spatial Transformer Network (STN) and a novel topological loss function. Experiments reveal that the proposed method improves the IoU metric by up to 12% w.r.t. a state-of-the-art model across five synthetic datasets and the World Cup 2014 dataset.
Bootstrapped CNNs for Building Segmentation on RGB-D Aerial Imagery
Oct 08, 2018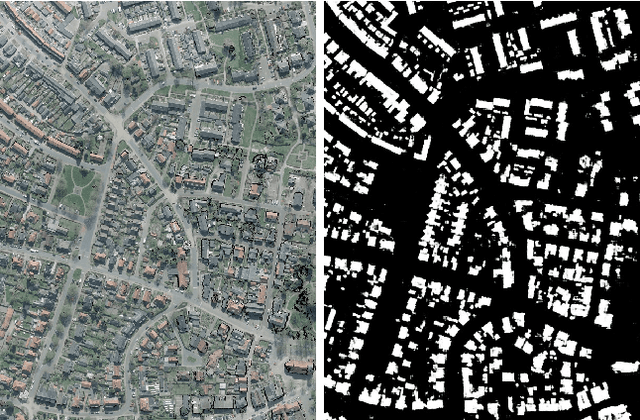

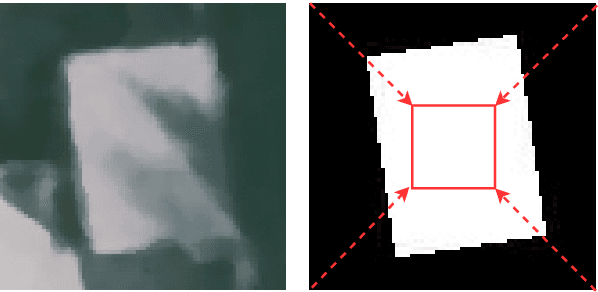
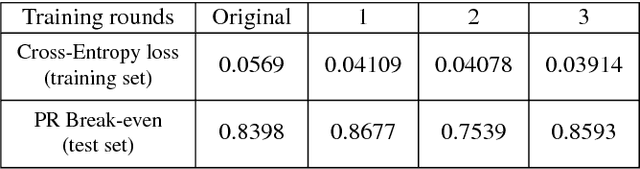
Abstract:Detection of buildings and other objects from aerial images has various applications in urban planning and map making. Automated building detection from aerial imagery is a challenging task, as it is prone to varying lighting conditions, shadows and occlusions. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are robust against some of these variations, although they fail to distinguish easy and difficult examples. We train a detection algorithm from RGB-D images to obtain a segmented mask by using the CNN architecture DenseNet.First, we improve the performance of the model by applying a statistical re-sampling technique called Bootstrapping and demonstrate that more informative examples are retained. Second, the proposed method outperforms the non-bootstrapped version by utilizing only one-sixth of the original training data and it obtains a precision-recall break-even of 95.10% on our aerial imagery dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge